To optimize radiolabeling with 99mTc of mannosylated Gantrez® nanoparticles loaded with the Brucella Ovis antigen (Man-NP-HS) and to carry out biodistribution studies in mice after ocular administration of the nanoparticles.
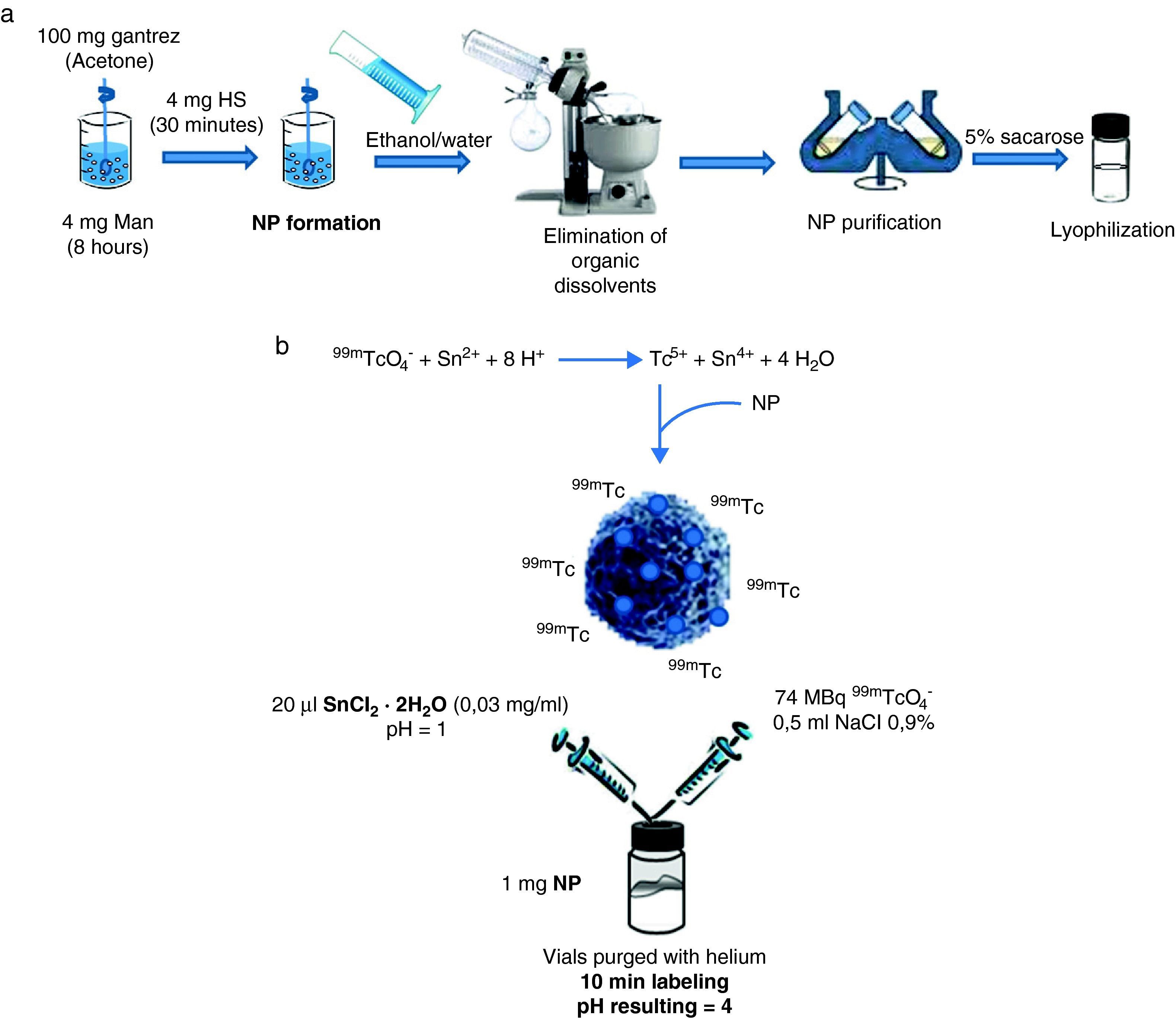
Material and MethodsMan-NP-HS nanoparticles were prepared by the solvent displacement method. They were purified, lyophilized and characterized. Then, they were radiolabeled with 74MBq of 99mTcO4− previously reduced with an acidic stannous chloride solution, working in absence of oxygen and at a final pH of 4. Radiolabeling yield was evaluated by TLC. Biodistribution studies were carried out in mice after ocular administration of the formulation and a control of free 99mTcO4−. Thus, animals were humanly killed at 2 and 24h after the ocular administration and activity in organs was measured in a Gamma counter.
