Caracterización de una muestra de pacientes hospitalizados por complicaciones de la infección COVID-19 con atención a potenciales determinantes pronósticos de su evolución e impacto del tratamiento rehabilitador en el desempeño funcional, motor y respiratorio.
MétodoEstudio descriptivo, retrospectivo, longitudinal de una cohorte de pacientes ingresados con diagnóstico de COVID-19 que requirieron tratamiento rehabilitador en el Hospital Universitario Virgen de las Nieves de Granada desde marzo a junio de 2020, evaluados al ingreso, alta y a los tres meses mediante escalas de condición física (IFIS), valoración funcional: general (Rankin, Barthel), respiratoria (mMRC, BORG) y marcha (FAC).
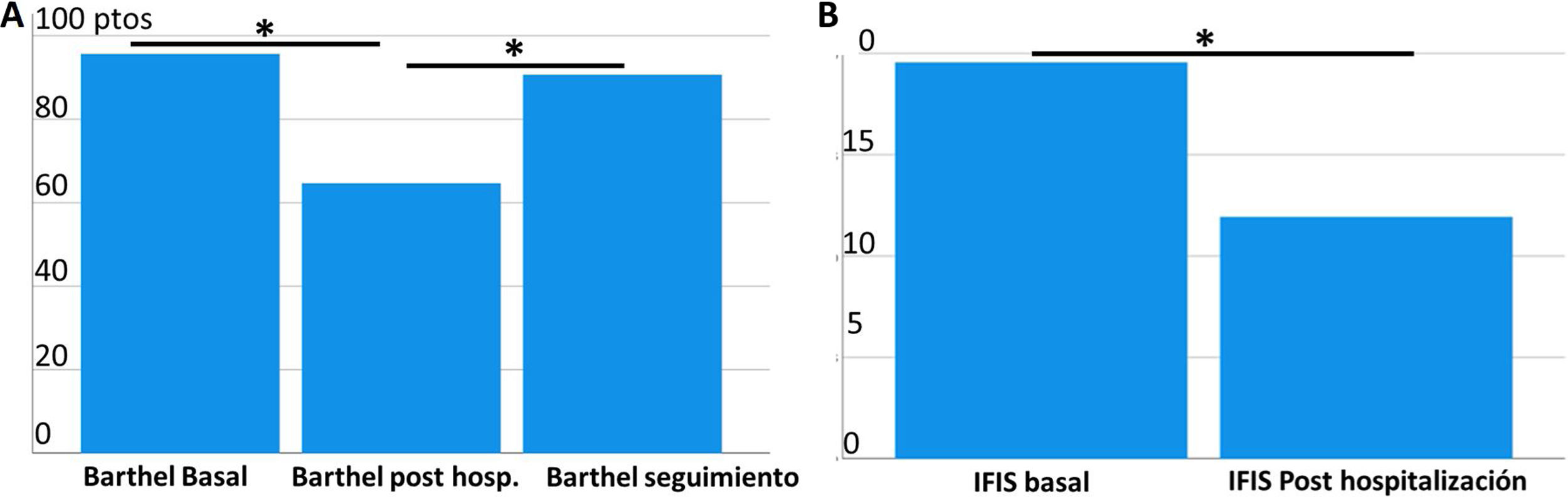
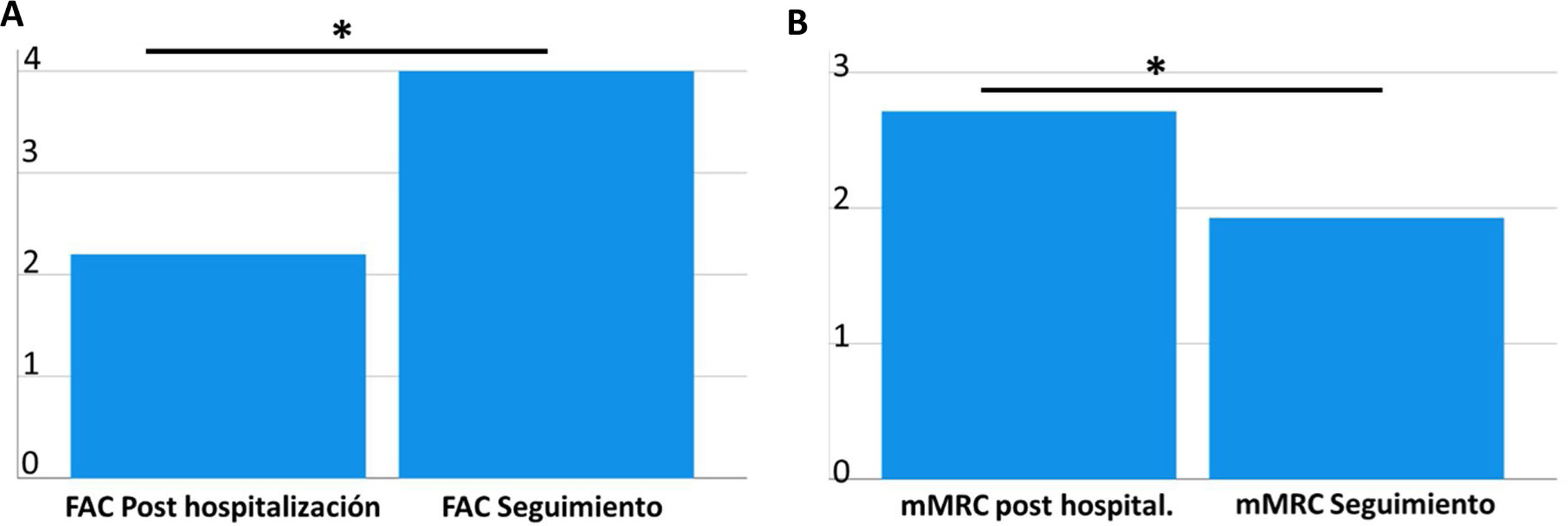
ResultadosSe incluyeron 30 pacientes, edad media 62,8 (54-70) años, 80% alguna comorbilidad: hipertensión 66,7%, obesidad 36,7%, diabetes 33,3%. Estancia hospitalaria media de 45,4 días, 86,7% requirió Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos (UCI) (29,1 días), de ellos 76,7% ventilación mecánica. El 86,7% de los pacientes presentaron alguna complicación, siendo mayor la polineuropatía/miopatía del paciente crítico (83,3% de los pacientes). Al alta, un 80% requirió ayuda para caminar. El índice de funcionalidad mostró una evolución en «U» al ingreso, alta y a los tres meses (Barthel 93,8; 60,0; 91,6, respectivamente). Se encontró un mayor deterioro funcional (Barthel < 60) en pacientes hombres, enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica (EPOC), hipertensión arterial (HTA), obesidad y proteína C reactiva (PCR) elevada al ingreso y evolución más favorable en aquellos con dímero D y linfocitos más elevados al ingreso.
ConclusiónLos ingresos hospitalarios por COVID-19 implican complicaciones a nivel funcional, respiratorio y de la marcha mayoritariamente graves pero reversibles parcialmente a los tres meses con tratamiento rehabilitador. Se describen factores potencialmente pronósticos que merecen estudios prospectivos.
The characterization of a sample of patients hospitalized with complications of the COVID-19 infection regarding potential prognostic factors, clinical evolution, and impact of rehabilitation treatment on functional, motor, and respiratory outcomes.
MethodDescriptive, retrospective, longitudinal study of a cohort of patients under rehabilitation treatment admitted at Virgen de las Nieves University Hospital in Granada from March to June 2020, assessed upon admission, discharge and at 3 rd month using physical condition scales (IFIS) and functional assessment: general (Rankin, Barthel), respiratory (mMRC, BORG) and gait (FAC).
Results30 patients with a mean age of 62.8 (54-70) years were included, 80% with comorbidity: hypertension 66.7%, obesity 36.7%, diabetes 33.3%. The mean hospital stay was 45.4 days, with 86.7% requiring ICU (29.1 days) and 76.7% of them required mechanical ventilation. An 86.7% of the patients presented with complications, mostly with polyneuropathy-myopathy of the critical patient (83.3%). At discharge, 80% required walking assistance. The functionality index showed a “U”-evolution at admission, discharge and at 3 rd month (Barthel 93.8; 60.0; 91.6 respectively). A greater functional decline (Barthel < 60) was found in male patients, COPD, HT, obesity, and elevated protein C reactive at admission; and a more favourable evolution in those with elevated D-dimer and lymphocyte values upon admission.
ConclusiónHospital admission for COVID-19 patients involve complications at the functional, respiratory and gait levels that are mostly serious but partially reversible at 3 months with rehabilitation treatment. Potential prognostic factors are described and deserve prospective studies.