Evaluar la asociación entre la estancia hospitalaria, funcionalidad alcanzada y el tiempo hasta el inicio del tratamiento fisioterapéutico en los pacientes admitidos a un servicio de cirugía de un hospital de alta complejidad.
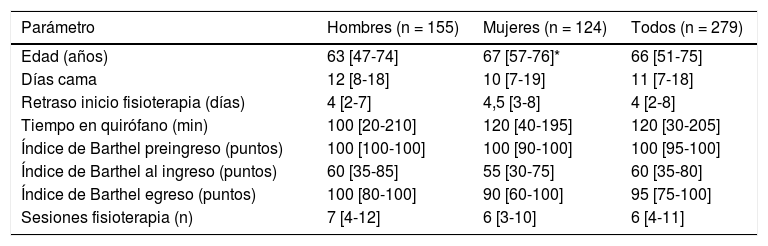
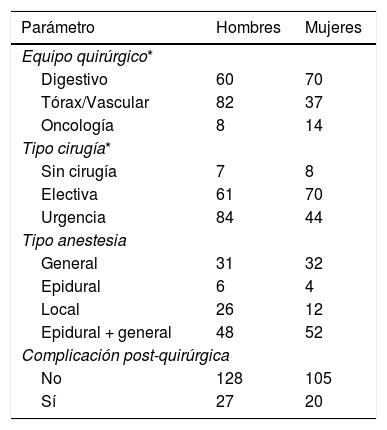
Materiales y métodosEstudio observacional, analítico de corte transversal. Se incluyeron 279 personas (124 mujeres). Los días de retraso en el inicio de fisioterapia, los días cama, la estancia hospitalaria prolongada (percentil 75 de días cama), y el nivel funcional fueron registrados para investigar la influencia del retraso en el inicio de atención fisioterapéutica sobre estas variables.
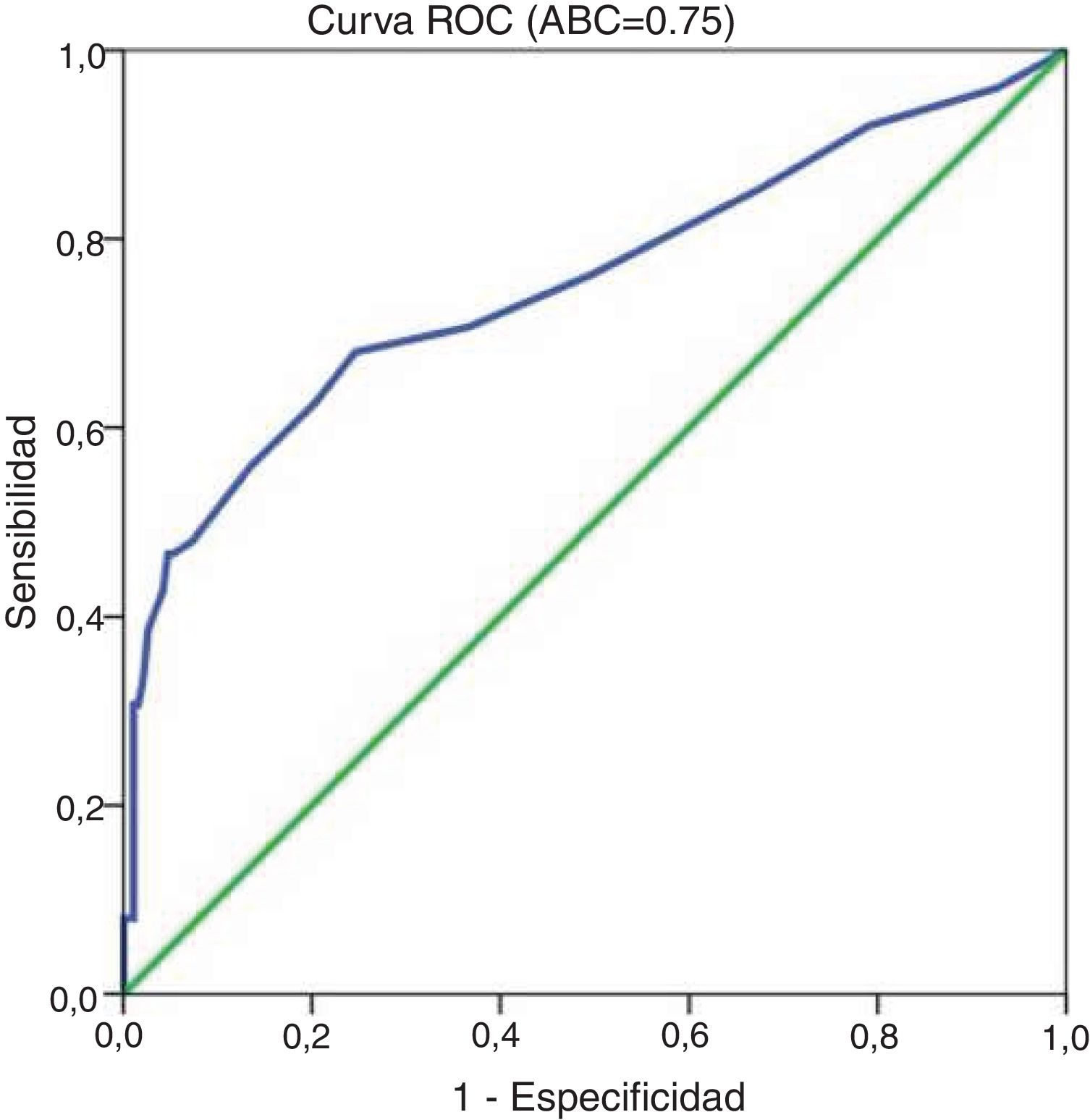
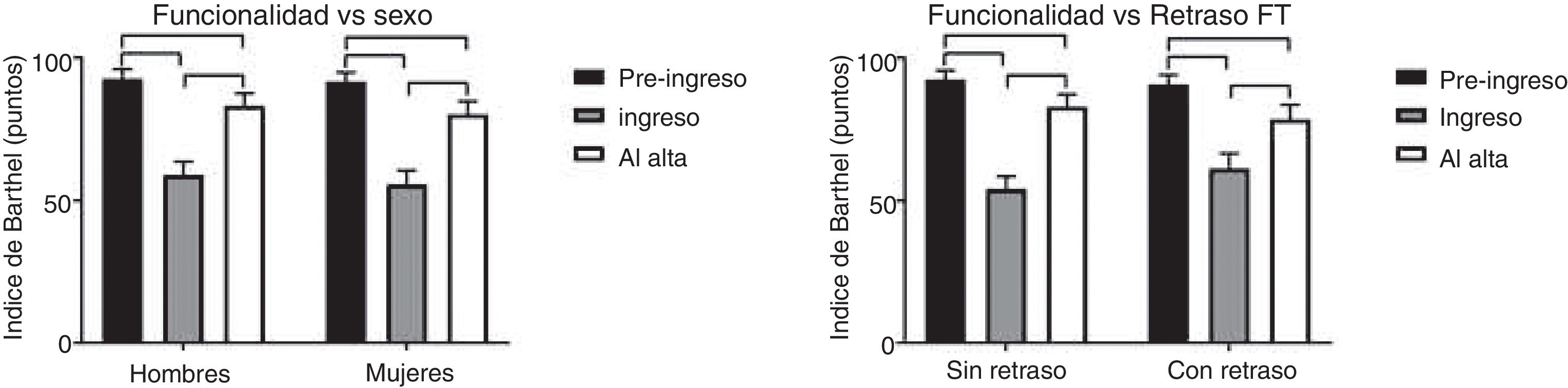
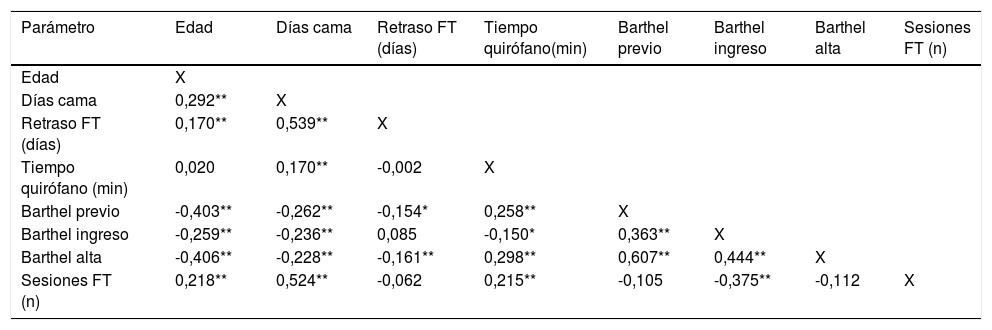
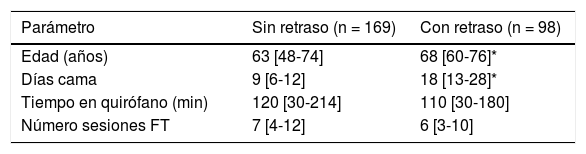
ResultadosEl número de días de retraso de atención fisioterapéutica estuvo altamente relacionado con el número de días cama (r2 = 0,74, p < 0,05). A su vez, un retraso mayor a cinco días en el inicio de atención fisioterapéutica se asocia al desarrollo de estancias hospitalarias prolongadas (p < 0,05). Sin embargo, la fisioterapia tuvo efectos similares sobre el nivel funcional, aun con retraso en su inicio (p > 0,05).
ConclusionesRetrasos en el inicio de atención fisioterapéutica se asociaron con estancias hospitalarias prolongadas en pacientes admitidos a un servicio de cirugía de un hospital de alta complejidad. Futuros estudios deberían investigar los factores asociados a este fenómeno.
To evaluate the association between hospital stay, functional status and physical therapy delay (PT delay) in patients admitted to a surgery unit of a high complexity hospital.
Materials and methodsObservational, analytic and cross-sectional study. We included 279 patients (124 women). Days of PT delay (calculated as the difference between hospital admission and start of PT), days of bed rest, prolonged hospital stay (75th percentile of bed rest days), and functional status were registered to investigate the influence of PT delay on these variables.
ResultsThe number of days of PT delay was strongly associated with the number of bed rest days (r2 = 0.74, p < 0.05). Moreover, a PT delay of five days or more was associated with extended lengths of stay in our sample (p < 0.05). However, physical therapy had similar effects on functional status, even when there were PT delays (p > 0.05).
ConclusionsPT delay is associated with extended length of stay in patients admitted to a surgery unit of a high complexity hospital. Future studies should investigate the associated factors that could explain the occurrence of PT delays in surgical patients.