Patients who survive a stroke present difficulty in complying with secondary prevention. Therefore, new strategies, such as health coaching, are needed to evaluate these interventions in clinical practice.
ObjectiveTo construct and validate the psychometric properties of a scale for evaluating health coaching in stroke patients.
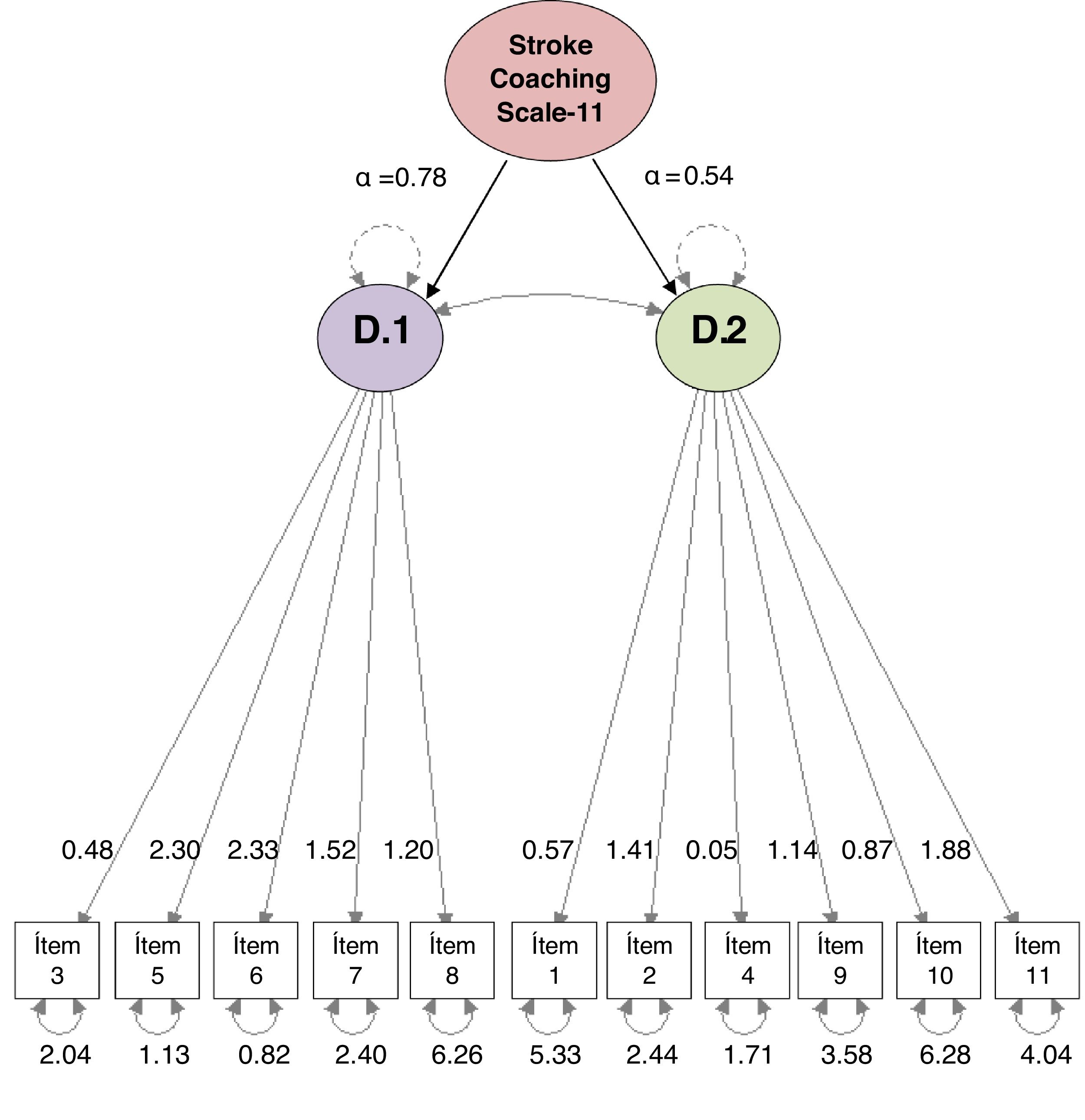
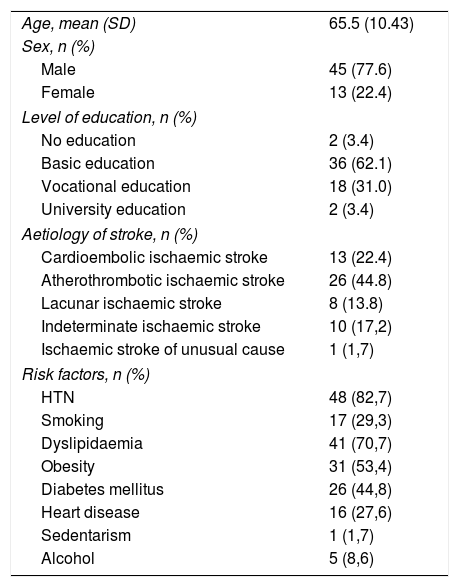
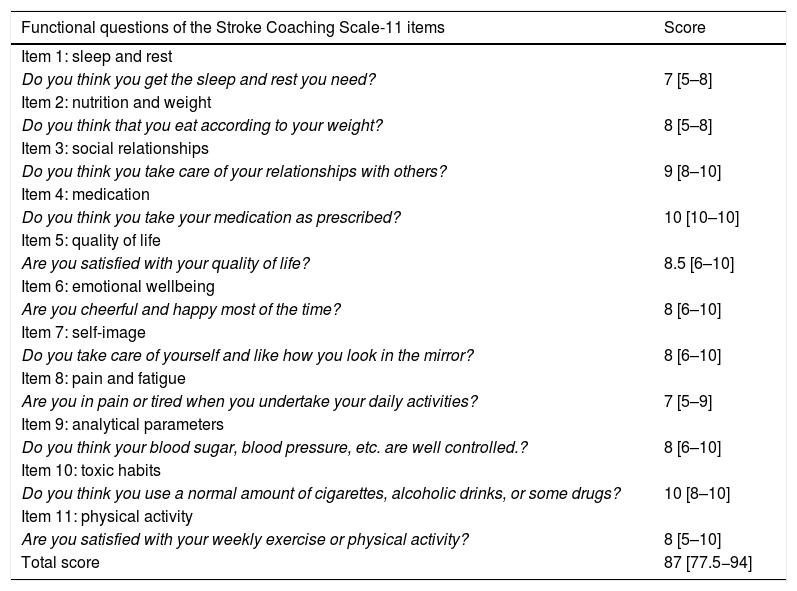
MethodObservational study of the construction and validation of a Spanish assessment scale for health coaching in a prospective cohort of stroke patients. It was conducted in two phases: 1) construction and 2) validation of the scale. In the first phase, after evaluation by a group of experts, 11 items of the scale were constructed, with a Likert-type response option (0–10). In the second phase, validation and analysis of construct and reliability was carried out using the test-retest technique, with a difference of 3 weeks in a consecutive and prospective probability sample of 58 participants. In addition, a confirmatory factor analysis of the model was performed, and the following fit indices were obtained: comparative fit index (CFI), Tucker-Lewis index (TLI), and root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) with a confidence interval (CI) of 95%.
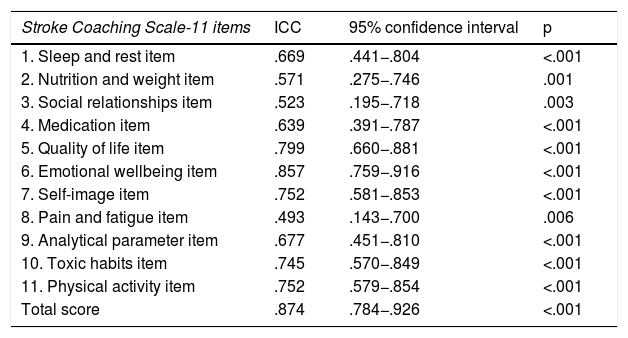
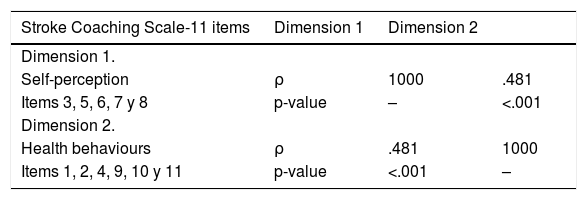
ResultsThe pilot test applied to a sample of 14 subjects obtained good reliability (Cronbach's alpha = .806). In the retest the level of reliability was maintained (Cronbach's alpha = .813) and the intraclass correlation coefficient of all items showed reproducibility after three weeks from the first completion. The correlation between the dimensions was significant, although the correlation coefficient was not high. The following scale fit indices were also calculated: CFI = .933, TLI = .914 and RMSEA = .068 (95% CI.000–.119), which showed adequate values.
ConclusionsThe Stroke Coaching Scale-11 items are a useful and valid instrument to assess health coaching in stroke patients.
