Headache is common in the general population and a frequent reason for medical consultation.
ObjectivesTo describe the characteristics of patients attending the Emergency Department (ED) for headache.
MethodsA descriptive study with prospective collection of 100 consecutive patients over 15 years old who attended our ED due to headache as the main complaint.
ResultsHeadache accounted for 1.4% of ED visits. The most common age range is between 31 and 45 years and the majority of the patients are females (61%). We diagnosed 67 primary and 33 secondary headaches. The most frequent diagnosis was migraine, with 36% of cases. One out of 3 patients had a history of headache and 4 out of 5 consulted by their own decision. Only a small percentage of patients were admitted as inpatients (12%), and 3 out of 5 were referred to Primary Care. Complementary tests were performed on 84% of the patients. One CT scan was performed for every 3 patients. A total of 80% patients was correctly diagnosed by the ED physicians.
ConclusionsHeadache is a frequent complaint in the ED, where primary headaches are the most common with migraine being the most frequent reason for consultation. In our setting, there is a good screening and diagnosis of headaches, as well as an adequate use of the available resources in the ED for their diagnosis and management.
La cefalea es muy frecuente entre la población general y un motivo habitual de consulta médica.
ObjetivosDescribir las características clínicas de los pacientes que acuden a Urgencias por cefalea.
MétodosEstudio descriptivo con recogida prospectiva de pacientes consecutivos mayores de 15 años que acuden al Servicio de Urgencias del Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla (HUMV) por cefalea como motivo principal de consulta.
ResultadosSe recogieron 100 pacientes. La cefalea como motivo de consulta supuso el 1,4% de las Urgencias atendidas. El grupo mayoritario fue el de edades comprendidas entre los 31 y 45 años, con predominio de mujeres (61%). Se diagnosticaron 67 cefaleas primarias y 33 secundarias. El diagnóstico más frecuente fue el de migraña, con un 36% del total de cefaleas. Uno de cada 3 pacientes tenía antecedentes de cefalea y 4 de cada 5 acudieron a Urgencias por decisión propia. Solo un pequeño porcentaje de los pacientes atendidos en Urgencias llegaron a ingresar (12%), y 3 de cada 5 fueron derivados a Atención Primaria. Se realizaron pruebas complementarias al 84% de los pacientes atendidos. Se realizó un TAC craneal por cada 3 pacientes. Un 80% de los pacientes fueron correctamente diagnosticados por los médicos de Urgencias.
ConclusionesLa cefalea es un motivo frecuente de consulta en los Servicios de Urgencias, siendo más habituales las cefaleas primarias y dentro de éstas, la migraña. En nuestro medio se realiza un buen cribado y diagnóstico de las cefaleas, así como un adecuado uso de los recursos disponibles en Urgencias para su diagnóstico y manejo.
Headache is a very frequent disorder in the general population, and involves a considerable socioeconomic burden; specifically, migraine has the greatest impact due to its high prevalence. This results in a great loss of patient quality of life and productivity, as well as high economic costs for society.1 It is currently considered the second leading cause of years lived with disability or poor health worldwide, for both sexes.2
Although the majority of patients with headache consulting the neurology department present primary headaches, emergency departments should be alert to the warning signs and symptoms of severe secondary headache.3 A small number of retrospective studies have sought to determine the frequency and distribution of diagnoses of patients attending the emergency department due to headache as the leading symptom.4–15 At emergency departments in our setting, headaches are estimated to represent the third leading reason for consultation, following stroke and epilepsy.6–8 Some studies analysing neurological care at emergency departments report that emergency consultations due to headache account for 1%–3% of the total.12,13,15
This study aims to prospectively analyse the percentage of patients attending the emergency department of a tertiary hospital due to headache as the main reason for consultation, to study the distribution of diagnoses and the referral pathways and resources used, and to evaluate concordance between the diagnoses established at the emergency department and the definitive diagnosis of those patients, with the help of a specialised neurologist.
Patients and methodsWe prospectively collected data from 100 consecutive patients older than 15 years (in our region, individuals aged 15 and younger are considered paediatric patients) who attended the emergency department of a tertiary hospital due to headache as the leading symptom. Sample size was not calculated a priori, and data analysis was based on the available data. The study period was 5 November to 2 December 2019. Emergency department physicians prospectively gathered data on all those patients attending due to headache as the leading symptom during their shifts, and also reviewed triage diagnoses. The initial clinical data on these patients were obtained through the emergency department reports included in patients’ electronic clinical records, which were reviewed in the following 48 hours, without exception. The study was approved by the ethics committee (code 20/01358).
The variables gathered were: demographic data, personal history, previous treatments, previous history of headache, source of referral to the emergency department, history of current headache, physical examination findings, complementary studies requested, length of stay at the emergency department, destination at discharge from the emergency department, and working diagnosis at the emergency department (Supplementary Material). We did not analyse the treatments applied during patients’ stay at the emergency department. These data were analysed on a daily basis by the research team. A headache specialist referred patients with uncertain diagnoses to the headache clinic. We followed up all these cases until a reliable diagnosis was established. This neurologist established the definitive diagnosis in accordance with the criteria of the current International Classification of Headache Disorders.16 Patients making more than one visit to the emergency department due to headache were counted only once.
ResultsWe recruited 100 patients in 27 days, which amounts to a mean of 3.7 patients/day and 1.2% of all emergency consultations (8119 during the study period). Of these, 8 made one further visit to the emergency department during the study period, and 2 made 2 additional visits. This represents a total of 112 visits to the emergency department during the study period, which raises the percentage of headache consultations at the department to 1.4%. Of the 100 patients analysed, 61 were women; age ranged between 17 and 87 years (mean [standard deviation], 47.7 [17.3]; median, 43.5).
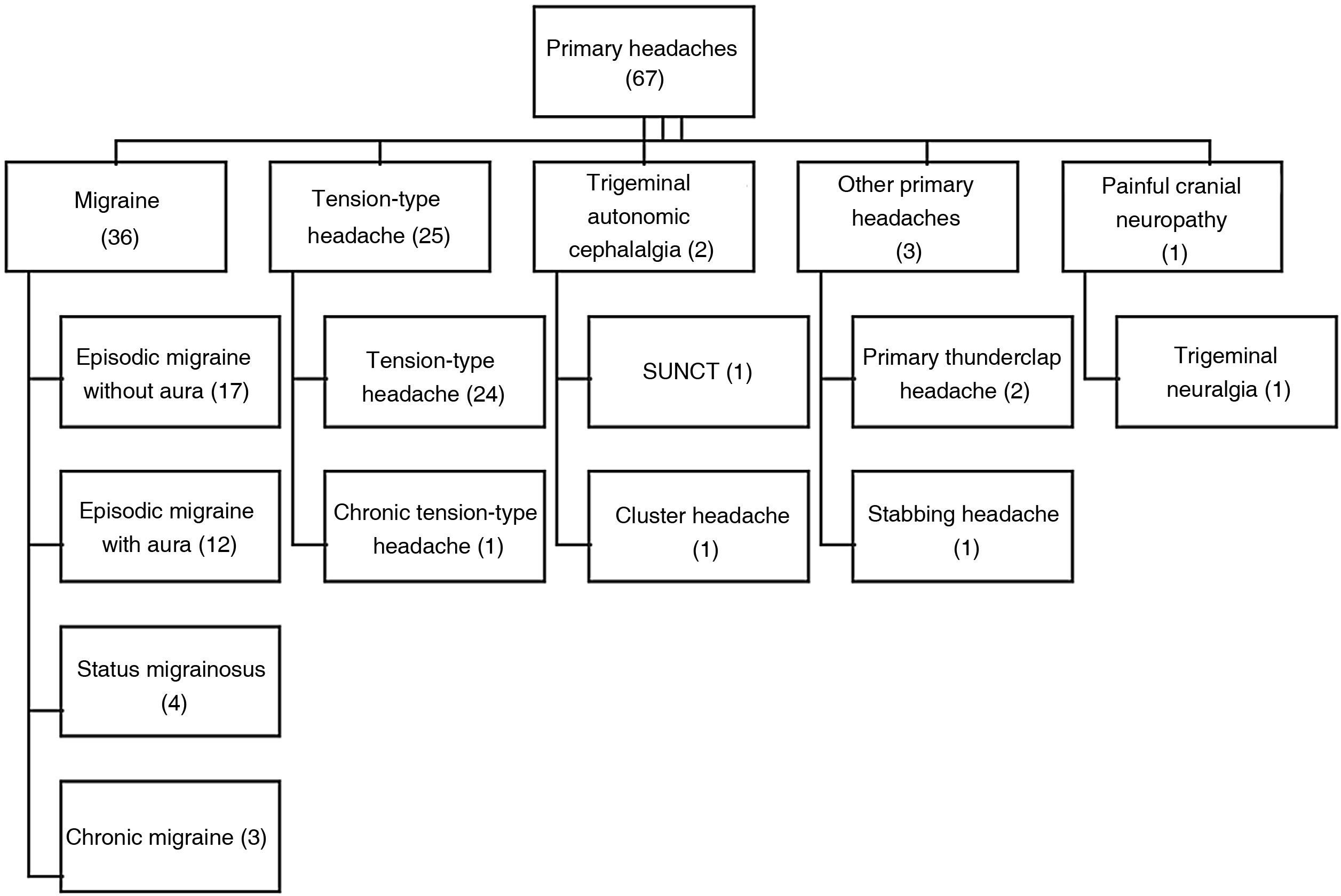
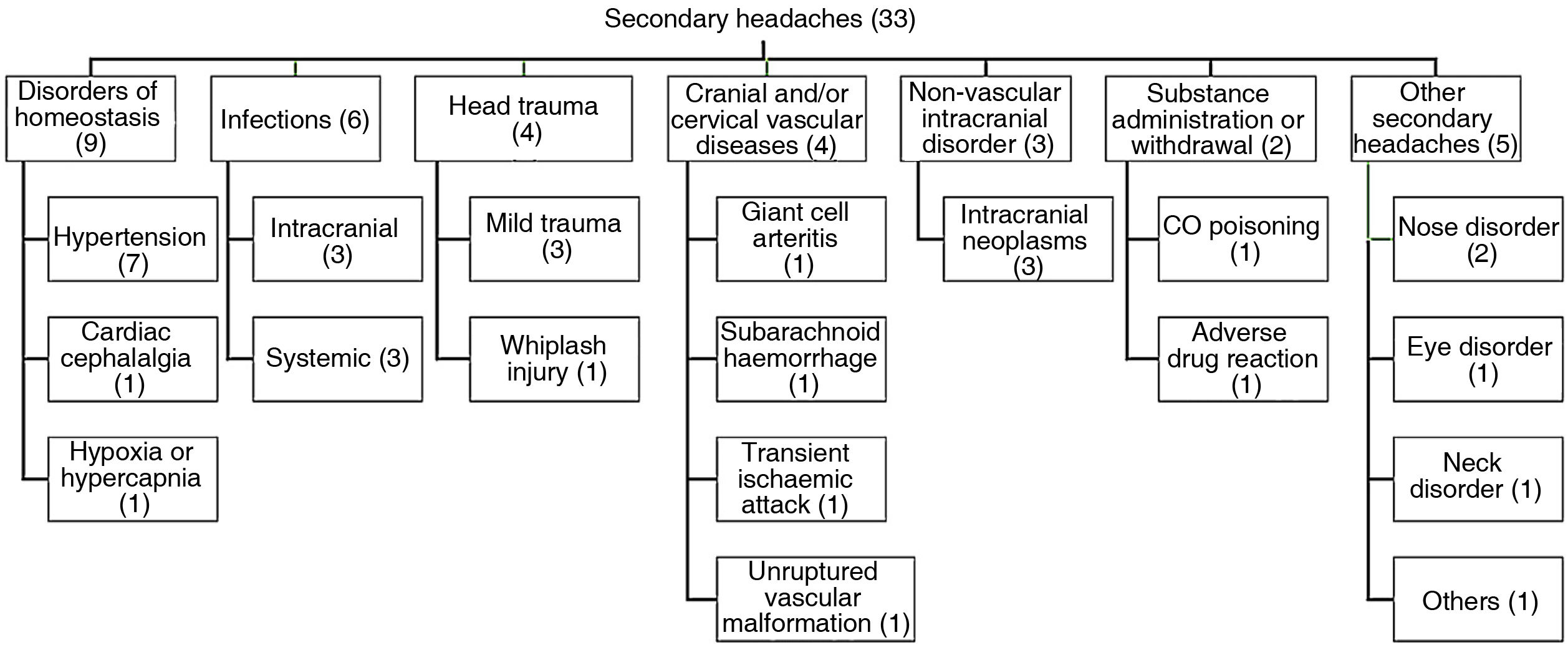
Distribution of diagnosesOf the total samples, 67 patients were diagnosed with primary headache and 33 with secondary headache. A total of 9 patients with primary headache met criteria for analgesic abuse. Fig. 1 shows the distribution of diagnoses of primary headache. Fig. 2 shows the distribution of diagnoses of the 33 cases of secondary headache.
