To evaluate the accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) in operable breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC).
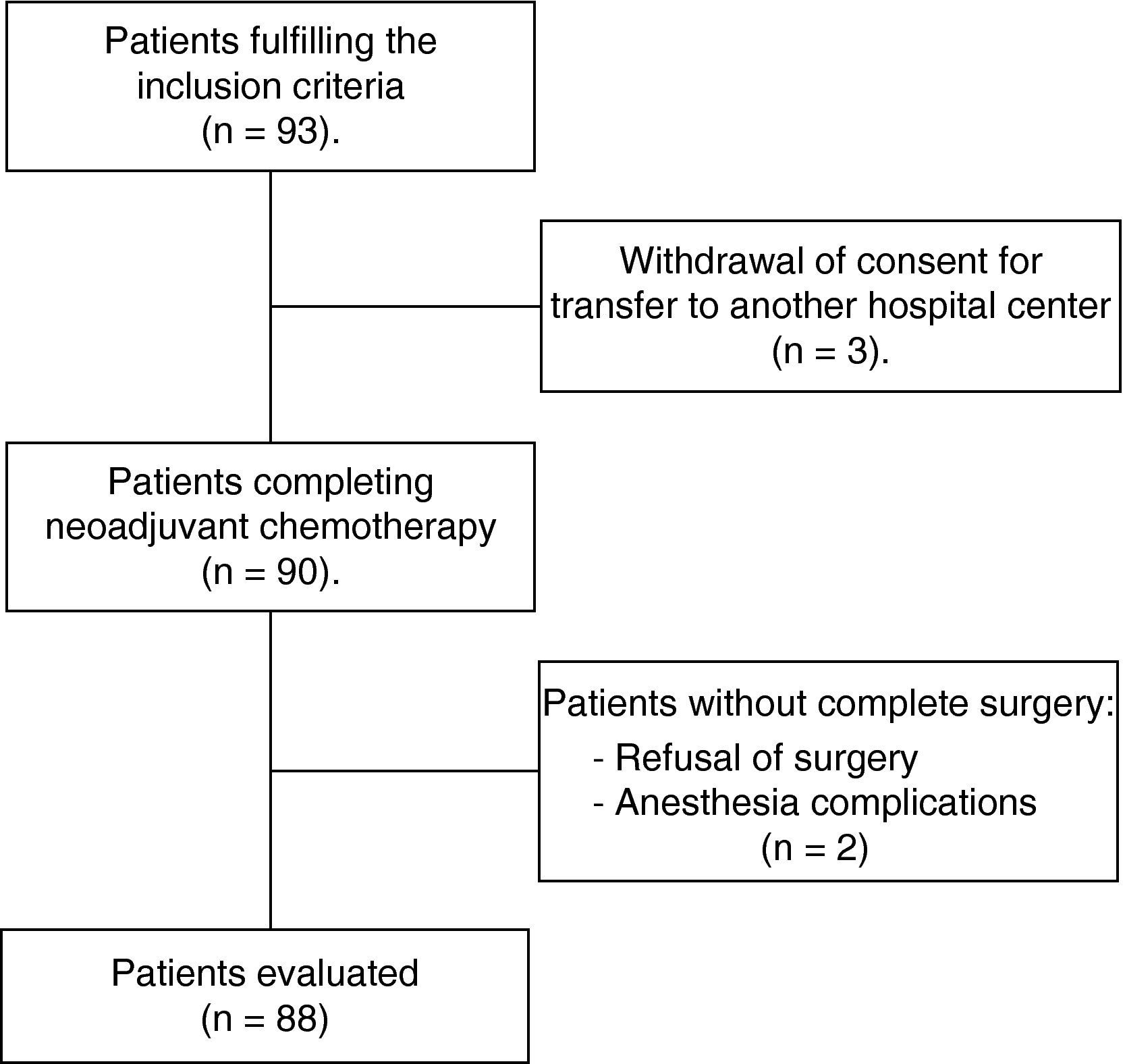
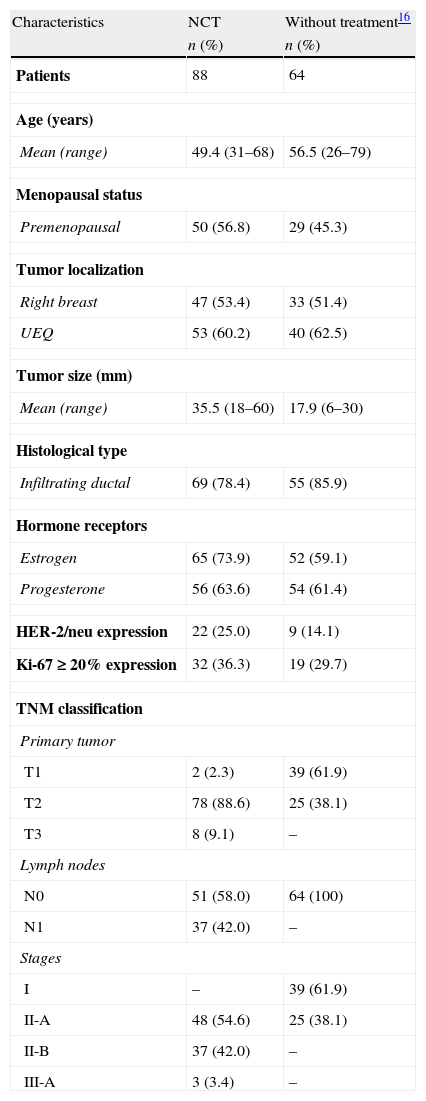
Material and methodsBetween January 2008 and 2011, 88 women, mean age 49.4 years, with infiltrating breast carcinoma, were studied prospectively. Patients were T1–3, N0–1, M0. Prior to surgery, the patients received chemotherapy (epirubicin/cyclophosphamide, docetaxel), and trastuzumab in Her2/neu-positive patients. Axillary status was established by physical examination, ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy of any suspicious lymph node. The day before surgery, 74–111MBq of 99mTc-albumin nanocolloid was injected periareolarly. All patients underwent breast surgery, with SLNB, followed by complete axillary lymph node dissection (ALND). Sentinel lymph node (SLN) was examined by frozen sections, hematoxylin–eosin staining and immunohistochemical analysis or One Step Nucleic Acid Amplification (OSNA).
ResultsMean tumor size: 3.5cm, histologic type: 69 invasive ductal, 16 invasive lobular and 3 others. Thirty-seven patients had clinical/ultrasound node-positive at presentation. Clinical response of primary tumor to NAC: complete in 38, partial in 45, and stable disease in 5 patients. A pathological complete response was achieved in 25. All patients were clinically node-negative after NAC.
