Analizar las características de los enfermos adultos graves de mayor edad, durante las 6 olas de la pandemia COVID-19.
MétodoEstudio retrospectivo, observacional y analítico sobre pacientes mayores de 70 años con ingreso en la UCI (marzo-2020/marzo-2022). Los pacientes se categorizaron en 3 grupos en función de la edad: 70-74 años, 75-79 años y >80 años. Se realizó inicialmente un análisis descriptivo y comparativo de la muestra, y un análisis de supervivencia a los 28, 60 y 90 días con el método de Kaplan-Meier. El análisis multivariable de la supervivencia se realizó ajustando un modelo de Cox.
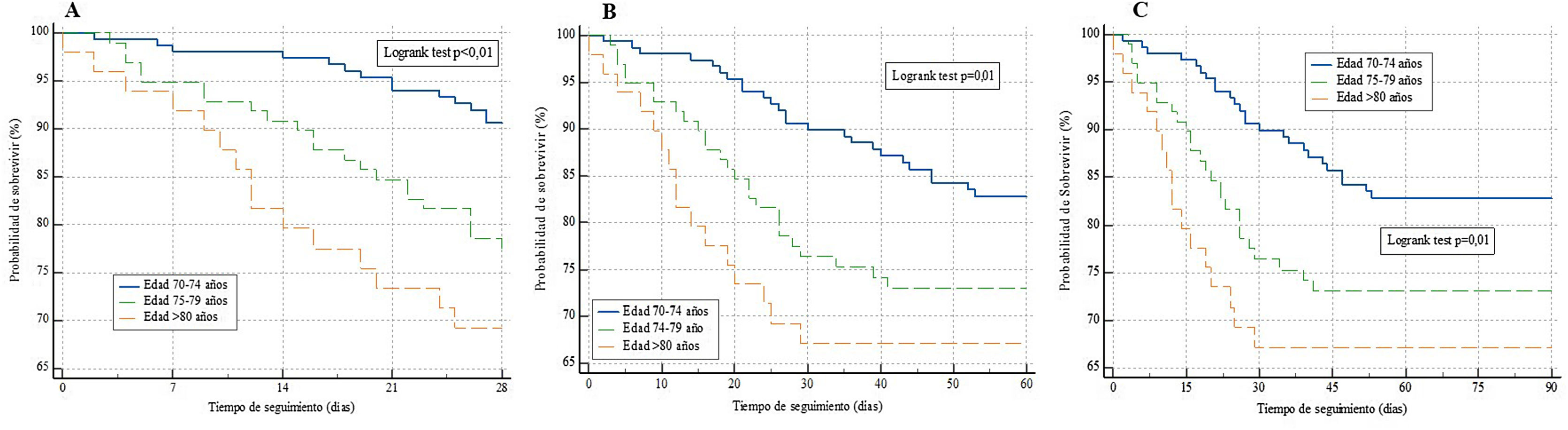
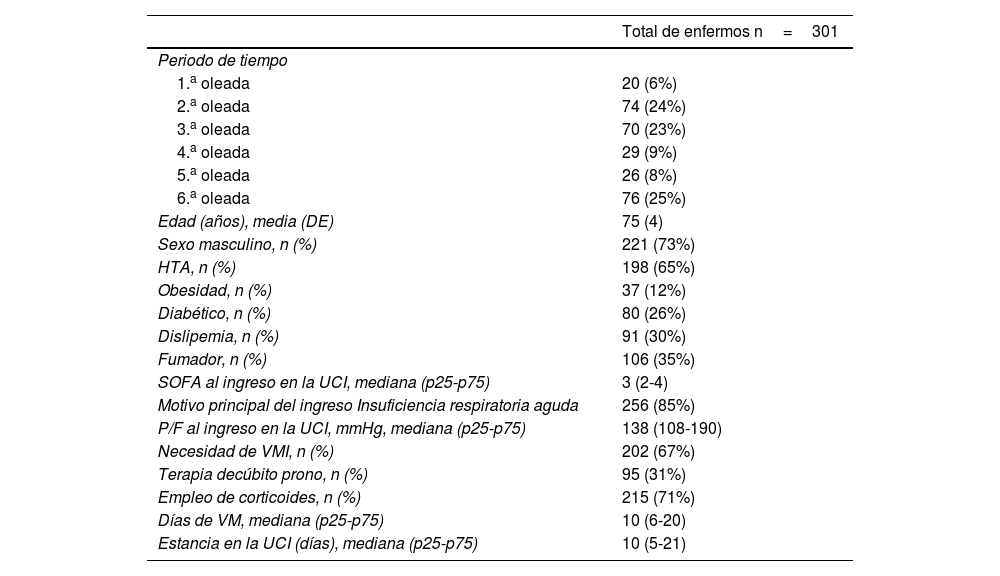
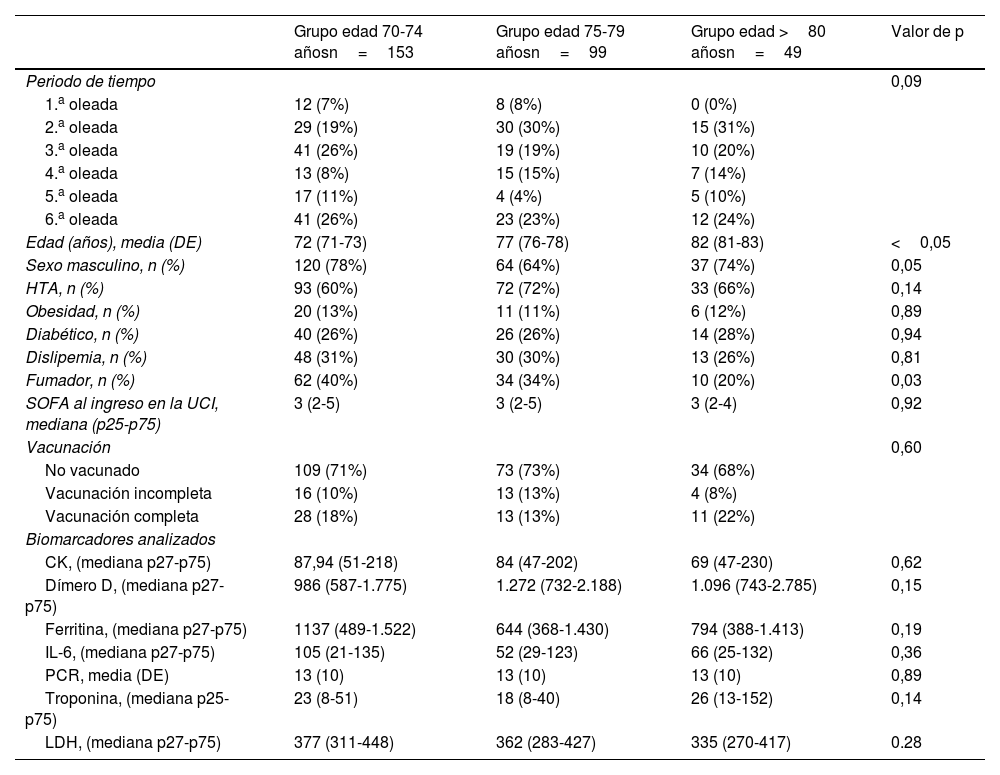
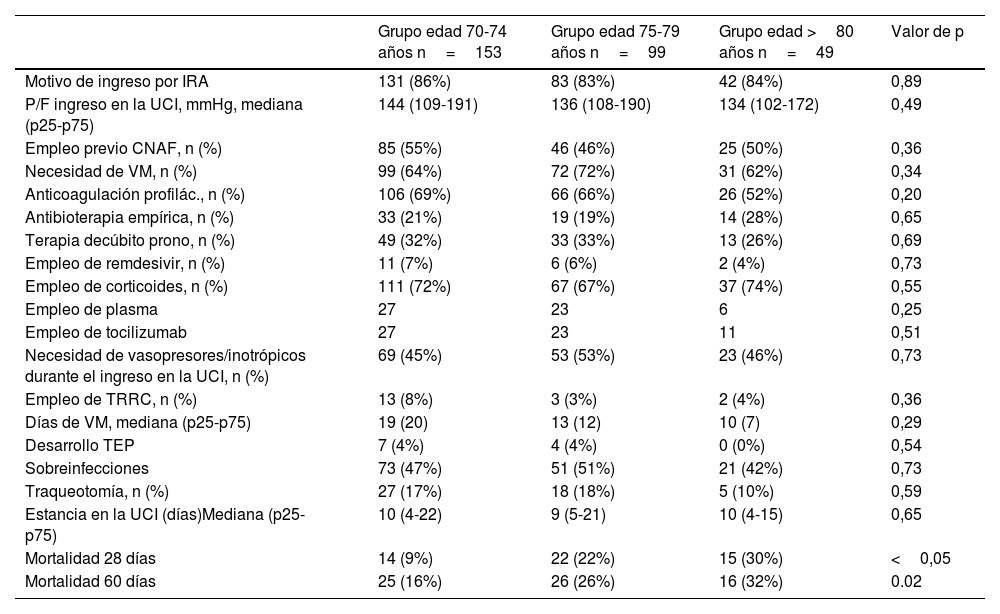
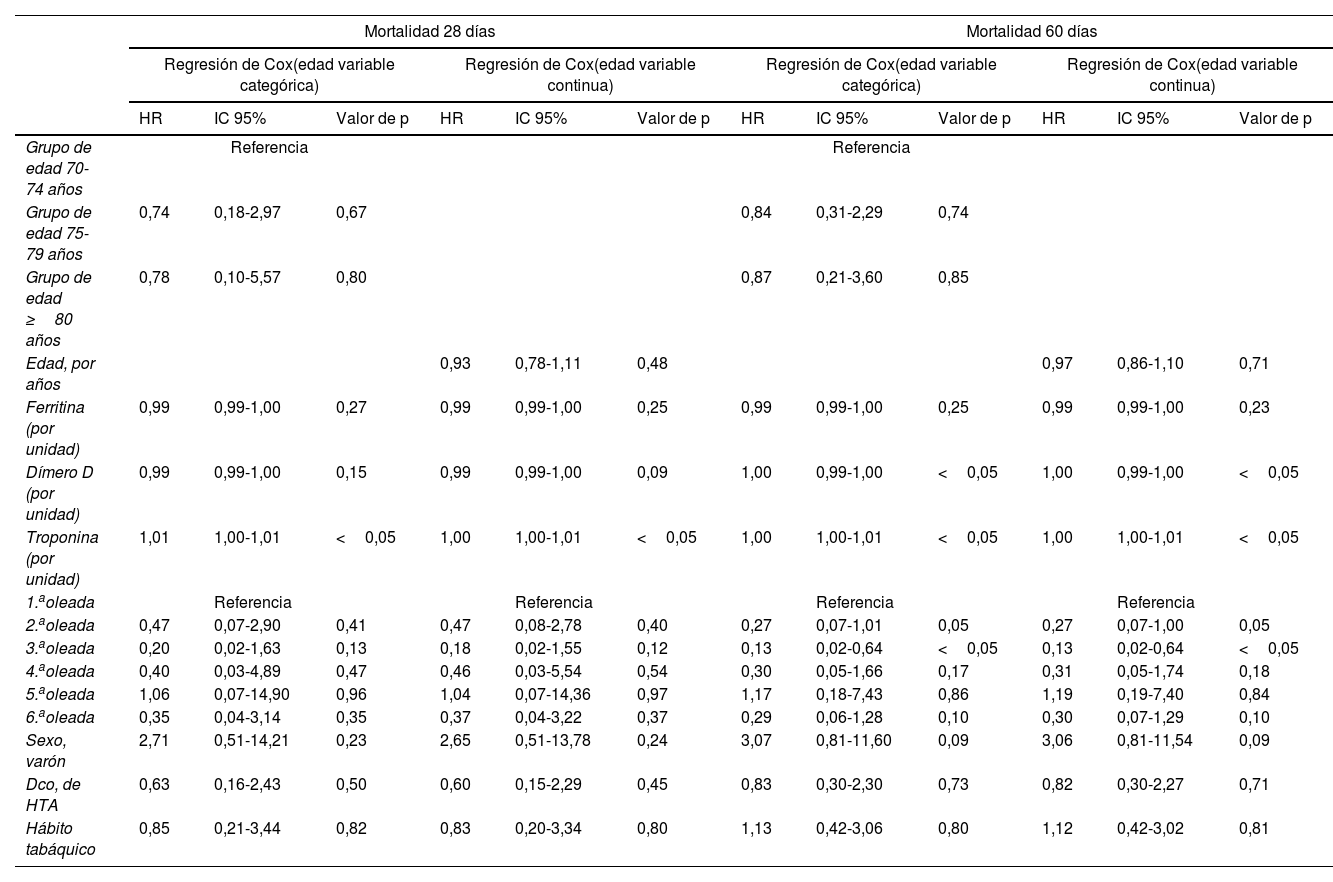
