To analyze the efficacy and safety of the procedure for placing self-expanding stents in the colon. To evaluate the factors associated with complications. To analyze the dose of radiation delivered in the procedure.
Material and methodsThis was a retrospective descriptive study of 478 procedures done at a single center to place self-expanding metallic stents in the colon. A total of 423 nitinol stents and 79 stainless steel stents were placed. We included all colonic obstructions, of which 446 had malignant causes and 8 had benign causes. We excluded patients with intestinal perforation, severe colonic bleeding, short life expectancy, or lesions located less than 5cm from the anus. We collected the dosimetric data and analyzed the technical success, clinical success, and complications during follow-up.
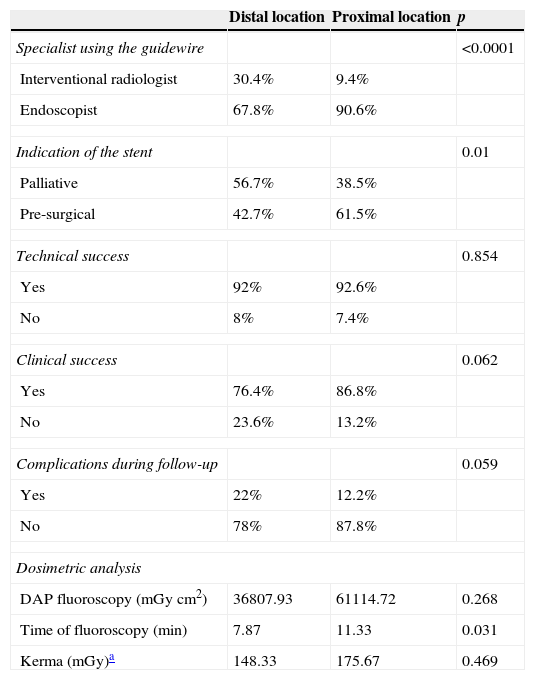
ResultsThe procedure was a technical success in 92.26% of cases (n=441) and a clinical success in 78.45% (n=375); complications occurred during follow-up in 18.5% of cases. Complications occurred more frequently with the stainless steel stents than with the nitinol stents (OR: 3.2; 95% CI: 1.8–5.7). The mean value of the dose area product was 35Gycm2. When instead of being done by the interventional radiologist working together with an endoscopist the procedure was done exclusively by the interventional radiologist, the time under fluoroscopy (p=0.001), dose area product (p=0.029), and kinetic energy released per unit mass (p=0.001) were greater.
ConclusionThe procedure for placing self-expanding colonic stents is efficacious and safe with an acceptable rate of complications. The doses of radiation delivered were low, and the radiation doses and time under fluoroscopy were lower when the procedure was done together with an endoscopist.
Analizar la eficacia y seguridad del procedimiento para colocar las prótesis autoexpandibles de colon. Evaluar los factores asociados a complicaciones. Realizar un análisis dosimétrico del procedimiento.
Material y métodosRealizamos un estudio descriptivo retrospectivo unicéntrico de 478 procedimientos para colocar prótesis metálicas autoexpandibles de colon. Se insertaron 423 prótesis de nitinol y 79 de acero inoxidable. Incluimos todas las obstrucciones de colon, 446 de etiología maligna y 8 de causa benigna. Excluimos los pacientes con perforación intestinal, hemorragia grave del colon, esperanza de vida corta y lesiones situadas a menos de 5cm del ano. Analizamos el éxito técnico, éxito clínico, las complicaciones durante el seguimiento y recogimos los datos dosimétricos.
ResultadosSe obtuvo éxito técnico en un 92,26% (n=441), éxito clínico en un 78,45% (n=375) y un porcentaje de complicaciones durante el seguimiento del 18,5%. Las prótesis de acero tuvieron más complicaciones (OR: 3,2; IC 95%: 1,8-5,7). El valor medio de producto dosis por área fue 35Gy.cm2. El de tiempo de fluoroscopia (p=0,001), producto dosis por área (p=0,029) y kerma (p=0,001) fueron mayores si el procedimiento fue realizado exclusivamente por fluoroscopia, en vez de conjuntamente por el endoscopista y el radiólogo intervencionista.
ConclusiónEl procedimiento para colocar prótesis autoexpandibles de colon es eficaz y seguro, con una tasa aceptable de complicaciones. Las dosis de radiación fueron bajas, con menos dosis y tiempos de fluoroscopia cuando el procedimiento se realizó de manera conjunta con el endoscopista.