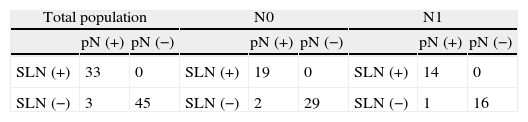
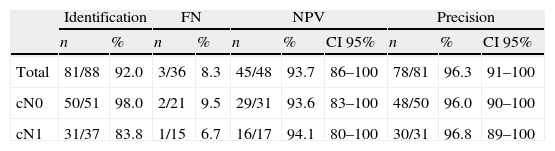
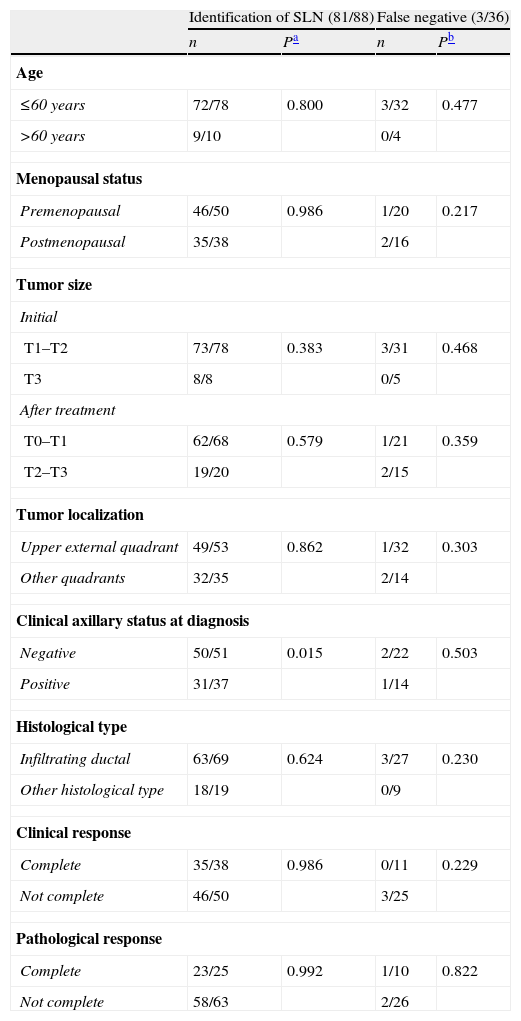
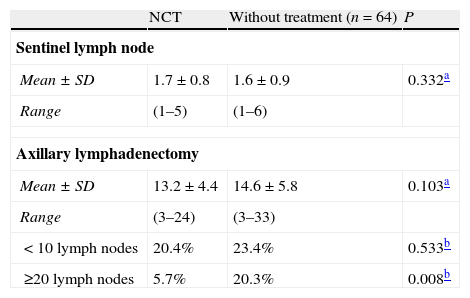
SLN identification rate was 92.0%. Six of 7 patients in whom SLN was not found had clinical/ultrasound positive axilla before NAC. SLN accurately determined the axillary status in 96.5%. False negative rate was 8.3%. In 69.4% of patients, SLN was the only positive node. The mean number of SLN removed was 1.7 and nodes resected from the ALND were 13.2.
ConclusionSLN biopsy after NAC can predict the axillary status with a high accuracy in patients with breast cancer, avoiding unnecessary ALND.
Validar la biopsia selectiva del ganglio centinela (BGC) en pacientes con cáncer de mama tratadas con quimioterapia neoadyuvante.
Material y métodosEstudio prospectivo de enero de 2008 a enero de 2011, 88 pacientes con una edad media de 49,4 años, con cáncer de mama infiltrante T1-3, N0-1, M0, tratadas con epirrubicina/ciclofosfamida, docetaxel y trastuzumab en Her2/neu positivas. El estatus axilar se estableció por exploración física, ecografía axilar y punción ecoguiada de ganglios sospechosos. El día antes de la cirugía se inyectaron periareolarmente 74-111 MBq de 99mTc-nanocoloide de albúmina. En todas se realizó cirugía mamaria, BGC y linfadenectomía axilar. El ganglio centinela (GC) se analizó por cortes de congelación, hematoxilina-eosina, inmunohistoquímica u OSNA.
ResultadosEl tamaño medio del tumor fue de 3,5 cm. Según el tipo histológico, 69 se clasificaron como ductal infiltrante, 16 como lobulillar infiltrante y 3 como de otro tipo. Treinta y siete pacientes tenían axila clínica/ecográfica positiva al diagnóstico. La respuesta clínica del tumor primario fue: 38 completa, 45 parcial, 5 no respuesta. En todas las pacientes la axila fue clínica/ecográfica negativa después del tratamiento. En 25 casos hubo respuesta patológica completa en el tumor primario.
El porcentaje de identificación del GC fue del 92,0%, 6 de las 7 pacientes sin migración eran axila clínica/ecográfica positiva al diagnóstico. En el 96,3% de los casos el GC determinó correctamente el estatus axilar. La tasa de falsos negativos fue del 8,3%. En el 69,4% de los casos el GC era el único afectado de la axila. El número medio de GC identificados fue 1,7 y el de ganglios axilares extirpados fue 13,2.
ConclusiónLa BGC es una técnica factible en pacientes con cáncer de mama tratadas con quimioterapia neoadyuvante, pudiendo evitar linfadenectomías innecesarias.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora