Analizar el rendimiento diagnóstico de la angio-TC pulmonar y comparar distintos valores de corte del dímero-D para el diagnóstico de tromboembolia pulmonar (TEP) aguda en pacientes con y sin infección por SARS-CoV-2.
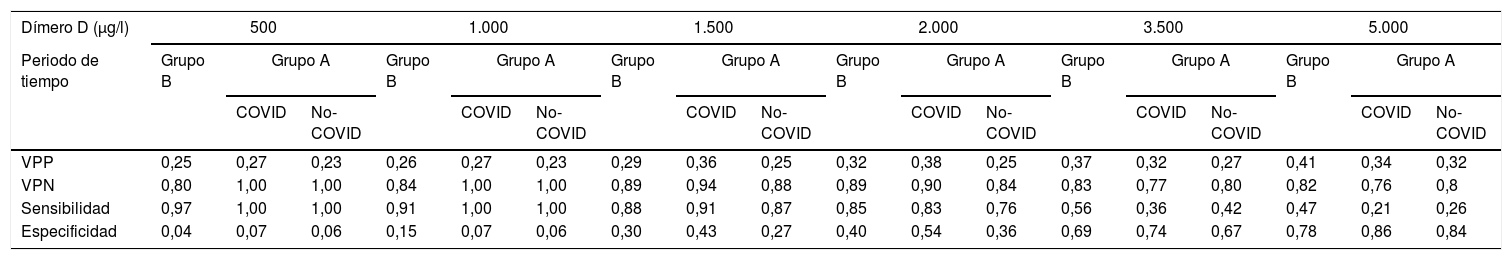
Materiales y métodosAnálisis retrospectivo de todas las angio-TC pulmonares realizadas consecutivamente por sospecha de TEP en un hospital de tercer nivel durante 2 periodos distintos. El primero de diciembre del 2020 a febrero del 2021 y el segundo de diciembre del 2017 a febrero del 2018. Se recogieron los resultados del dímero-D durante las 24h previas a la realización de las angio-TC pulmonares, así como el resultado de estas últimas para todos los pacientes incluidos. Se analizaron la sensibilidad, especificidad, valores predictivos, área bajo la curva (AUC) y patrón de tromboembolia para 6 valores distintos del dímero-D y la extensión del tromboembolia. Durante el periodo de la pandemia se registró si los pacientes tenían enfermedad por SARS-CoV-2.
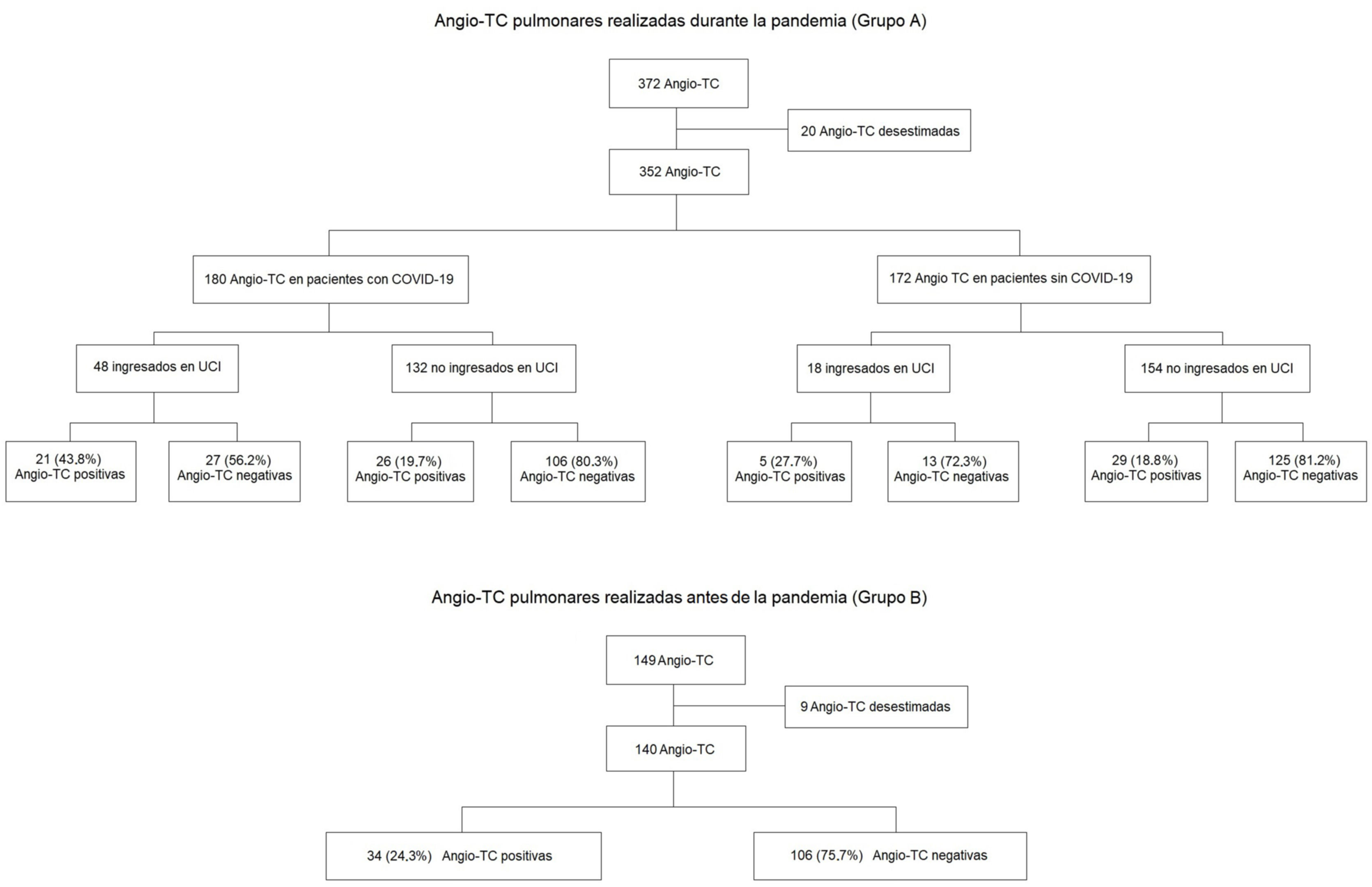
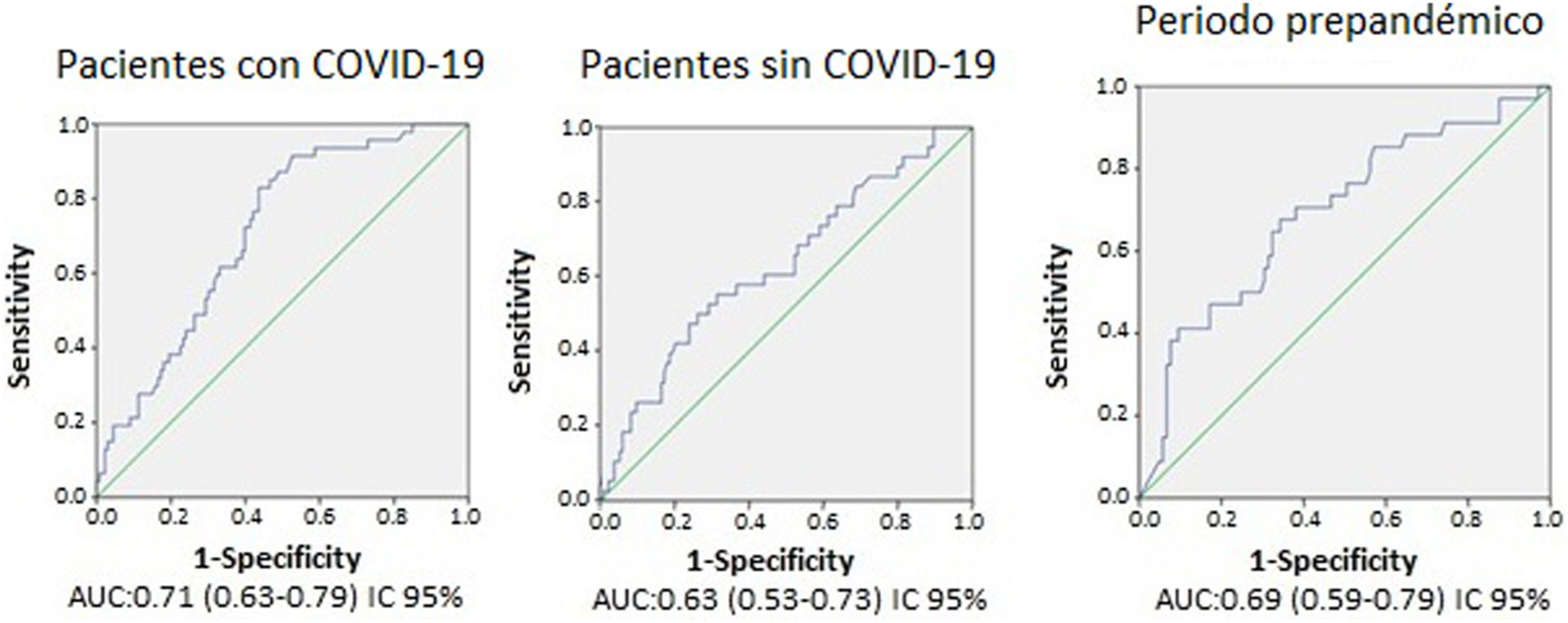
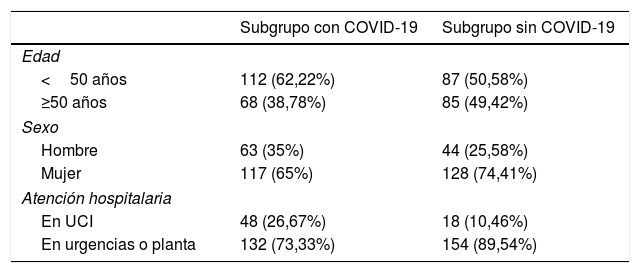
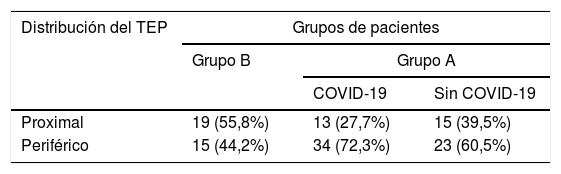
ResultadosTras desestimar 29 estudios de baja calidad, se incluyeron 492 para el análisis. De ellos, 352 fueron realizados durante la pandemia; 180 en enfermos con COVID-19 y 172 sin la enfermedad. La frecuencia absoluta de TEP diagnosticados durante la pandemia fue mayor (34 durante el periodo previo a la pandemia y 85 durante la