Los pacientes que sobreviven a un ictus presentan dificultades para cumplir con la prevención secundaria. Por ello, son necesarias nuevas estrategias, como el coaching-salud, que permitan evaluar estas intervenciones en la práctica clínica.
ObjetivoConstruir y validar las propiedades psicométricas de una escala de evaluación en coaching-saluden pacientes con ictus.
MétodoEstudio observacional de construcción y validación de una escala de evaluación en castellano de coaching-salud en una cohorte prospectiva de pacientes con ictus. Se condujo en dos fases: 1) construcción y 2) validación de la escala. En la primera fase, tras la evaluación por un grupo de expertos, se conformaron 11 ítems de la escala, con opción de respuesta tipo Likert (0–10). En la segunda fase, se realizó la validación y análisis de constructo y fiabilidad, mediante la técnica test-retest, con una diferencia de 3 semanas en una muestra probabilística consecutiva y prospectiva a 58 participantes. Además, se realizó un análisis factorial confirmatorio del modelo y se obtuvieron los siguientes índices de ajuste: índice de ajuste comparativo (CFI), índice de Tucker-Lewis (TLI) y error cuadrático medio de aproximación (RMSEA) con un intervalo de confianza (IC) del 95%.
ResultadosLa prueba piloto aplicada a una muestra de 14 participantes obtuvo una buena fiabilidad (Alfa de Cronbach = 0.806). En el retest el nivel de fiabilidad se mantuvo (Alfa de Cronbach = 0.813) y el coeficiente de correlación intraclase de todos los ítems mostró su reproducibilidad tras tres semanas desde la primera cumplimentación. La correlación entre las dimensiones fue significativa, a pesar de que el coeficiente de correlación no fue elevado. También se calcularon los siguientes índices de ajuste de la escala: CFI = 0.933, TLI = 0.914 y RMSEA = 0.068 (IC 95% 0.000−0.119), que mostraron valores adecuados.
ConclusionesLa Stroke Coaching Scale-11 ítems es un instrumento útil y válido para evaluar el coaching-salud en pacientes que han padecido un ictus.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.