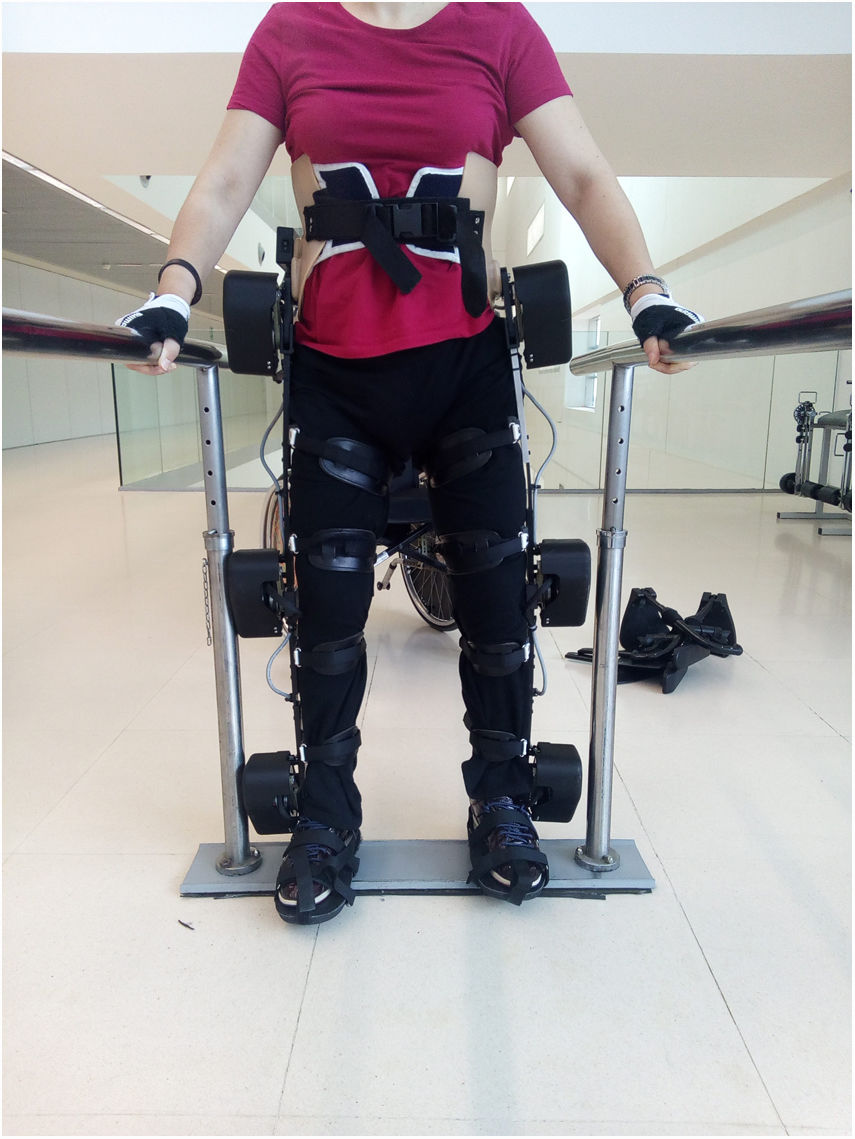
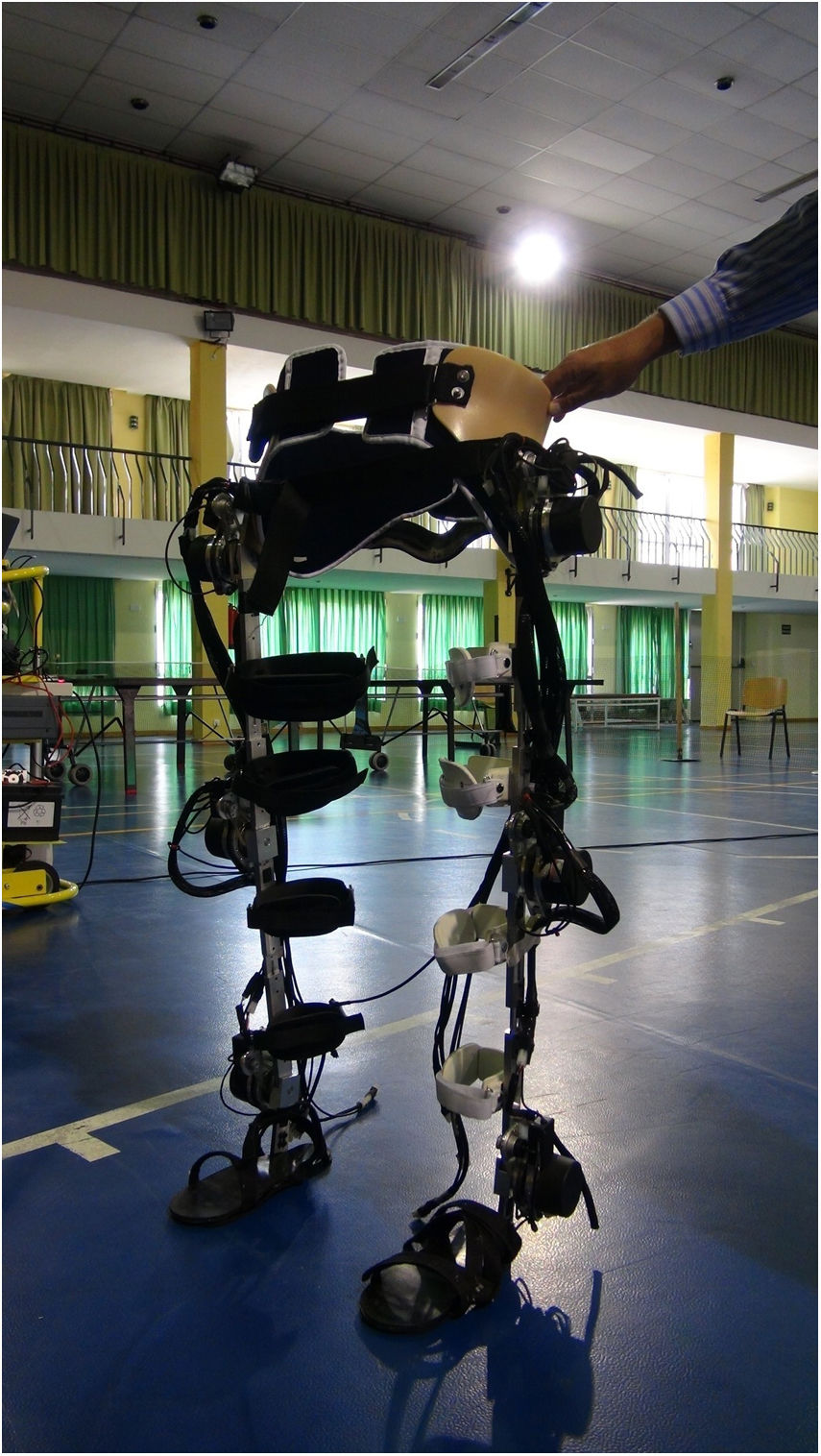
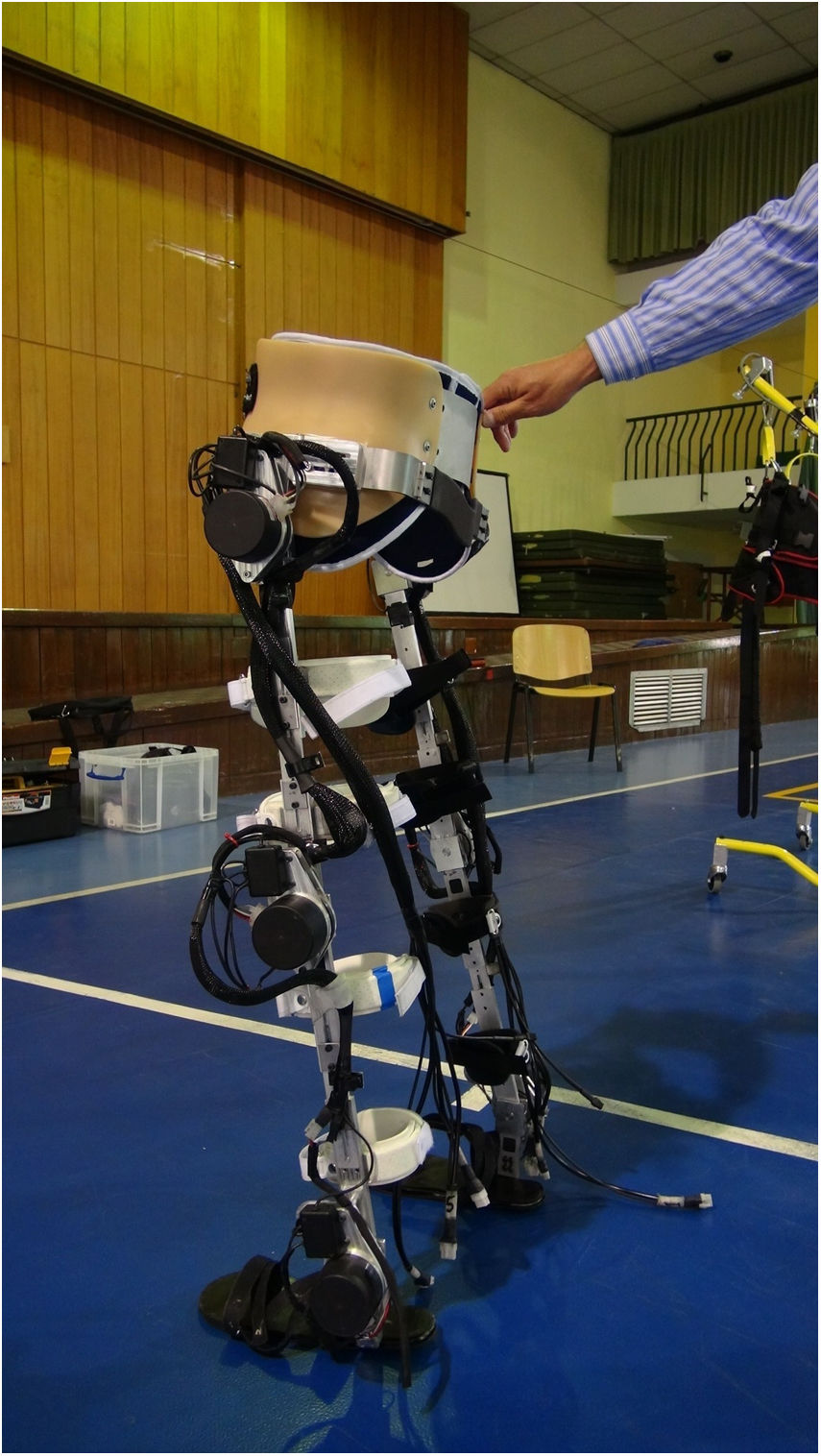
Los exoesqueletos robotizados han aparecido como una herramienta prometedora en la rehabilitación de la marcha de pacientes con lesión medular. El objetivo es valorar la aplicabilidad en un entorno clínico de un nuevo modelo de exoesqueleto robotizado (Exo H2) en la rehabilitación de la marcha de personas con lesión medular incompleta.
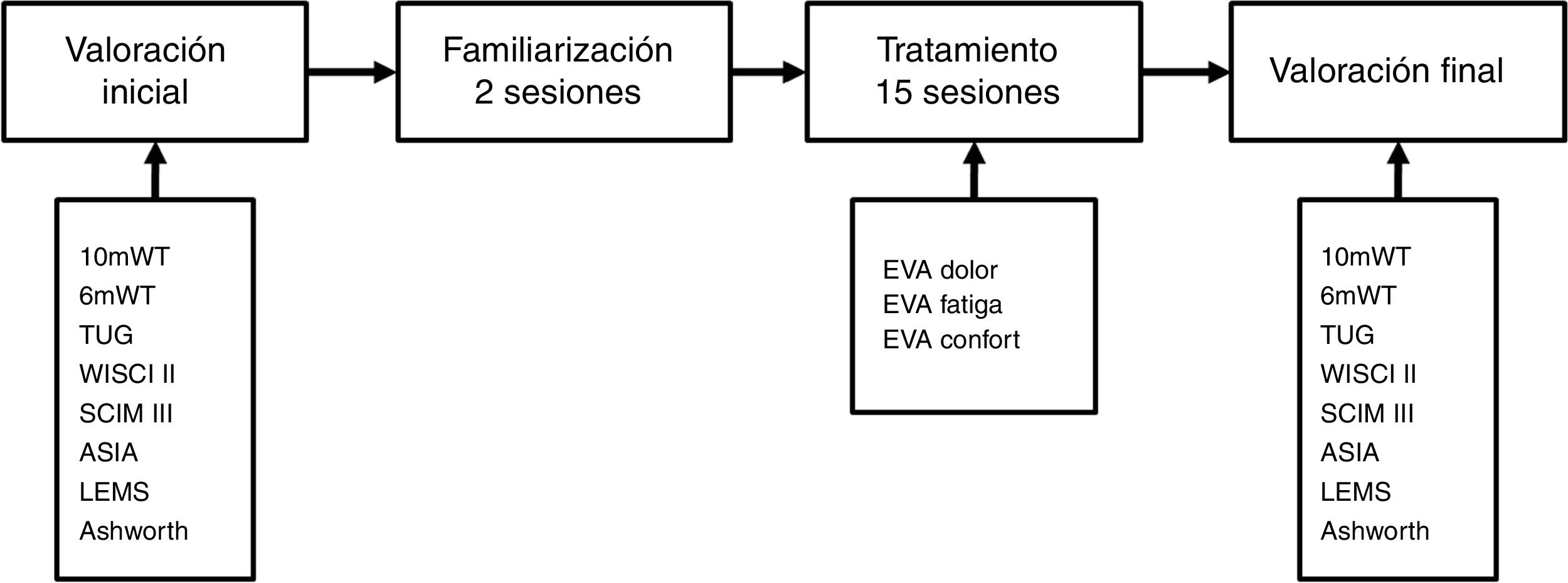
Material y métodosSe realizó el entrenamiento con el exoesqueleto Exo H2 durante 15 sesiones a pacientes con lesión medular incompleta subaguda. Se analizaron la aparición de eventos no deseados, la percepción del paciente en cuanto a dolor, fatiga y comodidad. Además, se realizó una prueba piloto sobre la posible eficacia del dispositivo analizando las características de la marcha antes y después del tratamiento medidas por el 10mWT, el 6mWT, el TUG, el WISCI-II, y la repercusión en la escala SCIM III.