pandemia, correspondiendo 47 de este último grupo a pacientes con COVID-19). No se encontraron diferencias significativas al comparar el AUC para los valores del dímero-D. Los valores óptimos calculados a partir de las curvas ROC fueron distintos (2.200, 4.800 y 3.200μg/l en pacientes con COVID-19, sin COVID-19 y en diagnosticados durante el periodo prepandemia, respectivamente). La distribución periférica de los trombos fue más frecuente en pacientes con COVID-19 (72%), respecto a los pacientes sin COVID-19 y los diagnosticados antes de la pandemia, con un OR de 6,6, IC del 95%: 1,5-24,6 (p<0,05) al compararla con la distribución central.
ConclusionesEl número de angio-TC realizadas y TEP diagnosticados durante la pandemia aumentó debido a la infección por SARS-CoV-2. Los valores de corte del dímero-D óptimos y la distribución del TEP fueron distintos en los grupos con y sin COVID-19.
To analyze the diagnostic performance of pulmonary CT angiography and to compare different D-dimer cutoffs for the diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism in patients with and without SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Materials and methodsWe retrospectively analyzed all consecutive pulmonary CT angiography studies done for suspected pulmonary embolism in a tertiary hospital during two time periods: the first December 2020 through February 2021 and the second December 2017 through February 2018. D-dimer levels were obtained less than 24hours before the pulmonary CT angiography studies. We analyzed the sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, area under the receiver operating curve (AUC), and pattern of pulmonary embolism for six different values of D-dimer and the extent of the embolism. During the pandemic period, we also analyzed whether the patients had COVID-19.
ResultsAfter excluding 29 poor-quality studies, 492 studies were analyzed; 352 of these were done during the pandemic, 180 in patients with COVID-19 and 172 in patients without COVID-19. The absolute frequency of pulmonary embolism diagnosed was higher during the pandemic period (34 cases during the prior period and 85 during the pandemic; 47 of these patients had COVID-19). No significant differences were found in comparing the AUCs for the D-dimer values. The optimum values calculated for the receiver operating characteristic curves differed between patients with COVID-19 (2200 mcg/L), without COVID-19 (4800 mcg/L), and diagnosed in the prepandemic period (3200 mcg/L). Peripheral distribution of the emboli was more common in patients with COVID-19 (72%) than in those without COVID-19 and than in those diagnosed before the pandemic [OR 6.6, 95% CI:1.5?24.6, p<0.05 when compared to central distribution].
ConclusionsThe number of CT angiography studies and the number of pulmonary embolisms diagnosed during the pandemic increased due to SARS-CoV-2 infection. The optimal D-dimer cutoffs and the distribution of the pulmonary embolisms differed between the groups of patients with and without COVID-19.