The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of high-dose rituximab (HD-R) in combination with autologous stem cell transplantation (auto-SCT) in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
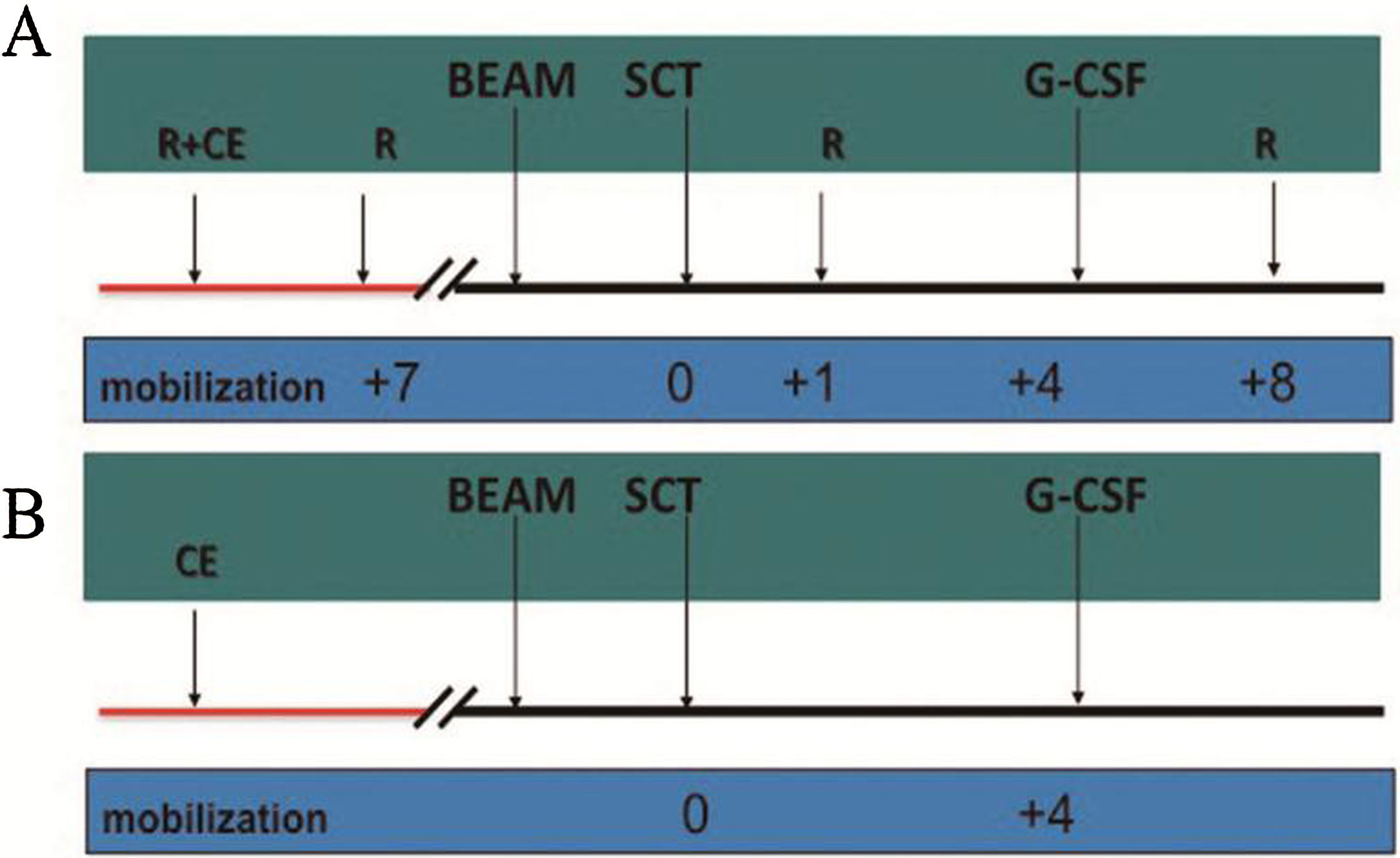
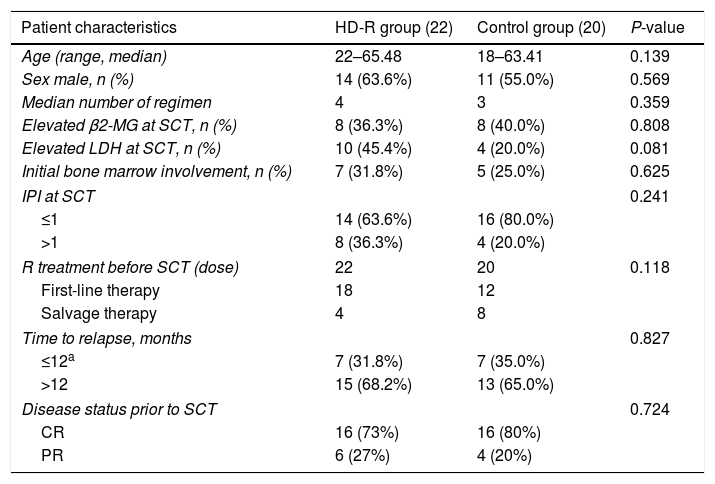
MethodsThere were 22 patients in the HD-R group, to whom rituximab was administered during stem cell mobilization (375mg/m2 1 day before and 7 days after chemotherapy) and after transplantation (1000mg/m2 on days +1 and +8). In the control group, the procedure was the same as that in the HD-R