Obesity is a factor that contributes to the morbidity of certain diseases and to worldwide mortality. MGAT1 is a glycosyltransferase involved in the synthesis of protein-bound and lipid-bound oligosaccharides and its polymorphisms are possibly involved in the etiology of obesity. We investigated the association of the rs4285184 polymorphism of the MGAT1 gene with obesity in adults in the State of Colima, Mexico.
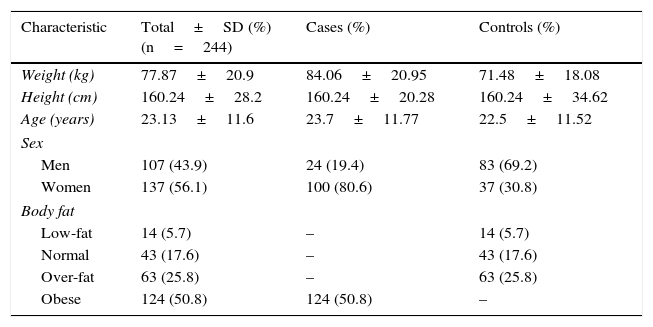
MethodsA case–control study was conducted that included 244 subjects. All of them were grouped according to their percentage of body fat, determined through bioelectrical impedance, and they were genotyped for the rs4285184 polymorphism of the MGAT1 gene through PCR-RFLP. The results were analyzed for their association with the percentage of body fat.
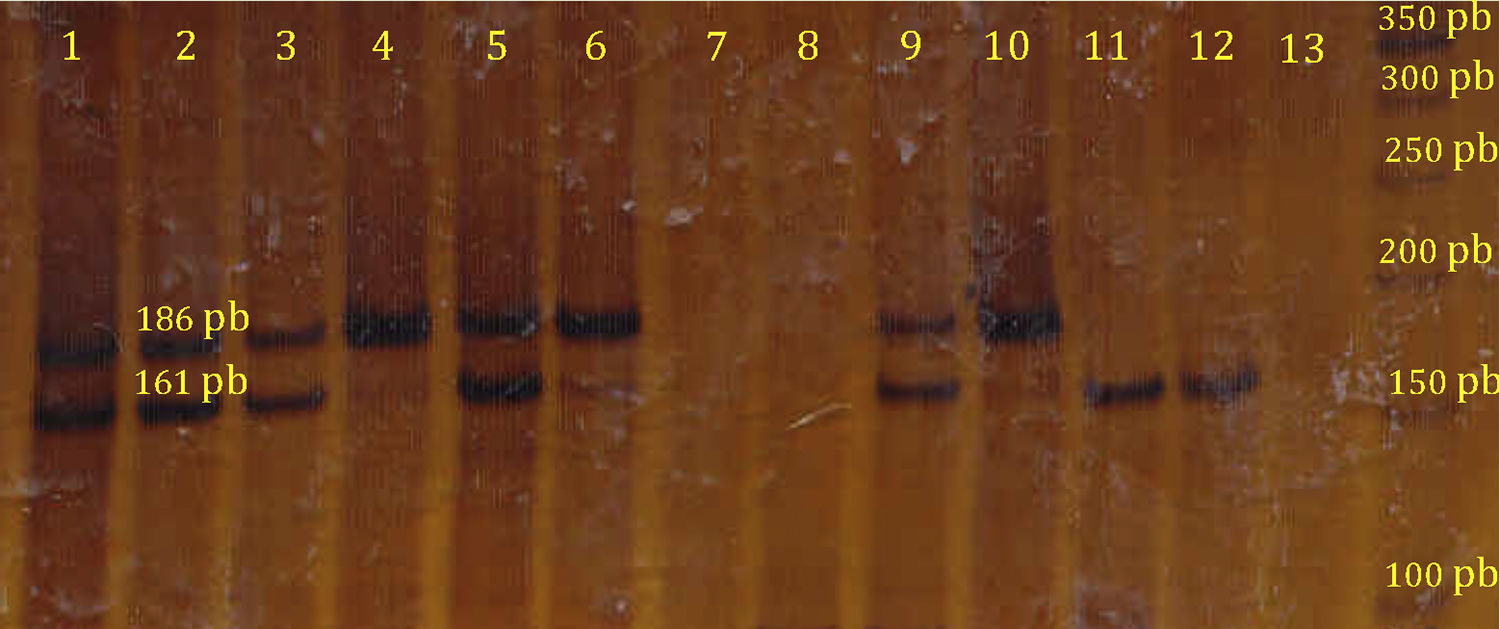
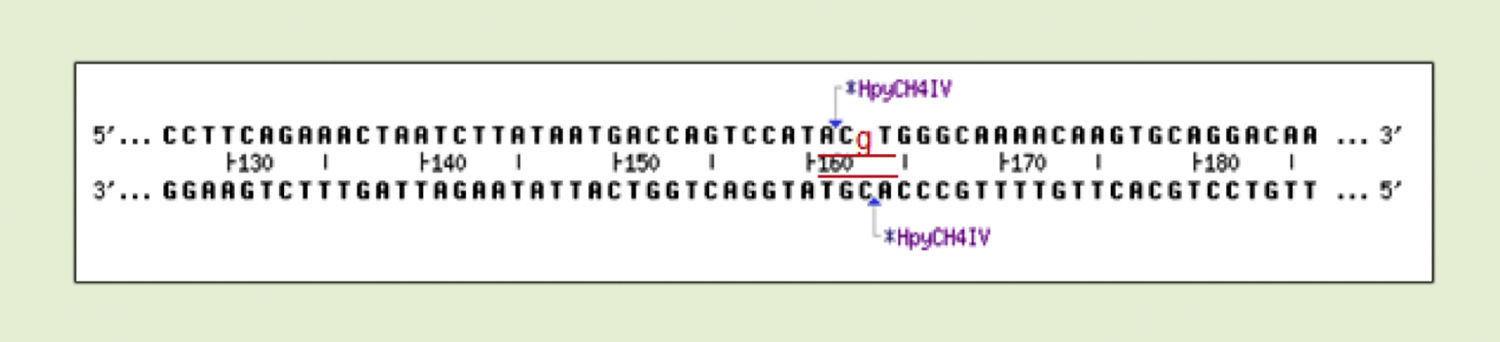
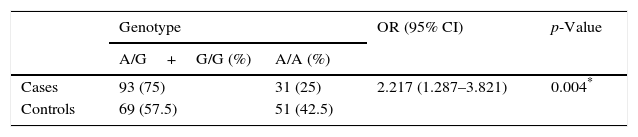
ResultsThe G allele had a frequency of 49.19 and 38.75% for the cases and controls, respectively (P=.020) (OR 1.53; 95% CI 1.068–2.193). The frequency of the A/G+G/G genotype was 75% in the obese patients, which was significantly higher compared with the 57.5% of the control group (P=.004) (OR 2.217; 95% CI 1.287–3.821).
ConclusionsThe presence of the rs4285184 polymorphism of the MGAT1 gene increased the risk for developing body fat associated with obesity in the Mexican population.
La obesidad es un factor que contribuye a la morbilidad de ciertas enfermedades, y a la mortalidad mundial. MGAT1 es una glucosiltransferasa implicada en la síntesis de los oligosacáridos ligados a proteínas y lípidos, y es posible que sus polimorfismos estén implicados en la etiología de la obesidad. Investigamos la asociación entre el polimorfismo rs4285184 del gen MGAT1 y la obesidad en adultos del estado de Colima, México.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio caso-control que incluyó a 244 sujetos. Todos ellos fueron agrupados con arreglo a su porcentaje de grasa corporal, determinado mediante impedancia bioeléctrica, y fueron genotipados para el polimorfismo rs4285184 del gen MGAT1 mediante PCR-RFLP. Se analizaron los resultados para buscar su asociación con el porcentaje de grasa corporal.
ResultadosEl alelo G reflejó una frecuencia del 49,19% y el 38,75% para los casos y controles, respectivamente (p= 0,020) (OR 1,53; IC 95% 1,068-2,193). La frecuencia del genotipo A/G+G/G fue del 75% en los pacientes obesos, cifra significativamente superior en comparación al 57,5% del grupo control (p=0,004) (OR 2.217; IC 95% 1,287-3,821).
ConclusionesLa presencia del polimorfismo rs4285184 del gen MGAT1 incrementó el riesgo de desarrollar grasa corporal asociada a la obesidad en la población mexicana.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora