Cuantificar los pacientes parkinsonianos en la Región de Murcia (RM), sus áreas y zonas de salud, hallar su prevalencia y los porcentajes.
Material y métodosSe incluyeron todos los pacientes de la RM registrados en Atención Primaria del Servicio Murciano de Salud con el código CIAP-2 N87. Se calcularon: número, prevalencias y porcentajes por grupos de edad y sexo, medias y rangos de edad y de años de evolución. Se realizó el estudio a la edad del diagnóstico y a la de la recogida de datos, analizando sus diferencias.
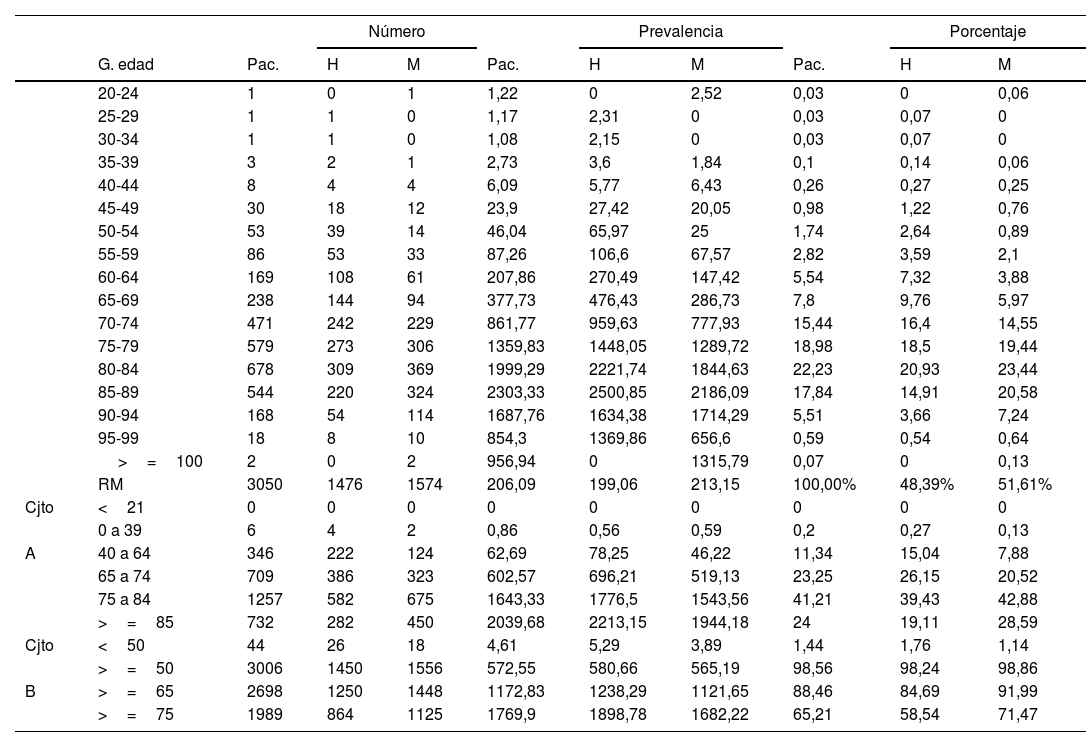
ResultadosSe obtuvieron 3.050 pacientes parkinsonianos (1.476 hombres y 1.574 mujeres) con unas prevalencias respectivas de 206,09 casos por 100.000 habitantes (206,09/105), 199,06/105 y 213,15/105, diferencias no significativas por sexos ni en número de pacientes (p=0,79) ni en prevalencias (p=0,52). Por grupos de edad fueron mayores las prevalencias en hombres (p<0,05) entre 50 y 99años (no entre 90 y 94 y ≥100años). De las 9 Áreas de Salud, las mayores prevalencias fueron en las áreas IVNoroeste, con 322,31/105, y VAltiplano, con 304,30/105, y la prevalencia menor, de 171,13/105, se observó en el Área VIIMurcia Este (p<0,05). De las 85 zonas de salud, la de mayor prevalencia fue Lorca-La Paca, con 510,51/105, y la de menor prevalencia, Murcia-Zarandona, con 78,48/105 (p<0,05).
ConclusionesPrimer estudio demográfico y de prevalencia pormenorizado de parkinsonismo en la RM. La prevalencia en la RM fue de 206,09/105. Por áreas de salud, las mayores prevalencias fueron en las de Noroeste y Altiplano, y por zonas de salud destacó la prevalencia de 510,51/105 de Lorca-La Paca. Este trabajo pretende ser útil para facilitar la planificación de recursos, con la consiguiente mejor atención sanitaria.
To quantify parkinsonian patients in the Region of Murcia (RM), their health areas and zones, and find their prevalences and percentages.
Material and methodsAll RM patients registered in Primary Care of the Murcian Health Service with the CIAP-2 code N87 were included. We calculated number, prevalence and percentages by age and sex groups, means and age ranges and years of evolution. The study was carried out at the age of diagnosis and at the age of data collection, analyzing their differences.
ResultsWe obtained 3050 parkinsonian patients (1476 men and 1574 women) with respective prevalences of 206.09 cases per 100,000 inhabitants (206.09/105), 199.06/105 and 213.15/105, not significant differences by sex or in number of patients (p=0.79) or in prevalence (P=.52). By age group, prevalences were higher in men (P<.05) between 50 and 99years of age (not between 90 and 94 and ≥100years). Of the 9 Health Areas, the highest prevalences were in areas IVNorthwest, with 322.31/105, and VAltiplano, with 304.30/105, and the lowest prevalence, of 171.13/105, was observed in Area VIIMurcia East (P<.05). Of the 85 Health Zones, the one with the highest prevalence was Lorca-La Paca, with 510.51/105, and the one with the lowest Murcia-Zarandona, with 78.48/105 (P<.05).
ConclusionsFirst demographic and detailed prevalence study of parkinsonism in the RM. The prevalence in RM was 206.09/105. By health areas, the highest prevalences were in the Northwest and Altiplano and by health areas a prevalence of 510.51/105 stood out. This work aims to be useful to facilitate resource planning, with consequent better health care.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEMERGEN, (https://www.semergen.es/index.php?seccion=biblioteca&subSeccion=revistaSEMERGEN ) y autentifíquese.