group but without rituximab. We observed the safety, tolerability, adverse effects and immune reconstitution of HD-R therapy. The log-rank test, univariate analysis and multivariate Cox regression analysis were used to evaluate the effect of HD-R on survival.
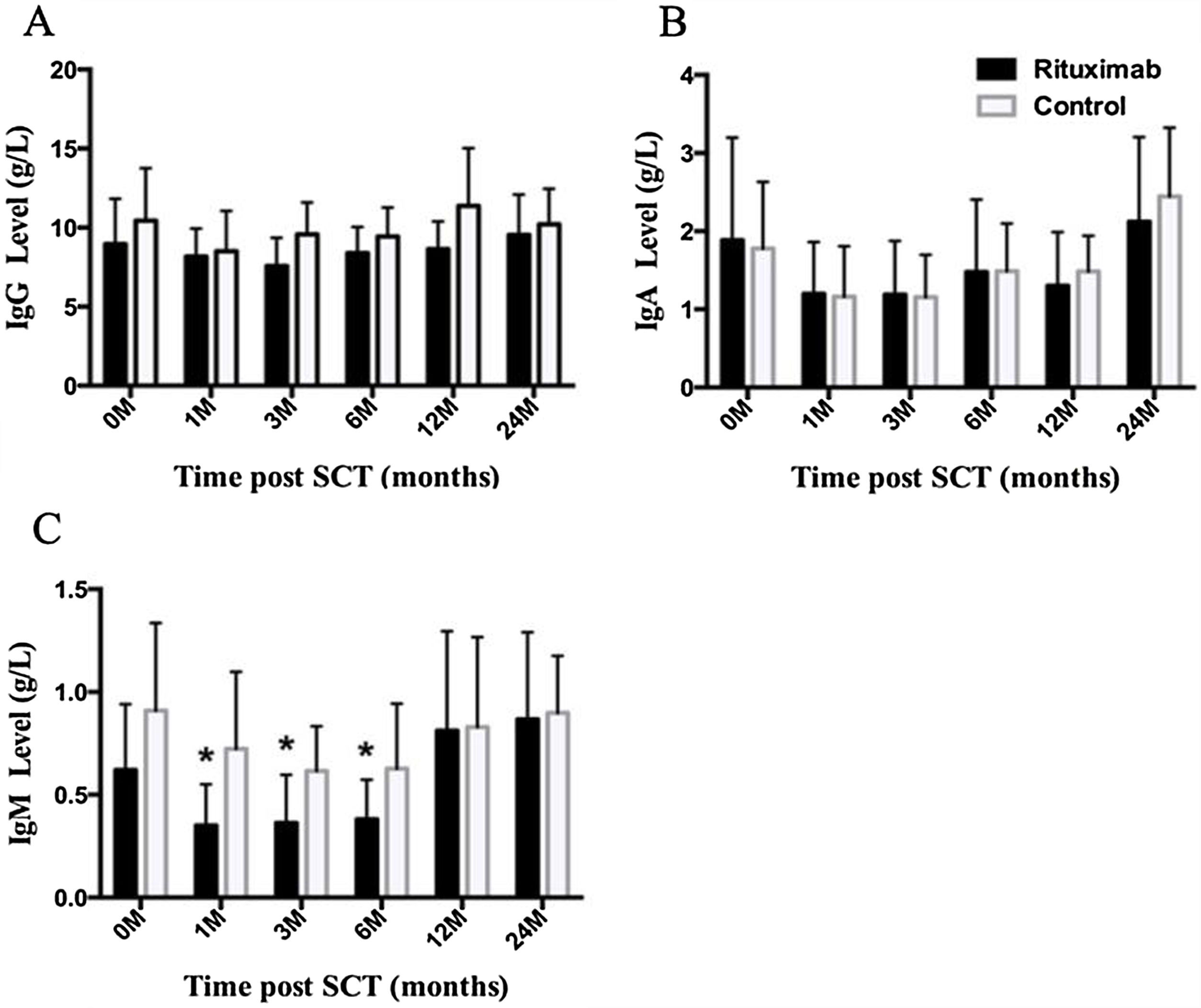
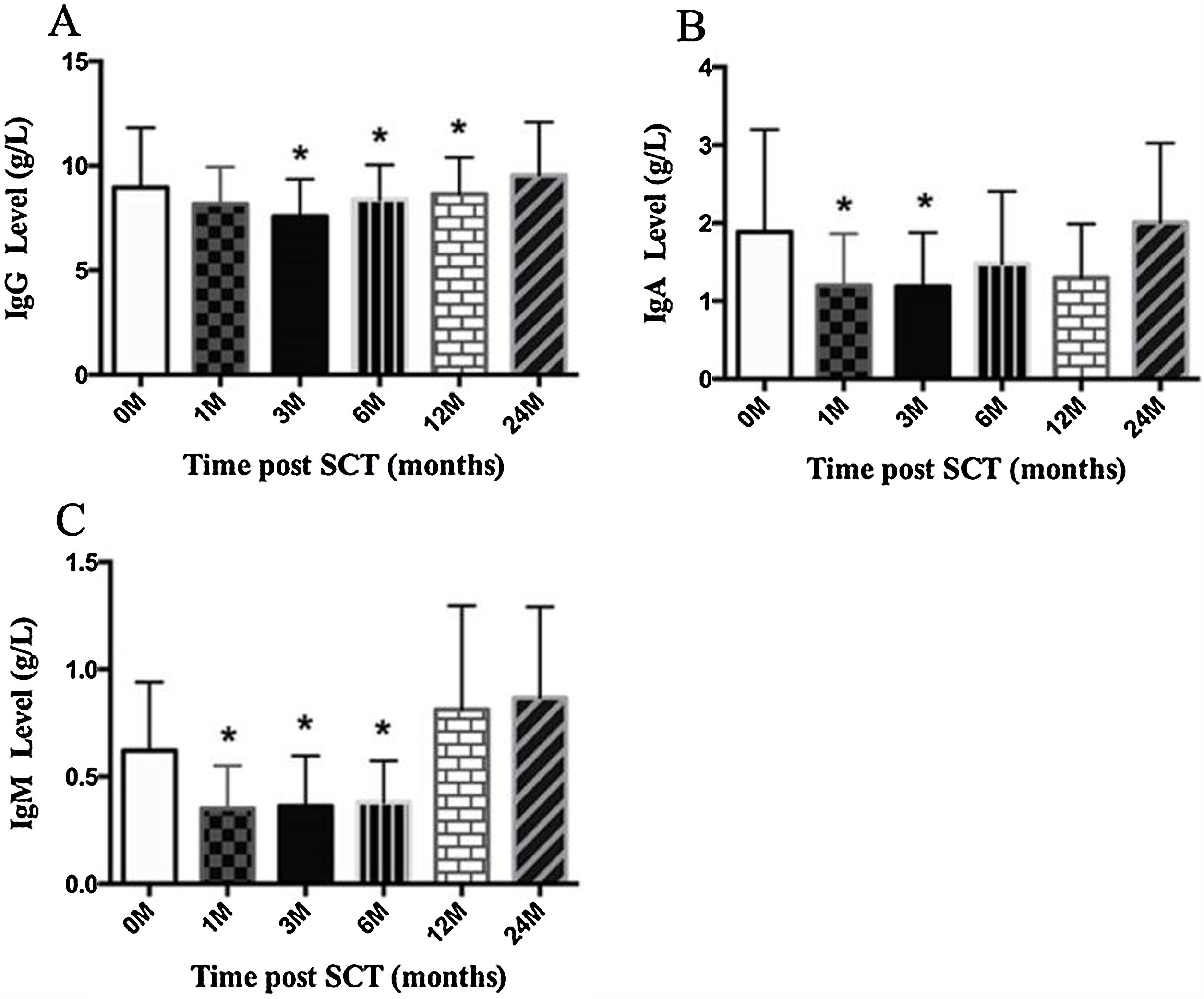
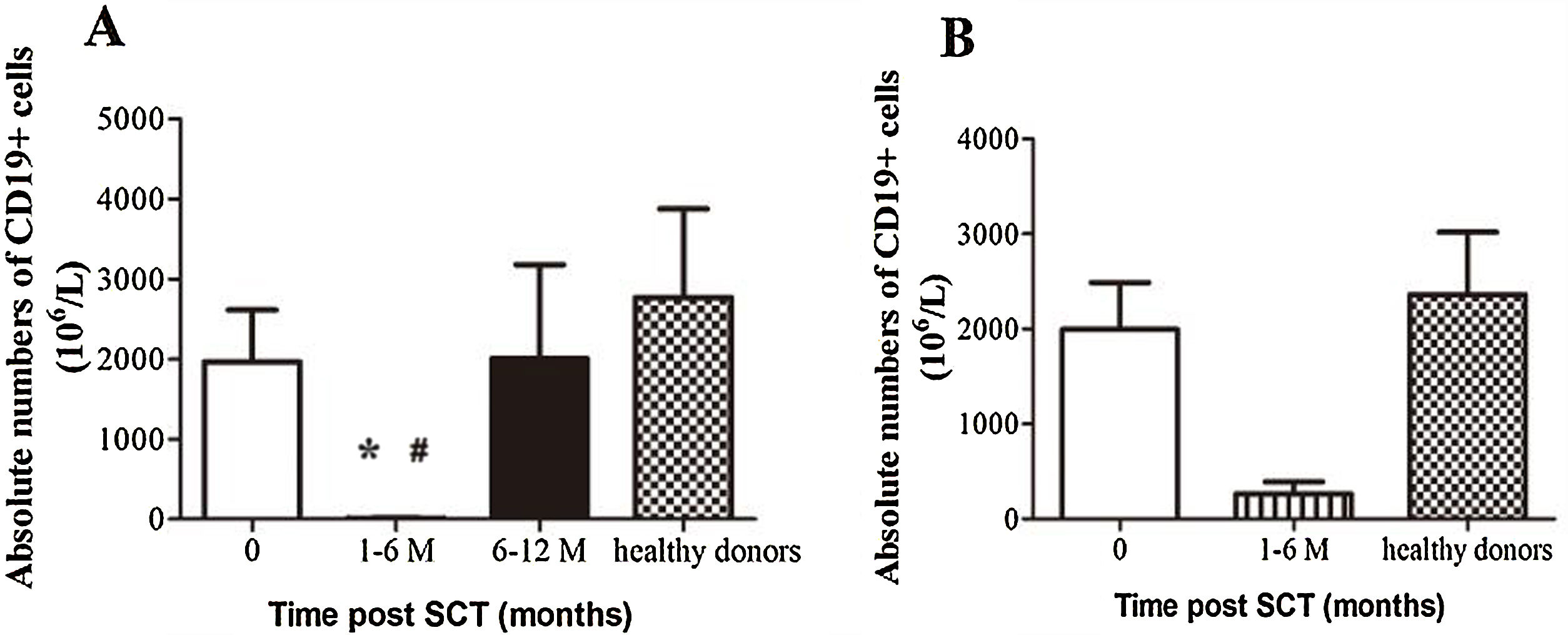
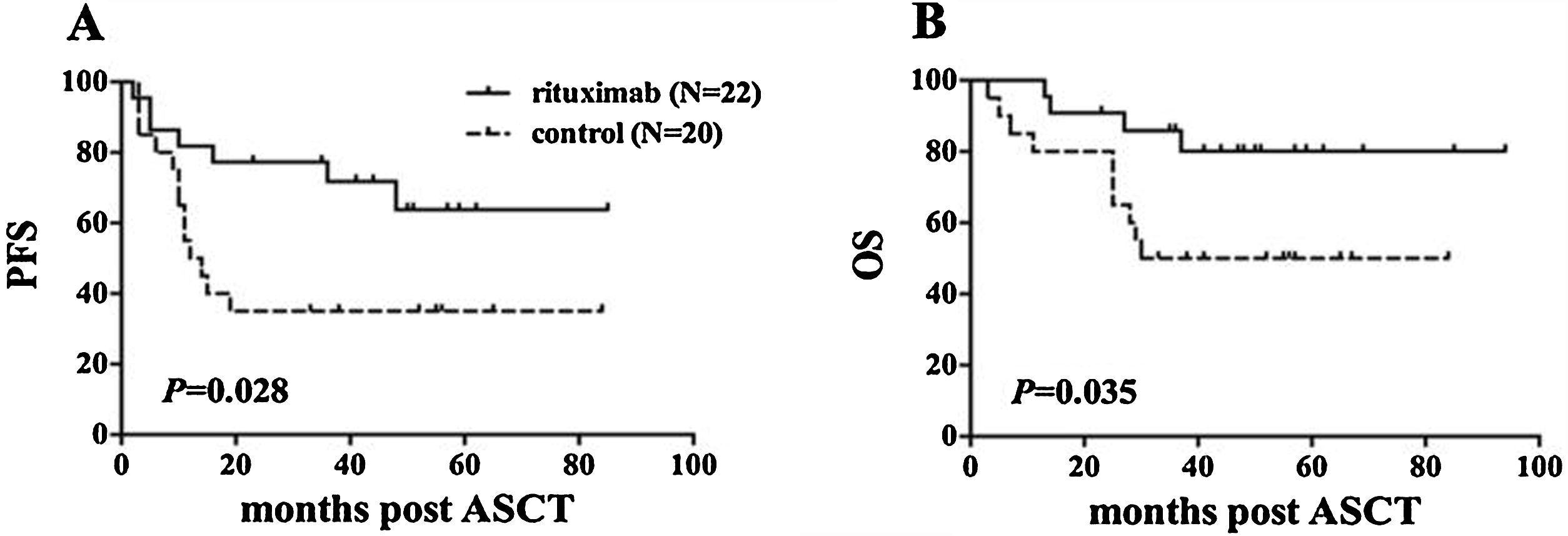
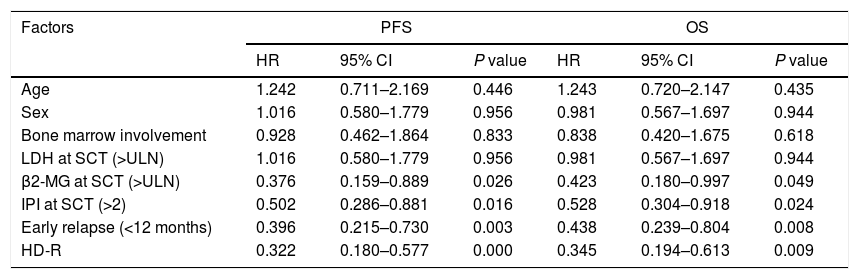
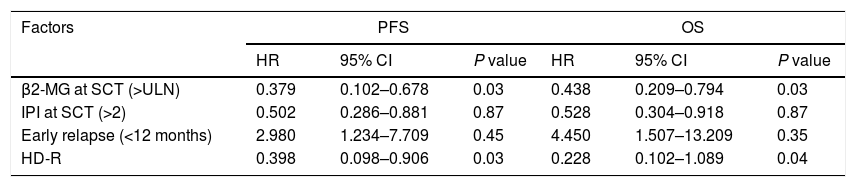
ResultsIn total, 22 relapsed or refractory DLBCL patients were treated with HD-R. No dose-limiting toxicities were observed except for CD19+ B cell reconstruction in the first 6 months after SCT. There were 20 relapsed or refractory DLBCL patients in the control group. The 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) greatly improved in the HD-R group compared to that in the control group (63.8% vs. 35.0%, P=0.028 and 80.1% vs. 50.0%, P=0.035, respectively). The univariate and multivariate analyses demonstrated that HD-R and the time to relapse were independent prognostic factors for OS and PFS.
ConclusionHD-R in combination with auto-SCT is a feasible and promising treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar la eficacia y la toxicidad de la combinación de altas dosis de rituximab (HD-R) y el trasplante de células madre autólogas (auto-SCT) en pacientes con linfoma B difuso de células grandes (LBDCG) en recaída o refractario.
MétodosEl grupo HD-R incluyó 22 pacientes a quienes se les administró rituximab durante la movilización de células madre (375mg/m2 un día antes y 7 días después de la quimioterapia) y tras el trasplante (1000mg/m2 los días +1 y +8). En el grupo control, el procedimiento fue el mismo que en el grupo HD-R, aunque sin rituximab. Observamos la seguridad, la tolerabilidad, los efectos adversos y la reconstitución inmune de la terapia HD-R. Utilizamos la prueba log-rank, el análisis univariante y el análisis de regresión de Cox multivariante para evaluar el efecto de HD-R en la supervivencia.
ResultadosEn total, 22 pacientes de LBDCG en recaída o refractario fueron tratados con HD-R. No se observaron toxicidades limitantes de dosis excepto para la reconstrucción de células CD19+ B en los primeros 6 meses tras SCT. El grupo control incluyó 20 pacientes de LBDCG en recaída o refractario. La supervivencia libre de progresión (SLP) a 3 años y la supervivencia general (SG) mejoró significativamente en el grupo HD-R en comparación con el grupo control (63,8 vs. 35%; p=0,028 y el 80,1 vs. 50%; p=0,035, respectivamente). Los análisis univariante y multivariante demostraron que HD-R y tiempo de recaída eran factores pronósticos independientes para SG y SLP.
ConclusiónLa combinación de HD-R y auto-SCT es un tratamiento factible y prometedor para pacientes con LBDCG en recaída o refractario.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora