Contribuir a dilucidar la fisiopatología de la disnea y de la intolerancia al esfuerzo en pacientes con síndrome post-COVID con pruebas funcionales y de imagen cardiopulmonares normales en reposo, a la vez que determinar su aptitud y el nivel de resistencia orgánica con el fin de individualizar los parámetros de trabajo para la rehabilitación física.
Material y métodosTras una anamnesis y exploración clínica en reposo, 27 sujetos (50±11,9 años) (14 mujeres) con síndrome post-COVID de más de 6 meses de evolución realizaron una prueba de esfuerzo cardiopulmonar (CPET) incremental, continua y máxima, con análisis de gases respirados y monitorización ECG continua, en un cicloergómetro de freno electromagnético. Los valores obtenidos fueron comparados con los de referencia, sexo y/o controles, usando los test chi-cuadrado, t de Student o ANOVA.
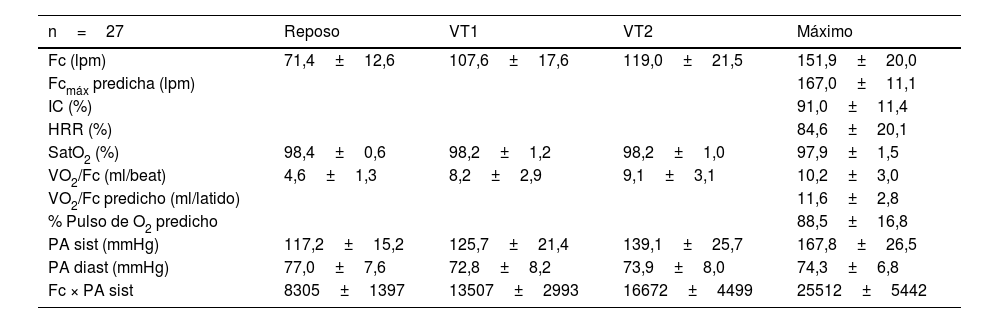
ResultadosLas exploraciones clínicas en reposo y las CPET fueron clínicamente normales, sin alteraciones cardiorrespiratorias relevantes, finalizando por agotamiento muscular de los miembros inferiores. Cabe destacar un IMC=29,9 ±5,8kg/m2 y un lactato basal de 2,1±0,7mmol/l. La valoración funcional de la resistencia orgánica mostró los siguientes resultados en relación con el VO2máx predicho: 1)VO2máx=80,5 ±18,6%; 2)umbral ventilatorio1 (VO2VT1): 46,0±12,9%; 3)VO2VT2: 57,2±16,4%; 4)tiempo de trabajo en acidosis: 5,6±3,0 minutos, y 5)lactato máximo: 5,1±2,2mmol/l.
ConclusionesLas CPET identificó la limitación del metabolismo aeróbico y el aumento precoz del metabolismo glucolítico como causas de la disnea e intolerancia al esfuerzo, determinó la aptitud para la rehabilitación física, e individualizó la misma en función del nivel de resistencia orgánica.
Contributing to elucidate the pathophysiology of dyspnoea and exertion intolerance in post-COVID syndrome patients with normal cardiopulmonary imaging and functional tests at rest, while determining their fitness and level of endurance in order to individualize working parameters for physical rehabilitation.
Material and methodsAfter an anamnesis and clinical examination at rest, 27 subjects (50±11.9 years) (14 women) with post-COVID syndrome of more than 6 months of evolution performed a continuous maximal-incremental graded cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET) with breath-by-breath gas-exchange monitoring and continuous ECG registration, on an electromagnetically braked cycle ergometer. The values obtained were compared with those of reference, gender or controls, using the Chi-square, t-Student or ANOVA test.
ResultsThe clinical examination at rest and the CPET were clinically normal and without adverse events. Reasons for stopping exercise were leg discomfort. It is only worth noting a BMI=29.9±5.8kg/m2 and a basal lactate concentration of 2.1±0.7mmol/L. The physiological assessment of endurance showed the following results relative to predicted VO2máx: 1)peakVO2=80.5±18.6%; 2)VO2 at ventilatory threshold1 (VO2VT1): 46.0±12.9%; 3)VO2VT2: 57.2±16.4%; 4)working time in acidosis: 5.6±3,0minutes; and 5)maximum lactate concentration: 5.1±2.2mmol/L.
ConclusionsThe CPET identified limited aerobic metabolism and early increase in glycolytic metabolism as causes of dyspnoea and exercise intolerance, determined fitness for physical rehabilitation, and individualized it based on the level of endurance.