To evaluate the epidemiological evolution and economic impact of COVID-19 pandemic in the European Union (EU) and worldwide, and the effects of control strategies on them.
Material and methodsWe collected incidence, mortality, and gross domestic product (GDP) data between the first quarter of 2020 and of 2023. Then, we reviewed the effectiveness of the mitigation and zero-COVID control strategies. The statistical analysis was done calculating the incidence rate ratio (IRR) of two rates and its 95% confidence interval (CI).
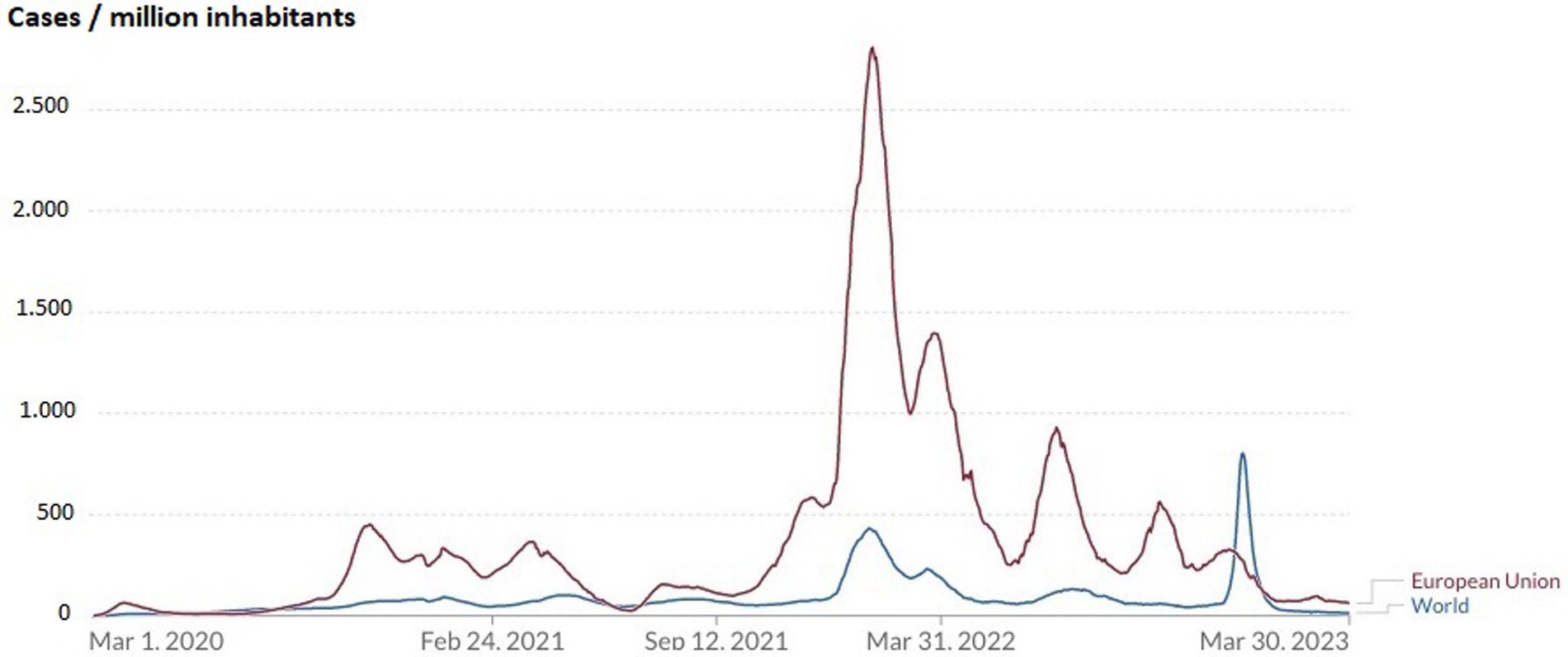
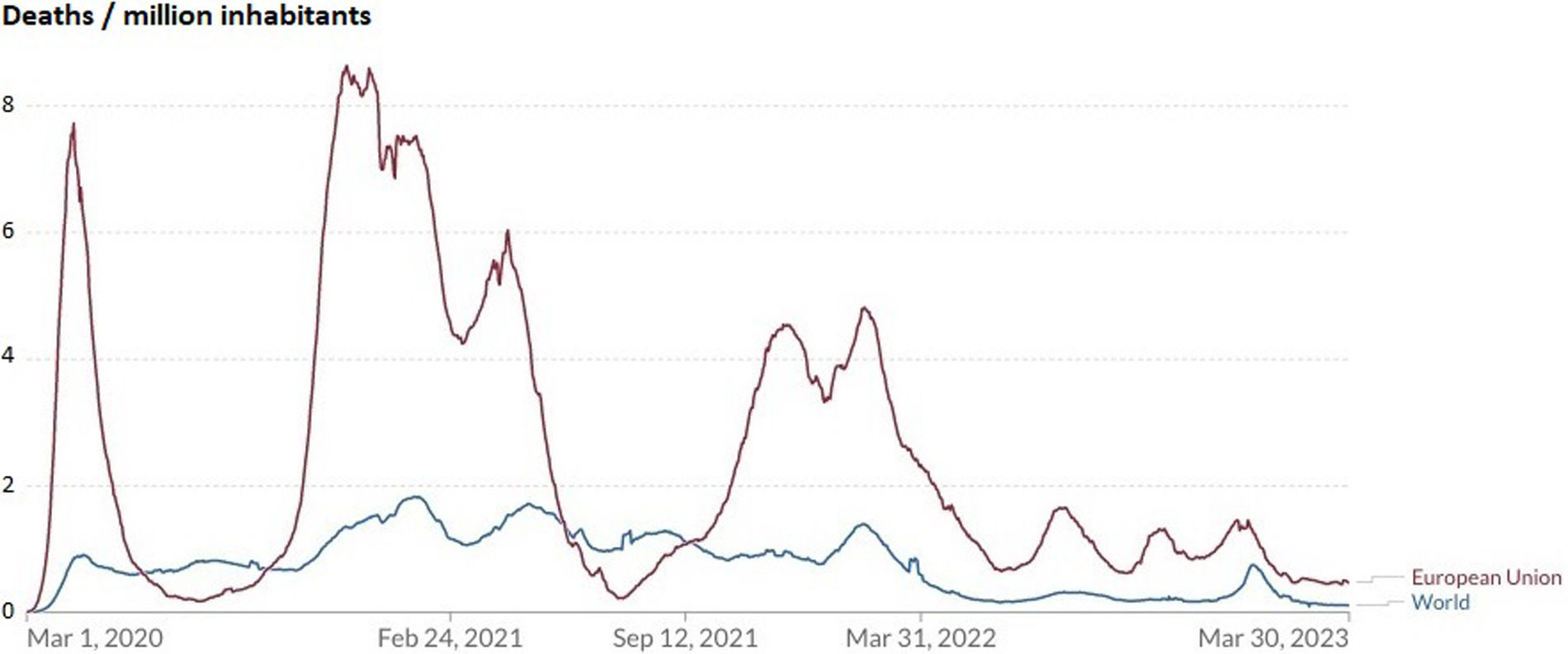
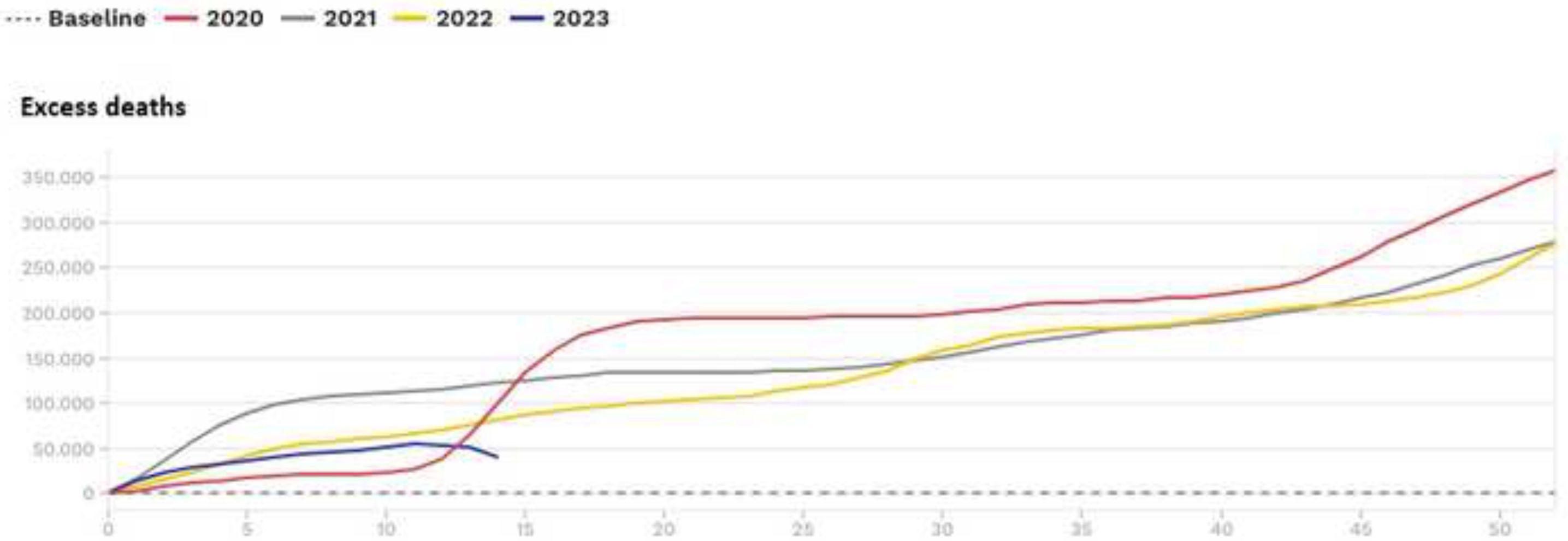
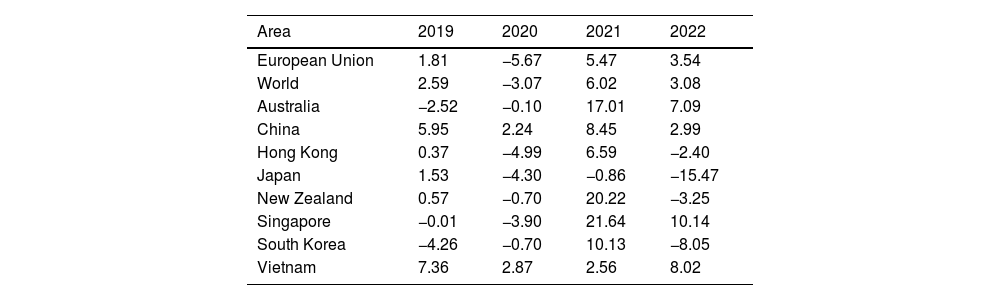
ResultsIn the EU, COVID-19 presented six epidemic waves. The sixth one at the beginning of 2022 was the biggest. Globally, the biggest wave occurred at the beginning of 2023. Highest mortality rates were observed in the EU during 2020–2021 and globally at the beginning of 2021. In mitigation countries, mortality was much higher than in zero-COVID