Statistical parametric mapping (SPM) is a widely used procedure for normalization of functional images. The aim of this study is the development of a normalization template of 123I-Ioflupane SPECT-imaging DaTSCAN®, GE Healthcare), not available in SPM5, and to validate it by comparing with other quantification methods.
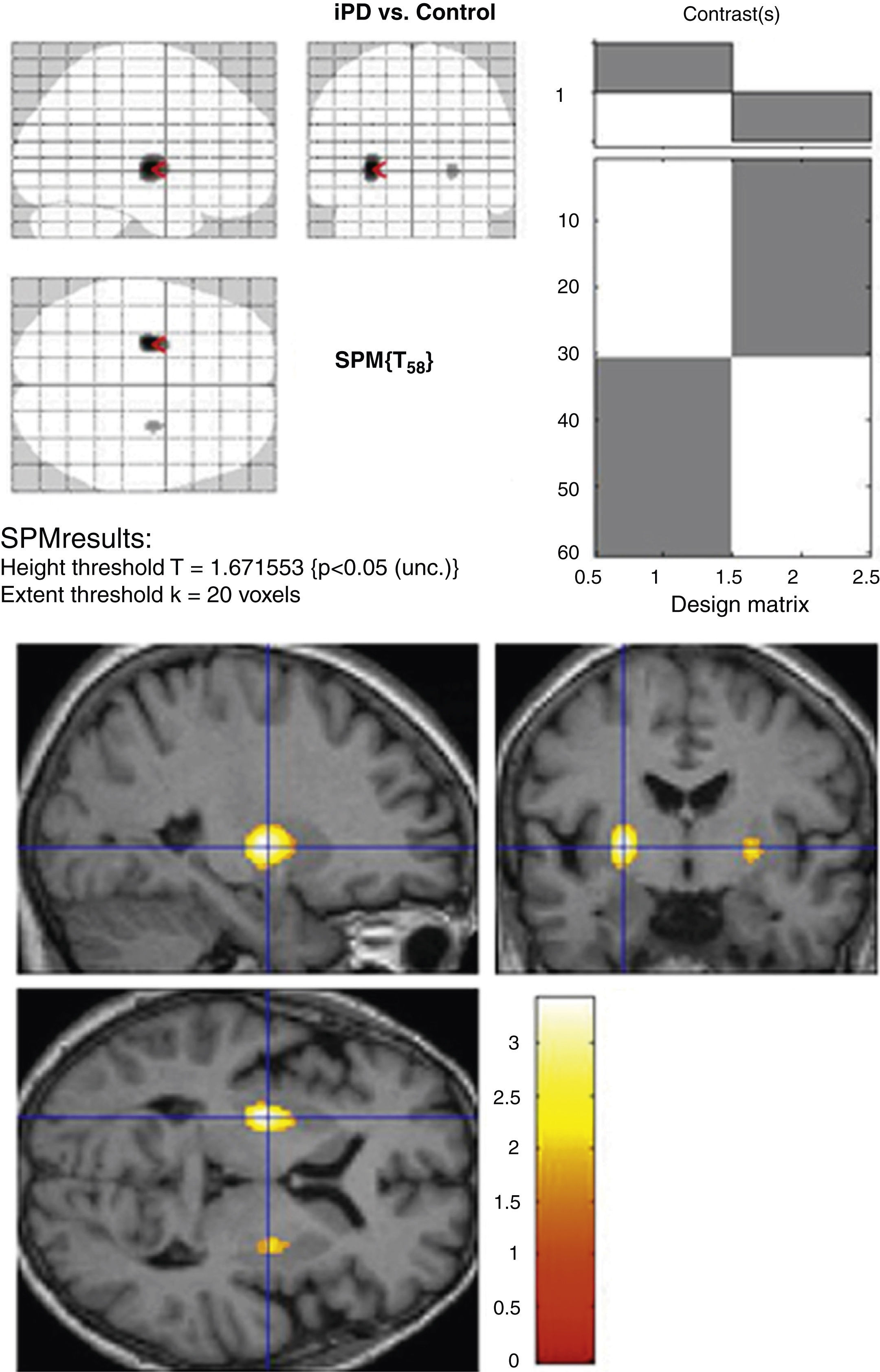
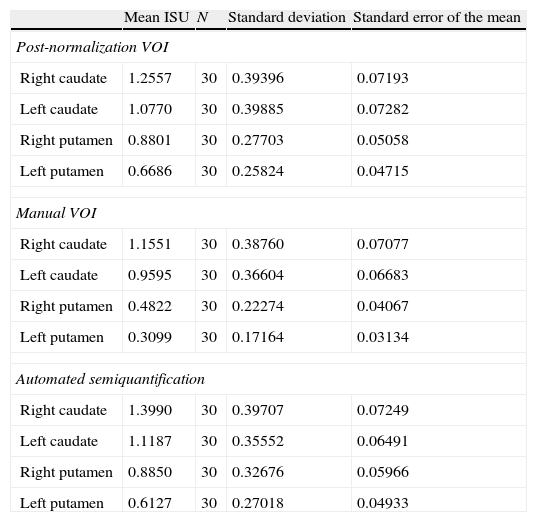
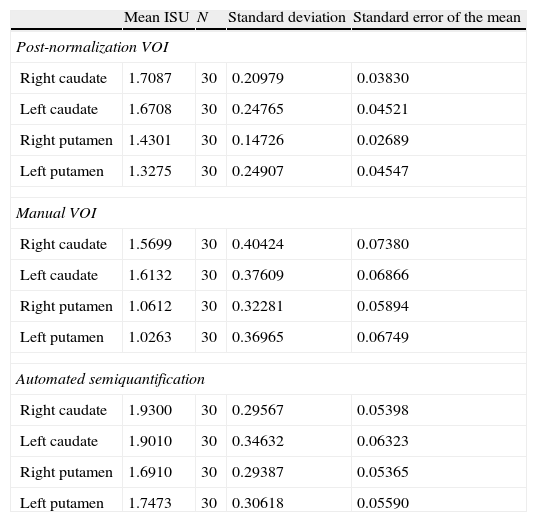
Material and methodsIn order to write the template we retrospectively selected 26 subjects who had no evidence of nigrostriatal degeneration and whose age distribution was similar to that of the patients in the usual practice of our Department: 2 subjects (7.6%) were <35 years, 9 between 35 and 65 years (34.6%) and 15>65 years (57.7%). All the studies were normalized with the T1-template, available in SPM5, and an average value of the image was obtained for each voxel. For validation we analyzed 60 patients: 30 with idiopathic Parkinson's disease patients (iPD) with right involvement (66.83±12.20 years) and 30 with essential tremor patients (ET) (67.27±8.33 years). Specific uptake rates (SUR) of different striatal regions were compared after image normalization with our template and the application of a semiautomated VOIs-map was created with Analyze v9.0 (©BIR, Mayo Clinic), against two quantification methods: a) manual adjustment of a ROIs-map drawn in Analyze, and b) semi-automated method (HERMES-BRASS) with normalization and implementation of VOIs-map.
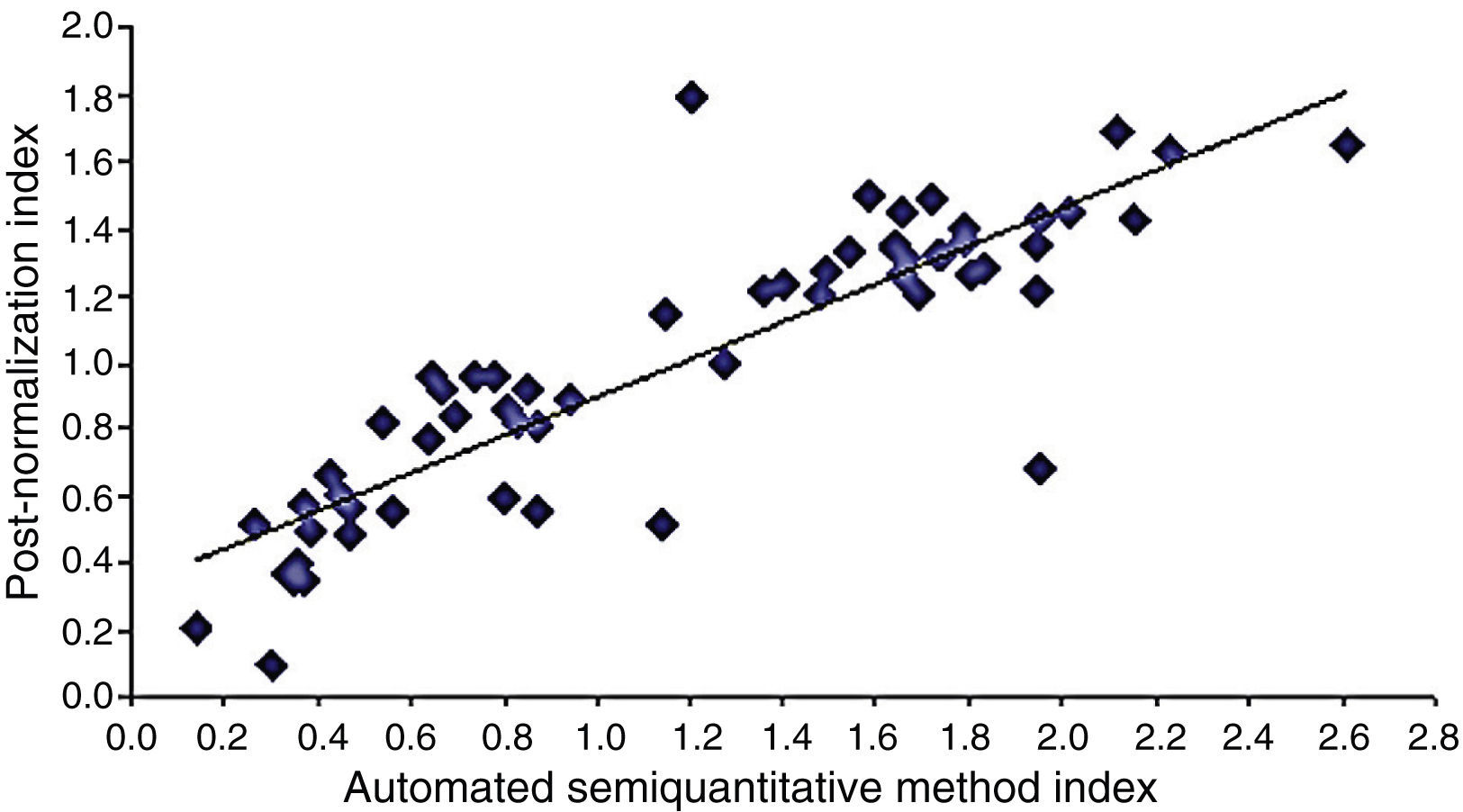
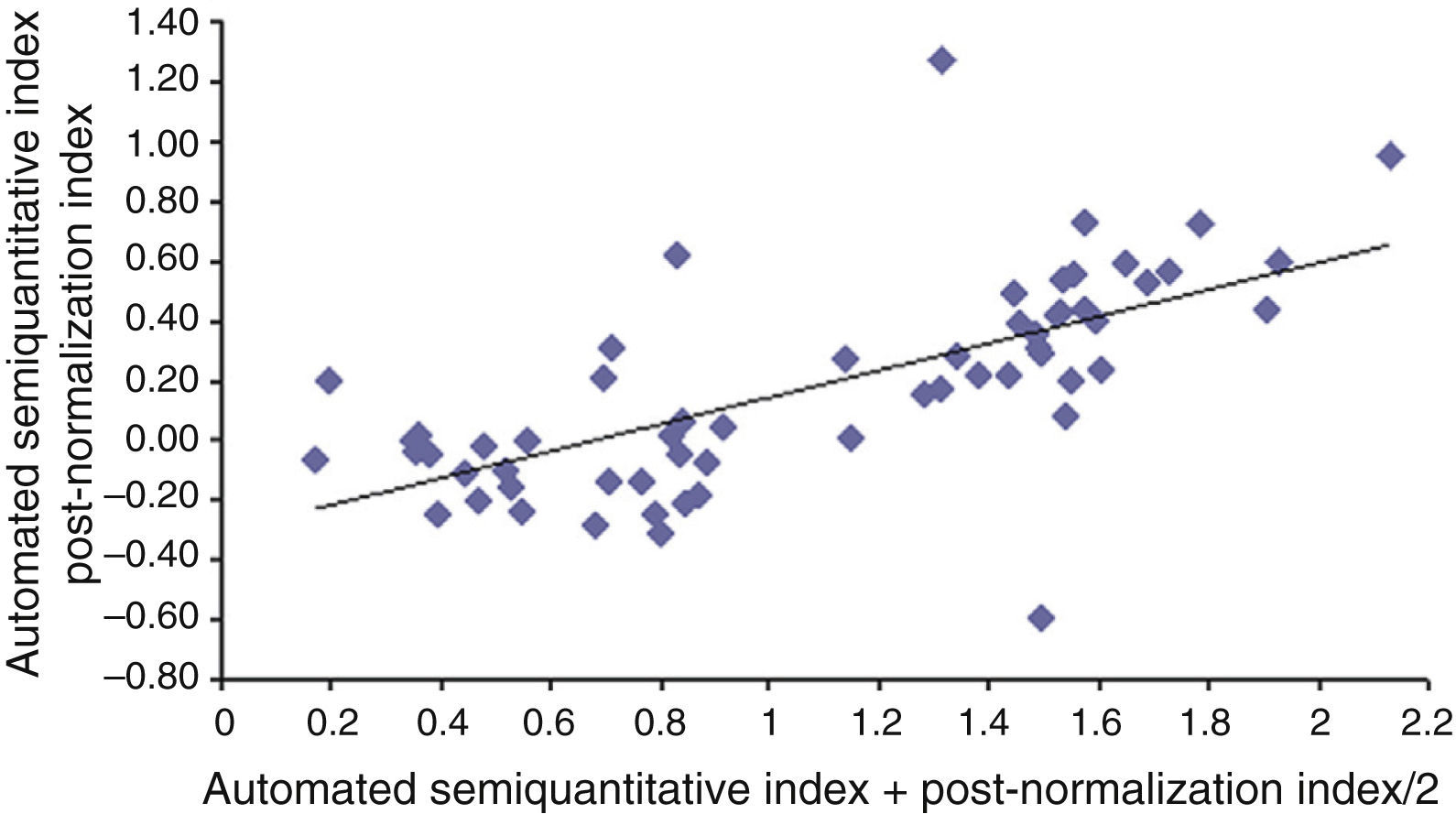
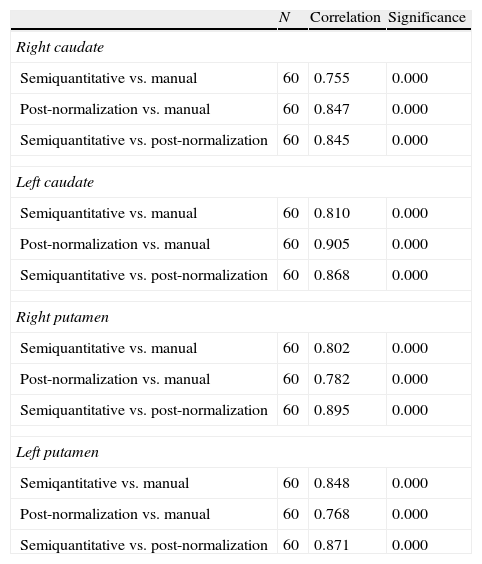
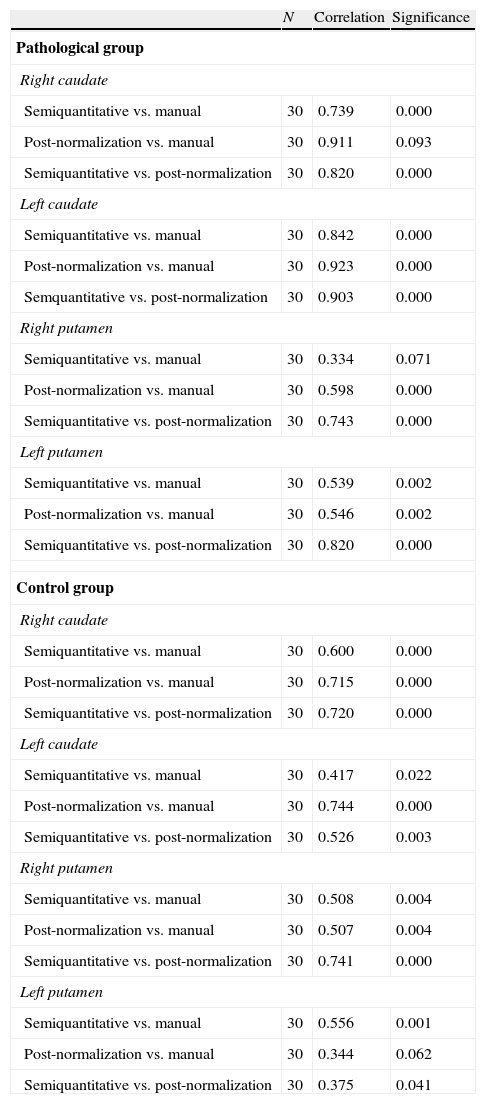
ResultsNo statistically significant differences in the iPD/ET discriminatory capacity among the three methods analyzed were observed (p<0.001). The correlation of SUR after normalization with our “template” was higher than that obtained by method b) (R>0.871, p<0.001). This difference was greater in patients with PD.
ConclusionsOur study demonstrates the efficacy of our SPM “template” for 123I-Ioflupane SPECT-imaging, obtained from normalization with “T1-template”.
El SPM (statistical parametric mapping, mapas estadísticos paramétricos) es un procedimiento de análisis ampliamente utilizado para la normalización de imágenes funcionales. El propósito de este trabajo es elaborar una plantilla (template) para la normalización de imágenes SPECT con 123I-Ioflupano (DaTSCAN®; GE Healthcare), no disponible en SPM5, y su validación respecto a otros métodos de cuantificación.