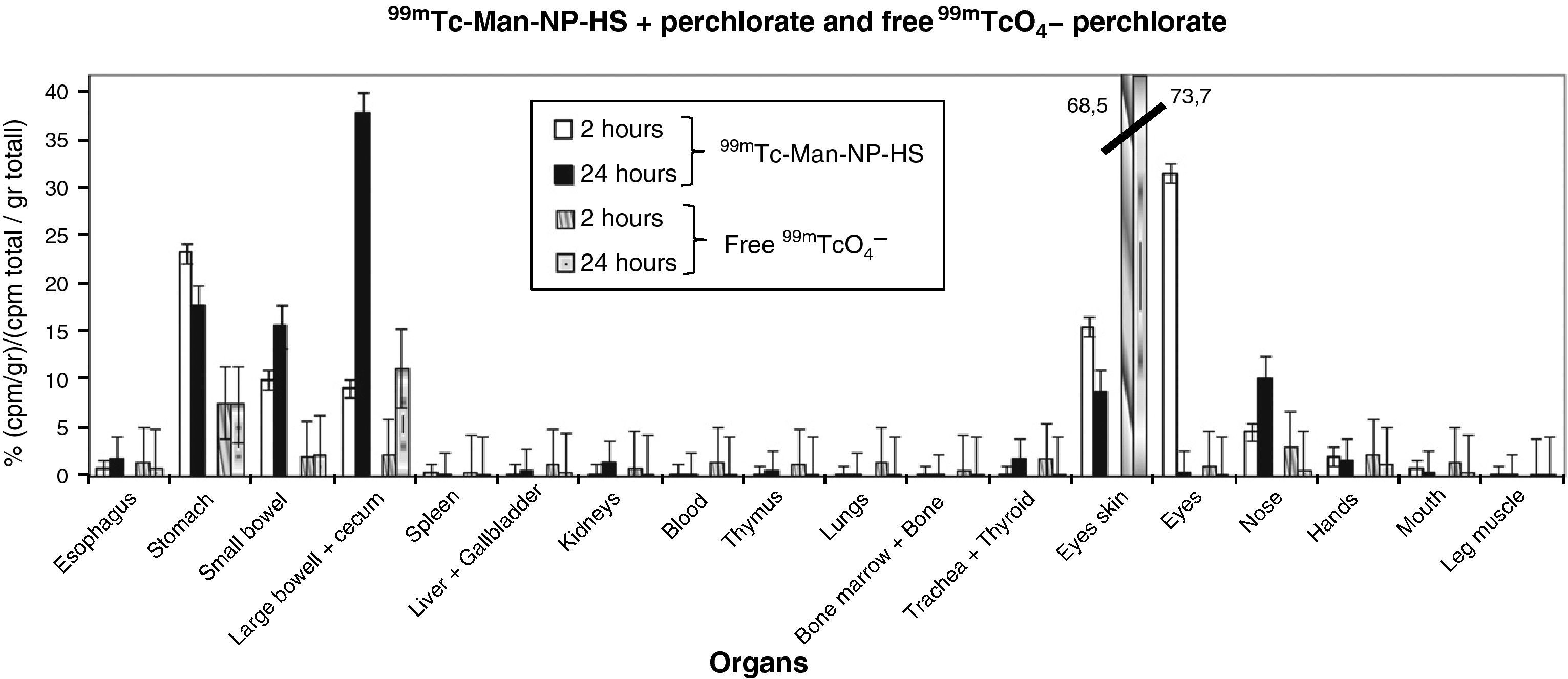
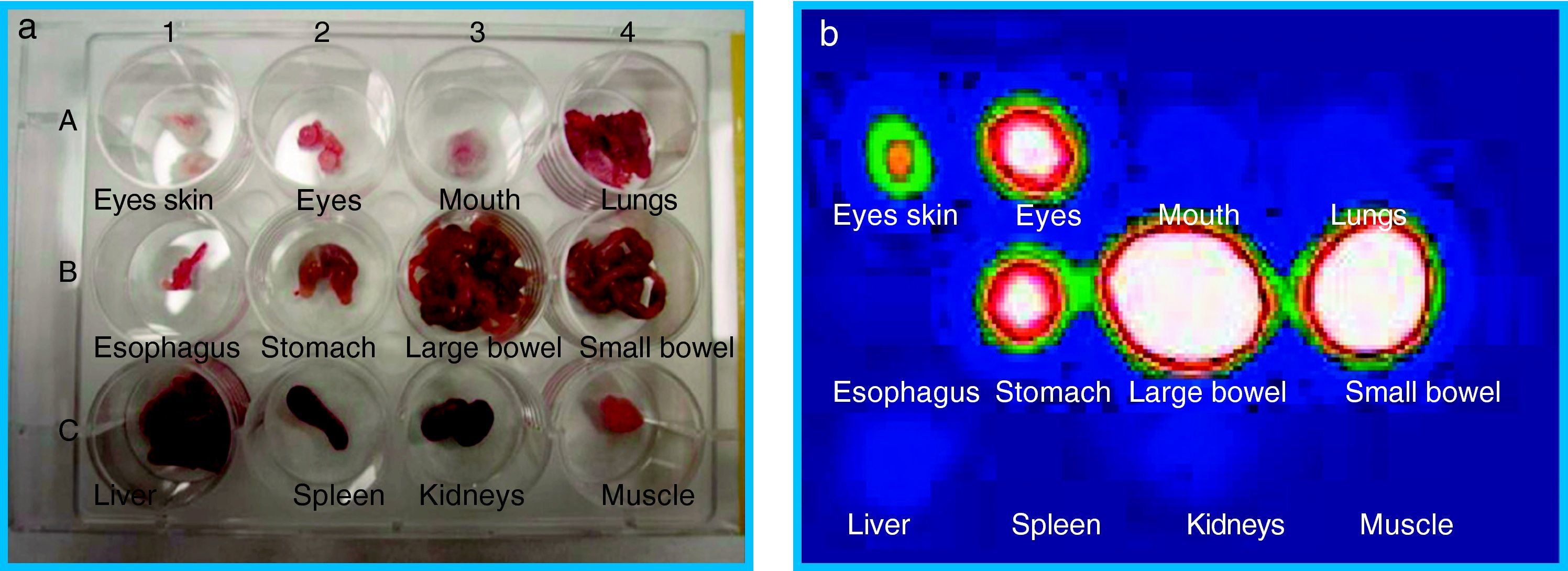
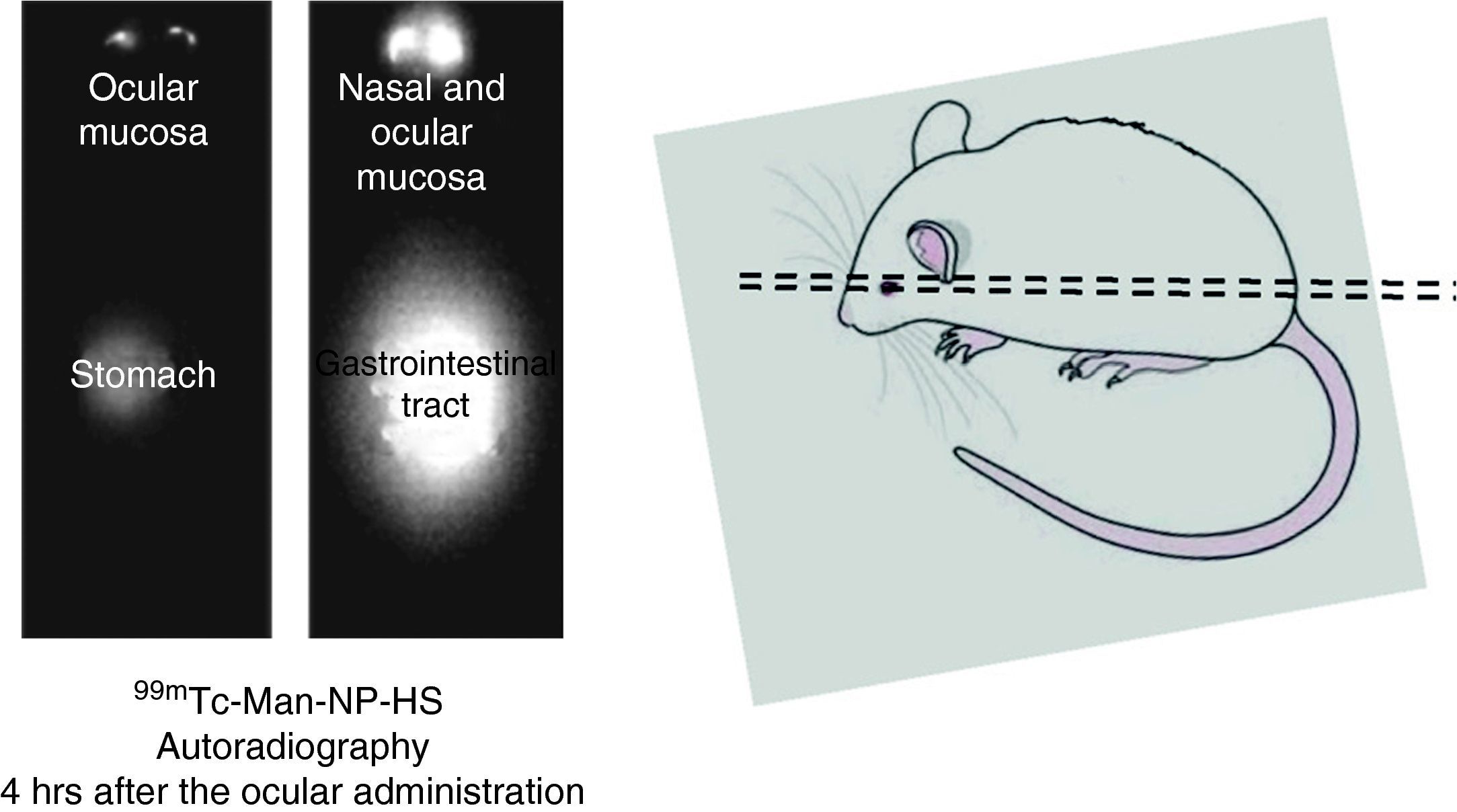
ResultsRadiolabeling yield obtained was greater than 90%. Biodistribution studies of 99mTc-Man-NP-HS showed radioactivity accumulated at 2 and 24h in nasal and ocular mucosa and gastrointestinal tract, in contrast to biodistribution of free 99mTcO4− that remained concentrated in the skin around the eye and gastrointestinal tract.
ConclusionBiodistribution studies of 99mTc-Man-NP-HS after ocular instillation have made it possible to demonstrate its biodistribution in nasal mucosa and gastrointestinal tract. This characteristic is essential as an antigenic delivery system throughout the ocular mucosa. This, together with its elevated immune response, effective protection and intrinsic avirulence make them a suitable anti-Brucella vaccine candidate.