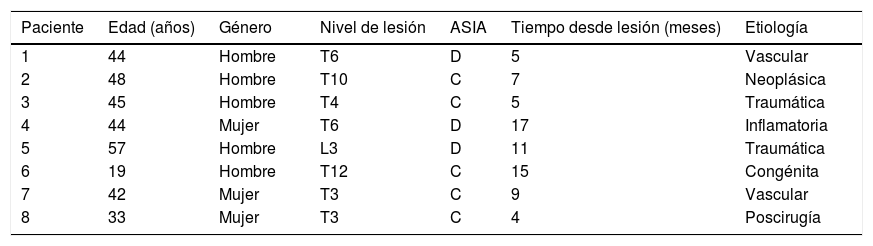
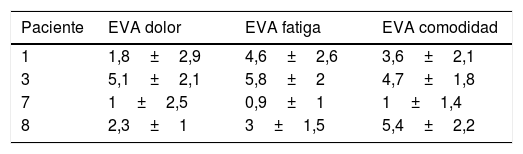
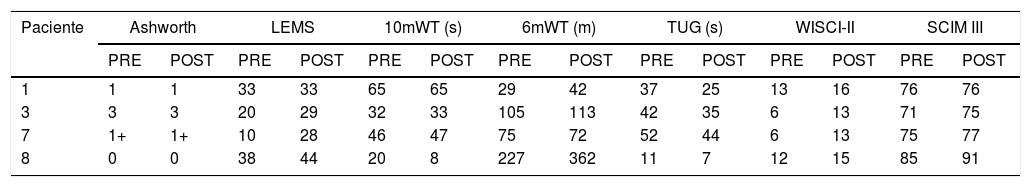
ResultadosDe los 8 pacientes reclutados, se pudieron analizar los datos de 4. No se reportó ningún efecto no deseado. El valor de EVA sobre el dolor fue de 2,28±1,55; sobre la fatiga fue de 3,75±1,55 y la comodidad fue de 4,17±1,68. Todos mejoraron en el WISCI-II, en el TUG y casi todos en el 10MWT y en el 6MWT.
ConclusionesEl funcionamiento del exoesqueleto Exo H2 fue consistente durante un protocolo clínico de rehabilitación de la marcha. Se mostró como una terapia segura, sin efectos no deseados y con buena tolerancia por parte de los pacientes. Estos resultados justifican la realización de ensayos clínicos con un tamaño muestral adecuado.
Robotic exoskeletons have emerged as a promising tool in gait rehabilitation in patients with a spinal cord injury. The aim of this study was to assess the clinical applicability of a new robotic exoskeleton model (Exo H2) in the rehabilitation of people with incomplete spinal cord injury.
Material and methodsExo H2 exoskeleton training was performed for 15 sessions in patients with incomplete subacute spinal cord injury. We analysed the appearance of undesirable events and the patient's perception of pain, fatigue and comfort. In addition, a pilot test was carried out on the possible effectiveness of the device by analysing gait characteristics before and after treatment measured by the 10mWT, the 6mWT, the TUG, the WISCI-II, and the impact on the SCIM III scale.
ResultsOf a group of 8 patients recruited, we were able to analyse data from 4. No undesirable effects were reported. The VAS value was 2.28±1.55 for pain, 3.75±1.55 for fatigue and 4.17±1.68 for comfort. All values improved on the WISCI-I and the TUG and almost all in the 10MWT and in the 6MWT.
ConclusionsThe performance of the Exo H2 exoskeleton was robust during a clinical protocol for gait rehabilitation. The treatment was safe, without undesirable effects and with good patient tolerance. These results might justify the performance of clinical trials with an adequate sample size.