Of all patients attended by the emergency department due to headache, 31 patients had history of headache, with 26 of this group being diagnosed with primary headache and 5 with secondary headache. Of all the patients analysed, 30 had previously visited the emergency department due to headache, of whom 24 were diagnosed with primary headache and 6 with secondary headache. Regarding the 6 patients with secondary headache who had previously attended the emergency department for this reason, 4 of them had history of headache whereas 2 did not.
Origin and destinationOf the 100 patients included in the study, 83 decided on their own to attend the emergency department, 12 were referred by their primary care physician (PCP), and 5 were referred by the primary care emergency department (PCED). Of the 67 patients with primary headache, 57 (85.1%) decided on their own to attend the emergency department, 7 (10.4%) were referred by their PCP, and 3 (4.5%) were referred by the PCED. Of the 33 patients with secondary headache, 26 (78.8%) decided on their own to attend the emergency department, 5 (15.1%) were referred by their PCP, and 2 (6.1%) were referred by the PCED. Destinations after examination at the emergency department were the following: 59 were referred to their PCP, 20 were discharged home and were not referred to any other department, 18 were referred to the neurology department, 12 were admitted to hospital, and 2 were referred to other specialist consultations. It should be noted that 11 patients were referred both to the neurology department and to their PCP (one referral does not preclude the other). In addition to the 18 patients directly referred from the emergency department, the headache specialist attended an additional 6 patients at the headache unit after reviewing their clinical records from the emergency department.
Thus, 88 patients were not finally admitted and were discharged from the emergency department. In these patients, the mean stay at the emergency department was 5 hours and 32 minutes (standard deviation, 5 hours and 14 minutes) (median, 4 hours and 35 minutes), although the length of stay at the emergency department was very variable, ranging from 14 minutes to 1 day and 15 hours. Among the patients diagnosed with migraine, one was admitted and the remaining 34 were discharged from the emergency department. The mean stay of these patients at the emergency department was 6.6 (6.8) (median, 4.95; range: 14 min–15 h). Thirty patients were attended by the on-call neurologist.
Complementary studiesOf the 100 patients analysed, 16 underwent no complementary test during their stay at the emergency department. Fourteen of these (87.5%) were diagnosed with primary headache, and 2 (12.5%) with secondary headache. The tests performed were the following: 75 blood analyses, 32 head CT scans, 19 simple radiographies (of the chest in 13 cases, neck in 2, abdomen in one, and spine in one), 4 MRI studies, 4 lumbar punctures, and one electroencephalography (in a patient who was admitted due to headache at the emergency department and finally diagnosed with hypertensive encephalopathy). Cranial CT scans at the emergency department were performed in 25.4 % of patients with primary headache and 45.5% of patients with secondary headache.