Optimizar el radiomarcaje con 99mTc de nanopartículas de Gantrez® manosiladas y cargadas con el antígeno de Brucella Ovis (Man-NP-HS) y llevar a cabo estudios de biodistribución en ratón tras la administración de las nanopartículas por vía ocular.
MetodologíaLas Man-NP-HS se obtuvieron por el método de desplazamiento de disolvente. Se purificaron, liofilizaron y caracterizaron. A continuación, se marcaron con 74MBq de 99mTcO4− previamente reducido con una disolución ácida de cloruro de estaño, trabajando en ausencia de oxígeno y con un pH final de 4. El rendimiento del marcaje se evaluó mediante TLC. Los estudios de biodistribución se llevaron a cabo en ratones tras la administración oftálmica de la formulación y de un control de 99mTcO4− libre. Para ello, se sacrificaron los animales a las 2 y a las 24 horas tras la administración ocular y se contaron los órganos en un contador gamma.
ResultadosSe obtuvo un rendimiento de marcaje superior al 90%. Los estudios de biodistribución de 99mTc-Man-NP-HS permitieron detectar la actividad concentrada en mucosa nasal y ocular y tracto gastrointestinal tanto a las 2 como a las 24 horas, frente a la biodistribución de 99mTcO4− libre que permaneció concentrado en la piel alrededor del ojo y en tracto gastrointestinal.
ConclusiónLos estudios de biodistribución de 99mTc-Man-NP-HS tras administración oftálmica han permitido demostrar su biodistribución en mucosas y tracto gastrointestinal, característica indispensable como sistema de liberación de antígenos a través de mucosa ocular. Esto, junto con su elevada respuesta inmune, efectiva protección y no virulencia, convierte a estas nanopartículas en una vacuna ideal anti Brucelosis.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora