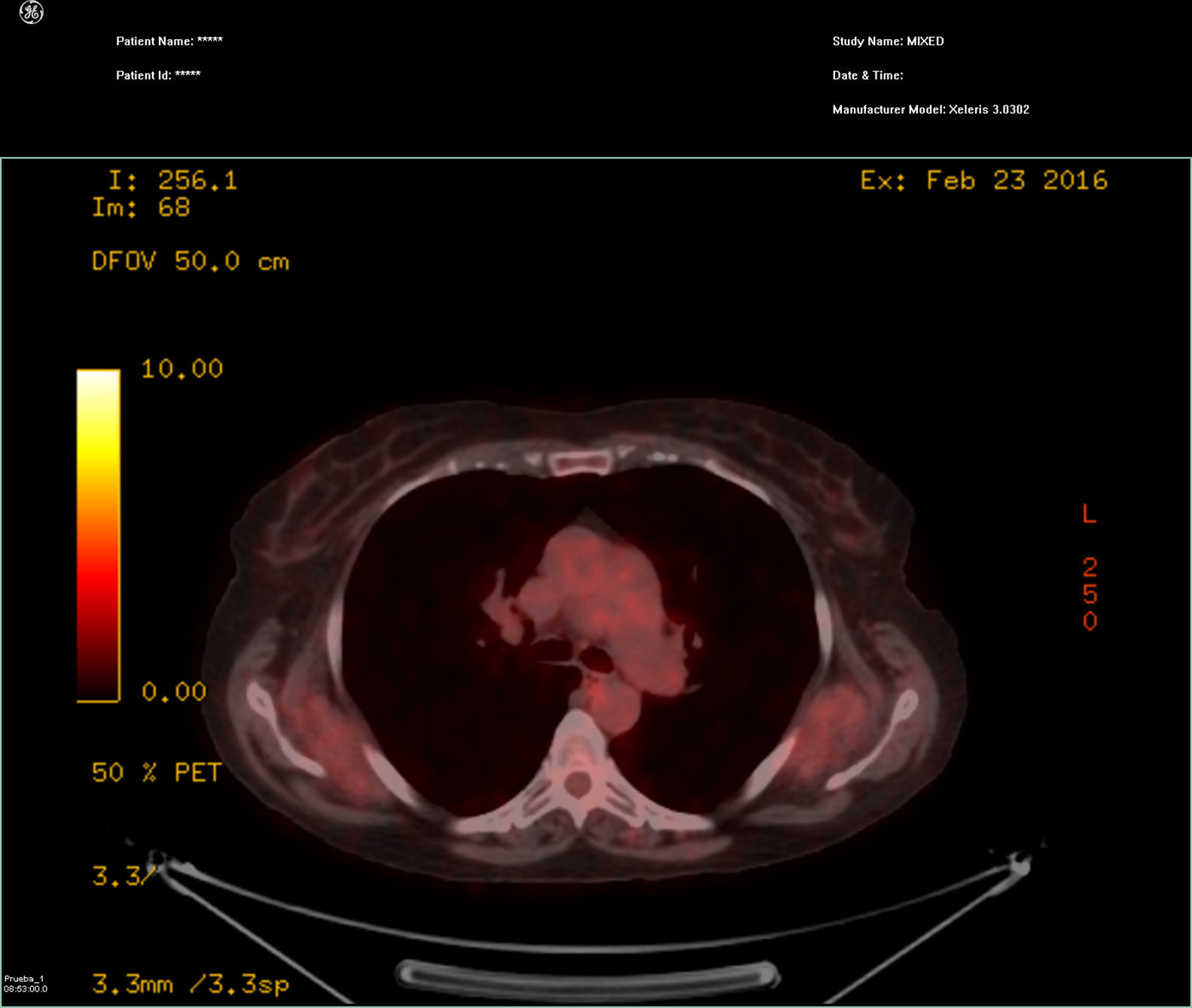
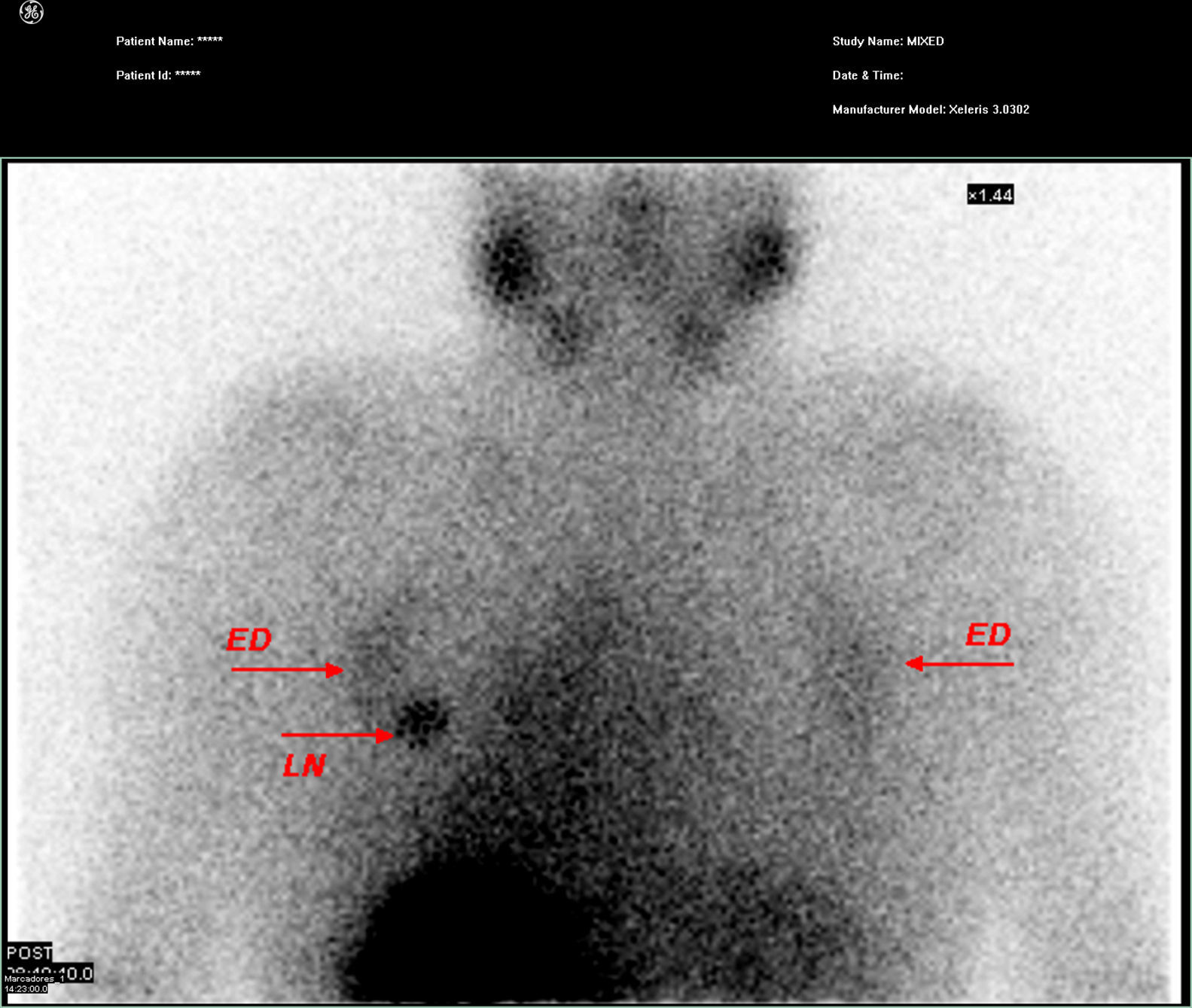
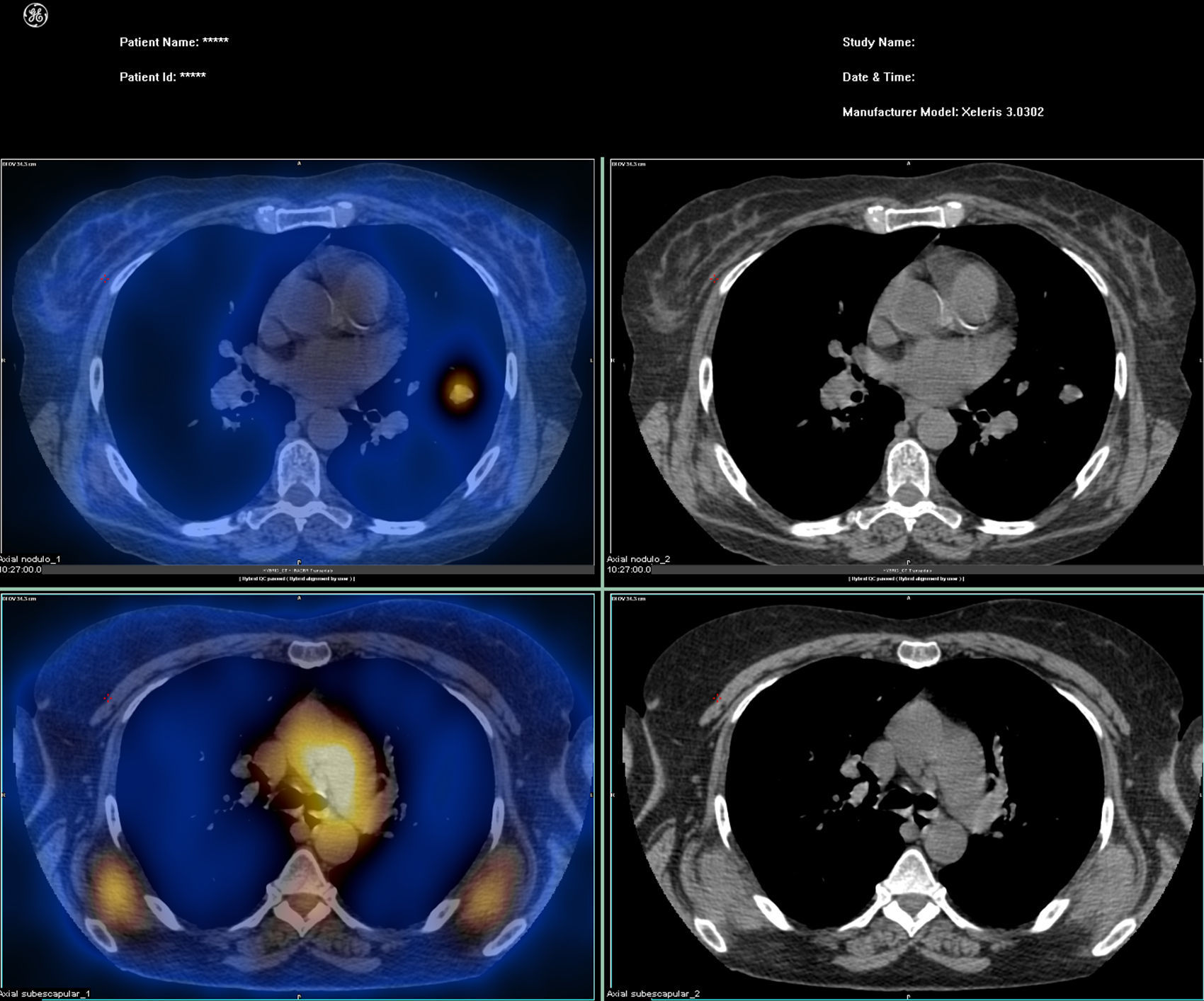
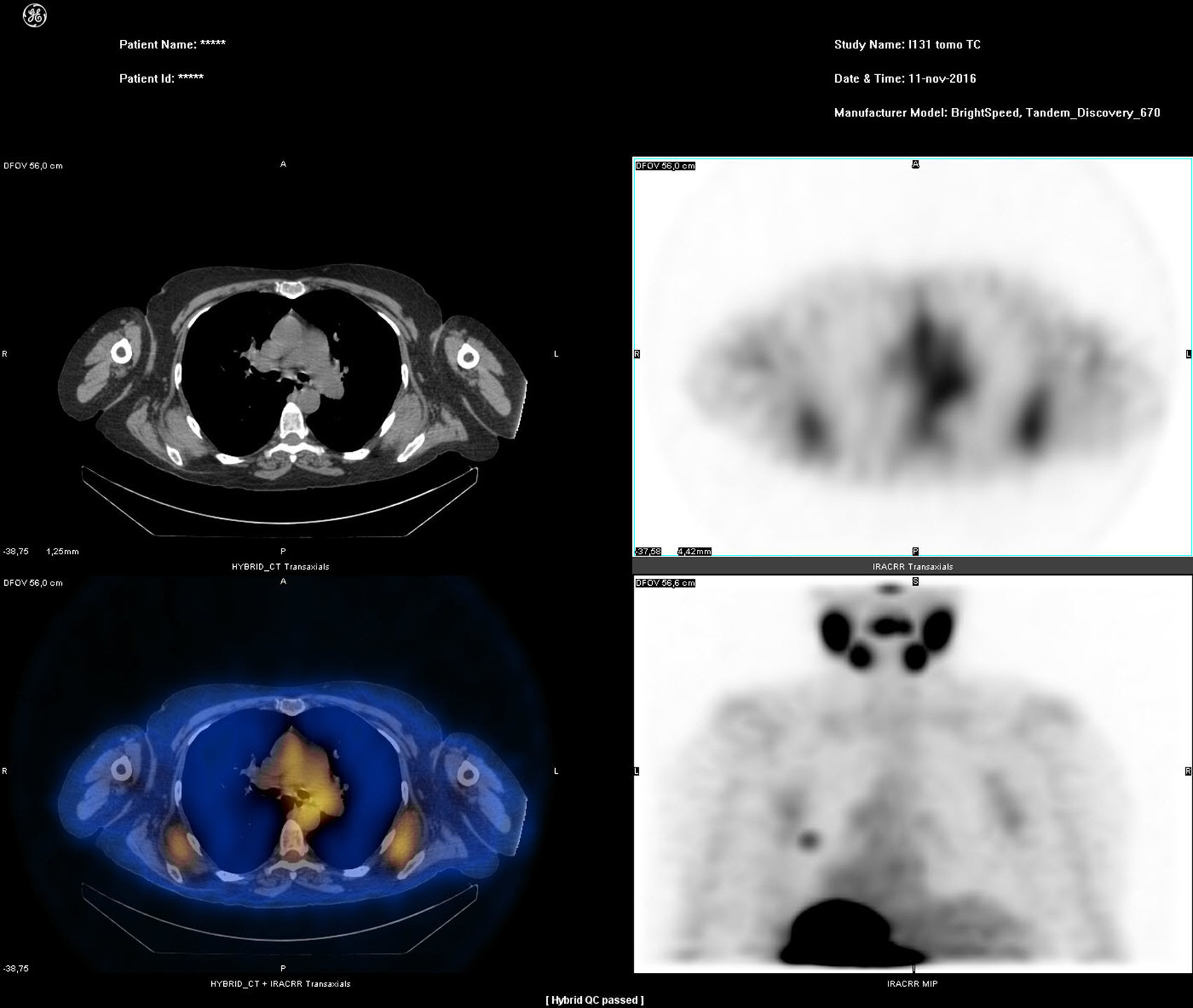
Radioiodine uptake in the thyroid tissue, metastasis of differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC), and in other tissues, depends on the expression of sodium-iodide symporter (NIS). Vascular permeability, effusions, inflammation, and other mechanisms may also play a role in the accumulation of radioactive iodine. A 63-year-old woman underwent radioiodine therapy, as well as a post-therapy whole-body scan,as she was suspected of having lung metastasis from thyroid carcinoma. The scan not only showed uptake at the lung metastasis but also a faint diffuse bilateral uptake in the posterior thorax. On SPECT/CT this uptake was located in a known ElastofibromaDorsi (ED) previously diagnosed by contrast CT and viewed in a FDG PET/CT. The radioiodine uptake in ED, especially if typical, is not a diagnostic problem in SPECT/CT study, but can be misleading in a study limited to a few planar images, particularly if the uptake occurs asymmetrically, or ED is located in a unsuspected area.
La captación de yodo radioactivo en el tejido tiroideo y en las metástasis del cáncer diferenciado de tiroides (DTC) y otros tejidos depende de la expresión del transportador de sodio-yodo (NIS). La permeabilidad vascular, derrames serosos, procesos inflamatorios y otros mecanismos tambièc)n pueden desempeñar un papel en la acumulación de yodo radioactivo. Una mujer de 63 años fue sometida a terapia con yodo radiactivo y a un estudio de cuerpo completo despuèc)s de la terapia, debido a la sospecha de metástasis pulmonar de carcinoma diferenciado de tiroides. La exploración no solo mostró captación en la metástasis de pulmón, sino tambièc)n una captación difusa leve en la región posterior del tórax en ambos lados; en el SPECT/TC esta captación se localiza en un ED ya conocido, previamente diagnosticado mediante TC con contraste y visto tambièc)n en un FDG-PET/CT. La captación de radioyodo en el ED, sobre todo si es típico, no plantea un problema de diagnóstico en el estudio de SPECT/CT, pero puede inducir a error en un estudio limitado a unas pocas imágenes planares, especialmente si la captación se produce de forma asimèc)trica, o el ED se encuentra en una localización insospechada.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)