ResultadosDe 301 enfermos, el menor número de ingresos se produjo durante la primera ola (20 [6%]), frente a la que fue la ola con mayor número de ingresos: la sexta ola (76 [25%]). Las curvas de supervivencia a los 28, a los 60 días y a los 90 días evidenciaron una mayor probabilidad de sobrevivir en los grupos de menor edad (p<0,01 y p=0,01, respectivamente). La troponina al ingreso (por unidad, ng/l), evidenció un asociación significativa con la mortalidad a 28 y 60 días (HR: 1,00; IC 95%: 1,00-1,01; p<0,05). Tomando como referencia la 1.ª oleada de la pandemia, el ingreso en 3.ª oleada se comportó como un factor de protección frente a la mortalidad a los 28 y 60 días de seguimiento (HR: 0,18; IC 95%: 0,02-0,64; p<0,05; HR: 0,13; IC 95%: 0,02-0,64; p<0,05, respectivamente).
ConclusionesEl momento de ingreso y biomarcadores, como la troponina, se constituyen en marcadores pronósticos independientes de la edad en la población añosa.
To analyze the characteristics of seriously ill elderly patients during the six waves of the COVID-19 pandemic.
MethodRetrospective, observational and analytical study of patients over 70 years of age admitted to the ICU (March-2020 to March-2022). Patients were categorized into three groups based on age: 70-74 years; 75-79 years; and >80 years. A descriptive and comparative analysis of the sample was initially performed; and a 28-, 60- and 90-day survival analysis using the Kaplan–Meier method. Multivariate survival analysis was performed by fitting a Cox model.
ResultsOf 301 patients, the lowest number of admissions occurred during the first wave (20 (6%)), compared to the wave with the highest number of admissions: the sixth wave (76 (25%)). The survival curves at 28 days, 60 days and 90 days showed a higher probability of survival in the younger age groups (P<.01 and P=.01, respectively). Troponin at admission (per unit, ng/l) showed a significant association with 28- and 60-day mortality (HR: 1.00; 95% CI: 1.00-1.01; P<.05). Taking the 1st wave of the pandemic as a reference, admission in the 3rd wave behaved as a protective factor against mortality at 28 and 60 days of follow-up (HR: 0.18; 95% CI: 0.02-0.64; P<.05; HR: 0.13; 95% CI: 0.02–0.64; P<.05, respectively).
ConclusionsThe time of admission and biomarkers, such as troponin, constitute prognostic markers independent of age in the elderly population.