La presencia de diferentes complicaciones durante el seguimiento de pacientes amputados alcanza el 10-80%. El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar el impacto de estas en el retorno laboral en casos de amputación traumática de extremidades inferiores.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó un estudio de tipo cohorte retrospectiva. Se recopiló información de variables clínico-demográficas, evaluando su asociación con diferentes complicaciones médico-quirúrgicas y desenlaces funcionales. Se crearon curvas de sobrevida para evaluar la tasa de retorno laboral en pacientes con y sin complicaciones.
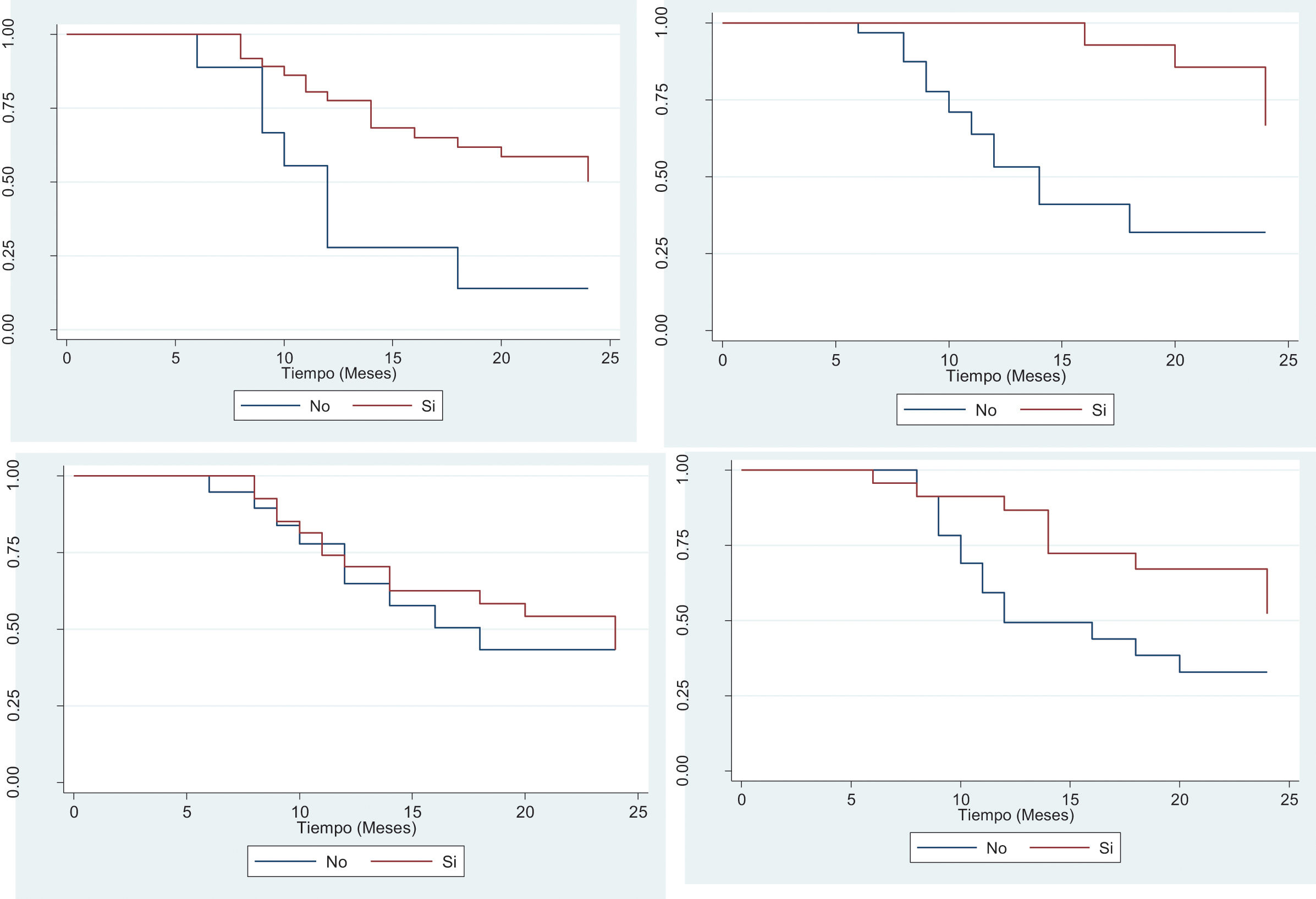
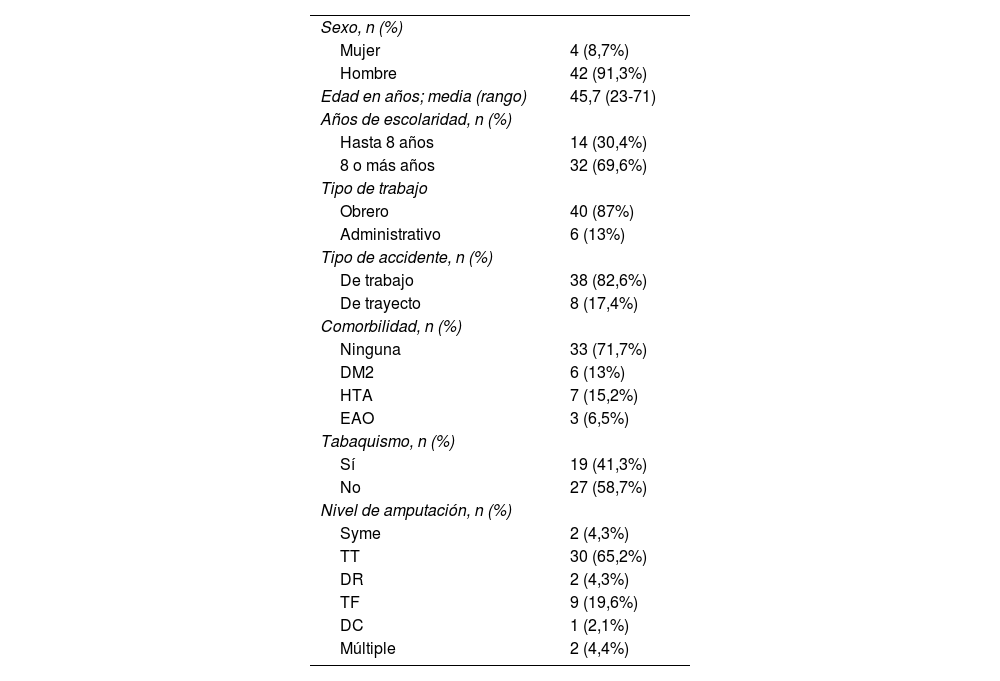
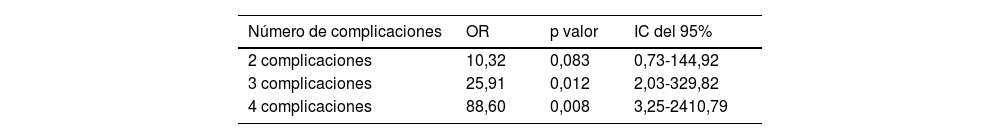
ResultadosSe incluyó a 46 pacientes con una edad media de 45,7 años (91,3% hombres, 71,7% sin comorbilidades). El nivel de amputación más frecuente fue el transtibial (65,2%). Dolor en miembro residual, dolor fantasma, complicaciones dermatológico-infecciosas y neuroma doloroso estuvieron presentes en el 80,4, el 58,7, el 50 y el 30,4% de los casos, respectivamente. La mitad de los pacientes había retornado a su trabajo al segundo año de seguimiento. Las tasas de retorno laboral fueron significativamente menores en pacientes con dolor en miembro residual (p=0,0083) y neuroma doloroso (p=0,0051).
ConclusiónLas complicaciones son frecuentes durante el seguimiento de pacientes con amputación traumática y, algunas de ellas, pueden impactar en la tasa de retorno laboral.
The presence of different complications whilst follow-up amputee patients reaches 10-80%. The main objective of this research is to assess the impact of these in the return-to-work of lower-limb traumatic amputation cases.
Materials and methodsA retrospective cohort research was carried out. Clinic-demographic variables information was recollected in order to assess its linkage to different medical-surgical complications and functional outcomes. Survival curves were created to evaluate the return-to-work of patients with and without complications.
ResultsA total of 46 patients, on average aged 45.7 years old (91.3% men, 71.7% without comorbidities), were included on this research. The most frequent level of amputation was transtibial (65.2%). Residual limb pain, phantom pain, dermatological-infectious complications and painful neuroma were registered in 80.4%, 58.7%, 50% y 30.4% of the cases respectively. Half of the patients had returned to their workplace after 2years of post-surgical follow-up. The return-to-work rates were significantly lower in patients suffering from residual limb pain (p=0.0083) and from painful neuroma (p=0.0051).
ConclusionComplications are frequent during traumatic-amputee patients’ follow-up and, some of them, may impact on the return-to-work rate.