countries (IRR=6.82 [95% CI: 6.14–7.60]; p<0.001). A GDP reduction was observed worldwide, except in Asia. None of the eight zero-COVID countries presented a GDP growth percentage lower than the EU percentage in 2020, and 3/8 in 2022 (p=0.054). COVID-19 pandemic caused epidemic waves with high mortality rates and a negative impact on GDP.
ConclusionThe zero-COVID strategy was more effective in avoiding mortality and potentially had a lower impact on GDP in the first pandemic year.
Evaluar la evolución epidemiológica y el impacto económico de la pandemia de COVID-19 en la Unión Europea (UE) y a nivel mundial, así como los efectos de las estrategias de control.
Material y métodosRecopilamos datos de incidencia, mortalidad y producto interior bruto (PIB) entre 2020 y el primer trimestre de 2023. Luego, revisamos la efectividad de las estrategias de mitigación y de COVID-cero. El análisis estadístico se realizó calculando la razón de tasas de incidencia (RTI) de dos tasas y sus intervalos de confianza (IC) del 95%.
ResultadosEn la UE, la COVID-19 presentó seis oleadas epidémicas. La sexta, a principios de 2022, fue la más grande. A nivel mundial, la ola más grande se produjo a principios de 2023. Las tasas de mortalidad más altas se observaron en la UE durante 2020-2021, y a nivel mundial, a principios de 2021. En los países de mitigación, la mortalidad fue mucho mayor que en los países COVID-cero (RTI=6,82 [IC95%: 6,14-7,60]; p<0,001). Se observó una reducción del PIB en todo el mundo, excepto en Asia. Ninguno de los ocho países COVID-cero presentó un porcentaje de crecimiento del PIB inferior al de la UE en 2020, y 3/8 en 2022 (p=0,054). La pandemia de COVID-19 provocó olas epidémicas con altas tasas de mortalidad y un impacto negativo en el PIB.
ConclusiónLa estrategia COVID-cero fue más efectiva para evitar la mortalidad, y potencialmente tuvo un menor impacto en el PIB en el primer año de la pandemia.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEMERGEN, (https://www.semergen.es/index.php?seccion=biblioteca&subSeccion=revistaSEMERGEN ) y autentifíquese.