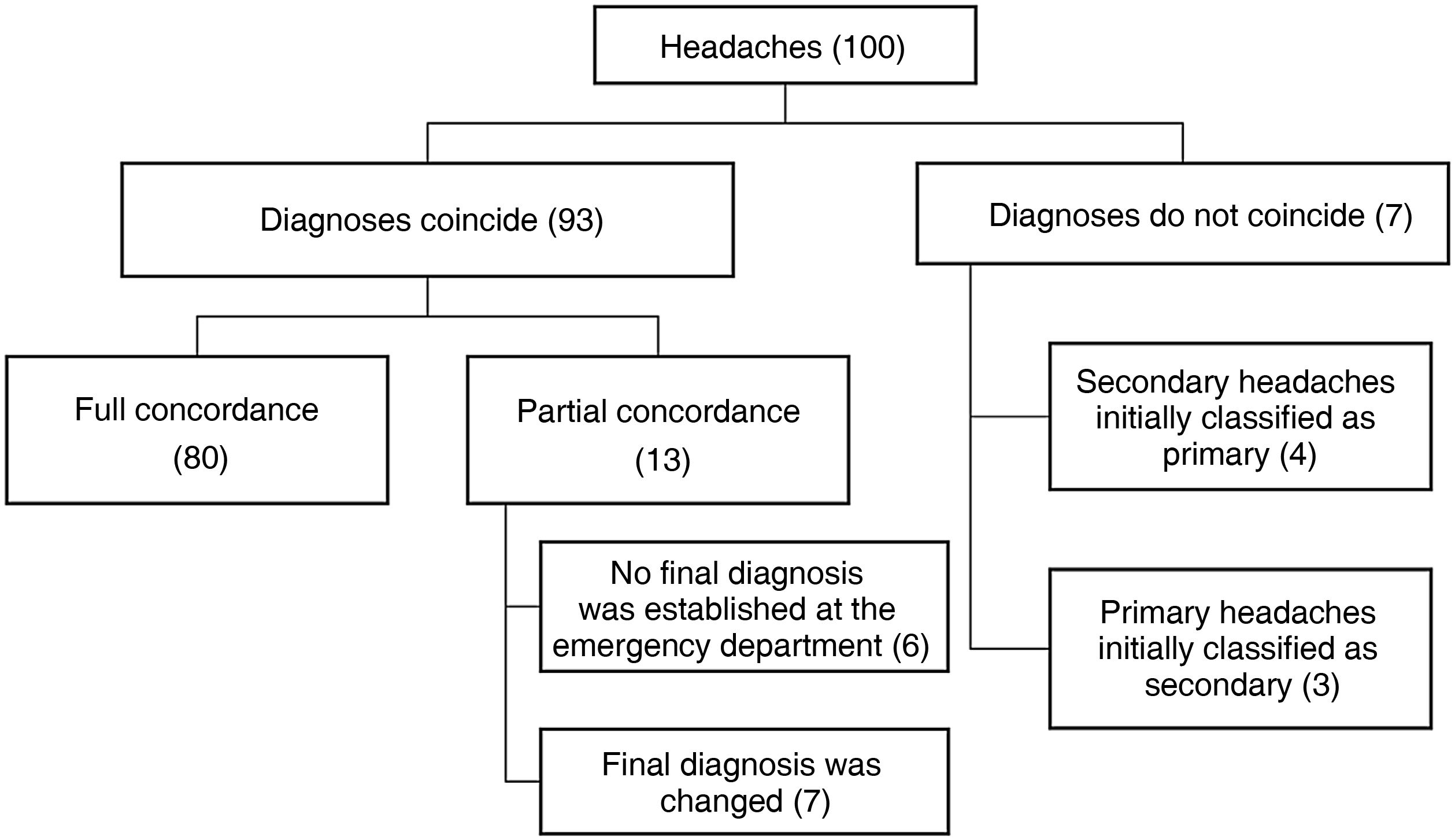
Final diagnosisIn 93 of the 100 patients studied, the general diagnosis (primary or secondary headache) established at discharge from the emergency department coincided with the definitive diagnosis established by the headache specialist. In the remaining 7 patients, diagnoses differed greatly. In the 93 patients with coinciding diagnoses, agreement was total in 80 patients and partial in 13 (Fig. 3). Eleven of the latter 13 cases were classified at the emergency department as “non-organic or primary headaches” with no specific diagnosis, and finally diagnosed with migraine (7 cases), tension-type headache (3 cases), or short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache with conjunctival injection and tearing (one case). The 2 patients with secondary headaches were initially diagnosed with chest pain and partial respiratory failure, and finally with cardiac cephalalgia and headache secondary to a respiratory disorder, respectively.
Of the 7 cases with diverging diagnoses, 4 were initially classified as primary headache but reclassified as secondary in the final review, as follows: 2 were secondary to cranial and/or cervical vascular diseases; in both cases, patients returned to the emergency department, where they were finally diagnosed with subarachnoid haemorrhage. The other 2 cases were initially classified as tension-type headache or headache without warning signs, but finally classified as headache attributed to arterial hypertension. The remaining 3 patients were initially diagnosed with probable secondary headache and finally diagnosed with primary headache (tension-type headache in all 3 cases).
DiscussionThe main finding in our study is that 1.4% of patients attending the emergency department of a tertiary hospital presented headache as the leading symptom. Although headache is a frequent reason for consultation at the emergency department, few national or international studies have analysed the frequency and distribution of diagnoses of headache.4–15 Despite the heterogeneity of the published studies, the rate of 1.4% of emergency consultations is within the range reported by other researchers (1%–3%).12,13,15 The main advantage of our study in comparison with other published studies is that patients are systematically and prospectively analysed with the direct participation of headache specialists. This is an important consideration, since retrospective data collection in patients presenting headache at the emergency department is biased by the final diagnosis. For example, while a patient with meningitis or subarachnoid haemorrhage may attend the emergency department due to headache, this would not be reported as the reason for consultation if we consider only the final diagnosis.
Despite the limitation that we did not study in detail the specific diagnoses of all patients consulting the emergency department, due to the high volume, but rather only those of patients with headache, our findings confirm that headache is one of the main reasons for emergency consultations. Patients attending the emergency department due to headache were predominantly women aged between 30 and 50 years. This coincides with the demographic characteristics of the main primary headaches, especially migraine, which was the most frequent reason for consultations, followed at great distance by tension-type headache. The proportion of primary vs secondary headaches (2 out of every 3 headaches were primary) greatly varies between the different published studies,3–14 although our findings are consistent with those of studies from nearby geographical areas.5 It is important to highlight that a third of the patients were diagnosed with secondary headache, and our series includes several examples of the importance of diagnosing high-risk secondary headaches at the emergency department.3
In our sample, the great majority of patients attending the emergency department decided on their own to do so, and only a minority were referred by their PCP or by the PCED. This probably explains the relatively high percentage of patients diagnosed with tension-type headache at the emergency department in this study. Patients referred to the emergency department by their PCP or PCED were more frequently diagnosed with secondary than with primary headache, which may lead us think that some clinical sign in these patients led the physician to refer them. The percentage of patients referred from primary care is similar to that reported in the study by Vidal-Castelló et al.5 Furthermore, this study highlights the high percentage of patients who, despite presenting headache with primary characteristics, spontaneously attend the emergency department with no warning signs. Our findings unquestionably reflect the misuse of emergency departments in Spain, and also show that the management of these patients with primary headache in health centres is not always satisfactory.17,18
Regarding the destination of the patients attended at emergency departments, more than half were referred to primary care, whereas only one in 5 was referred to the neurology department; all these patients were diagnosed with primary headache. In our study, slightly over one in 10 patients were admitted to hospital, most of whom were diagnosed with secondary headache. This shows that, although the great majority of secondary headaches are not severe, a small percentage may be potentially severe, and therefore require specialised care and hospital admission. Studies in the literature report heterogeneous data on this subject, but our data coincide with the percentages observed in recent studies in Spain.5,19 This is clearly influenced by the easy access to neurological care and the interest in headache at the different neurology departments in Spain.
The majority of patients underwent one or more complementary tests, with only a minority not undergoing any (less than one in 5 patients). The most frequently performed test, in the case of both primary and secondary headache, was blood analysis, followed by head CT scan. However, CT scans were proportionally more frequent in patients with secondary headache than in those with primary headache, due to the need to rule out any underlying disease. Furthermore, the least frequent and most specific tests were those performed in patients who were admitted to hospital: lumbar puncture and MRI, which are practically exclusive to secondary headaches. One CT scan was performed for every 3 patients attended. Compared to the results reported by Vidal-Castelló et al.,5 CT scans were more frequent in our series (one in 3 patients vs somewhat less than one in 5). In any case, we do not consider these numbers high for a tertiary hospital, probably due to the fact that CT is easy to request by emergency departments; in fact, it is very easy in our centre.
Finally, our study included a review of the diagnoses established at the emergency department, and assignment of a final diagnosis to each patient. The majority of diagnoses coincided. Our results show that appropriate screening is performed at the emergency department to differentiate between primary and secondary headache, as only 7% of diagnoses did not coincide. However, due to their specificity, some diseases cannot be diagnosed at the emergency department, whose main aim is to identify those patients with warning signs who may present a severe condition.