Material y métodosPara la elaboración del template seleccionamos retrospectivamente los estudios SPECT de 26 sujetos sin evidencias de degeneración nigroestriatal, con distribución de edad similar a la de los pacientes que se incluyen en la práctica habitual de nuestro servicio: 2 sujetos < 35 años (7,6%), 9 entre 35-65 años (34,6%) y 15 > 65 años (57,7%). Todos los estudios fueron normalizados con el template-T1, disponible en SPM5, obteniendo una imagen promedio del valor para cada vóxel. Para la validación analizamos 60 pacientes: 30 con enfermedad de Parkinson idiopática (EPi) con afectación del hemicuerpo derecho (66,83±12,20 años) y 30 pacientes con temblor esencial (TE) (67,27±8,33 años). Se compararon los índices de captación específica (ICE) de las distintas regiones estriatales, obtenidos tras la normalización de las imágenes con nuestro template y aplicando un mapa de VOIs semiautomatizado creado en Analyze v9.0 (©BIR, Mayo Clinic), con otros 2 métodos de cuantificación: a) ajuste manual de un mapa de ROIs elaborado en Analyze, y b) mediante un método semicuantitativo automatizado (HERMES-BRASS) que realiza normalización y aplicación de un mapa de VOIs.
ResultadosNo observamos diferencias estadísticamente significativas en la capacidad discriminatoria EPi/TE entre los 3 métodos analizados (p<0,001). La correlación de los ICE tras la normalización con nuestro template fue mayor con la obtenida por el método b) (R>0,871; p<0,001). En los pacientes con EPi esta diferencia fue más acusada.
ConclusionesNuestro estudio demuestra la eficacia de nuestro template de SPM para SPECT con 123I-Ioflupano, obtenido a partir de la normalización con el template-T1.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora