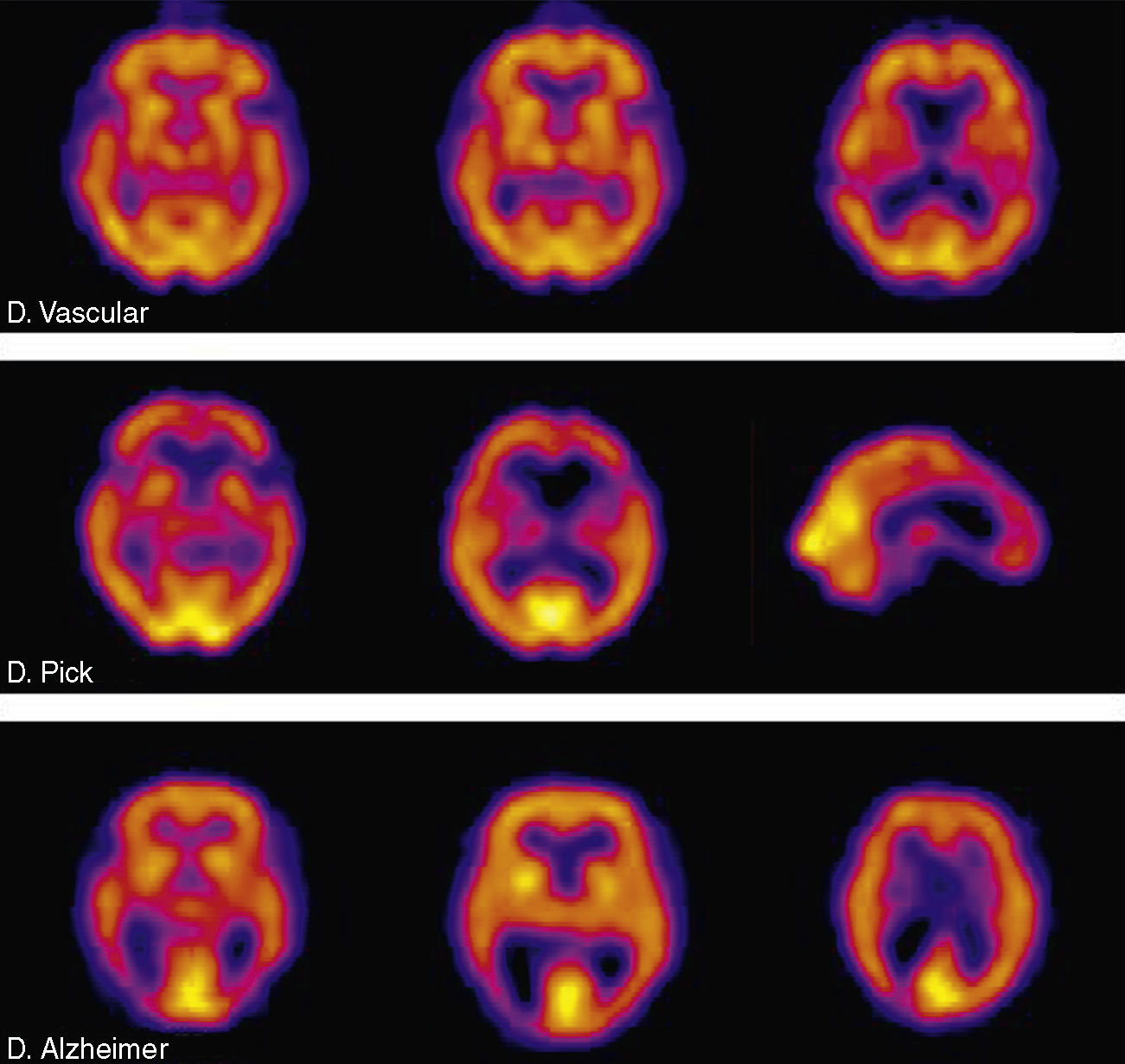
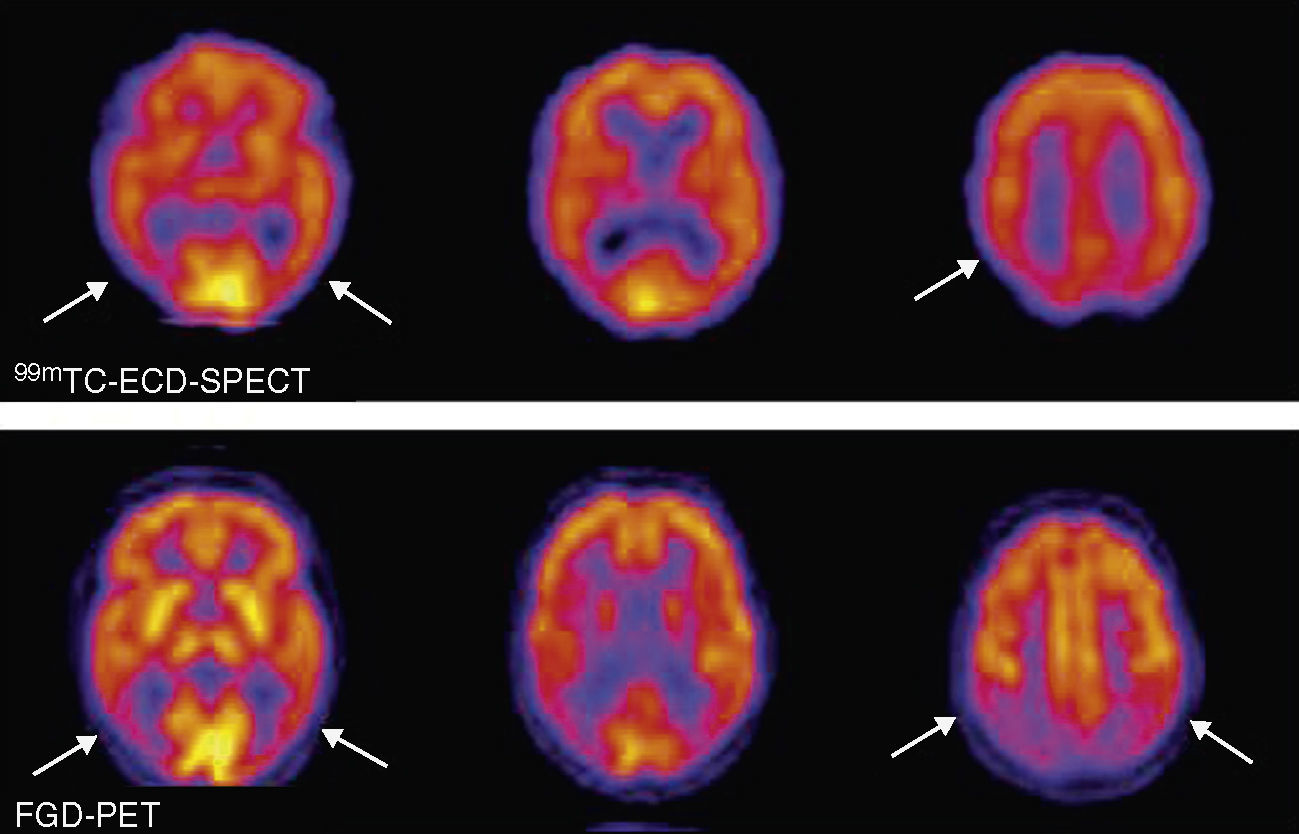
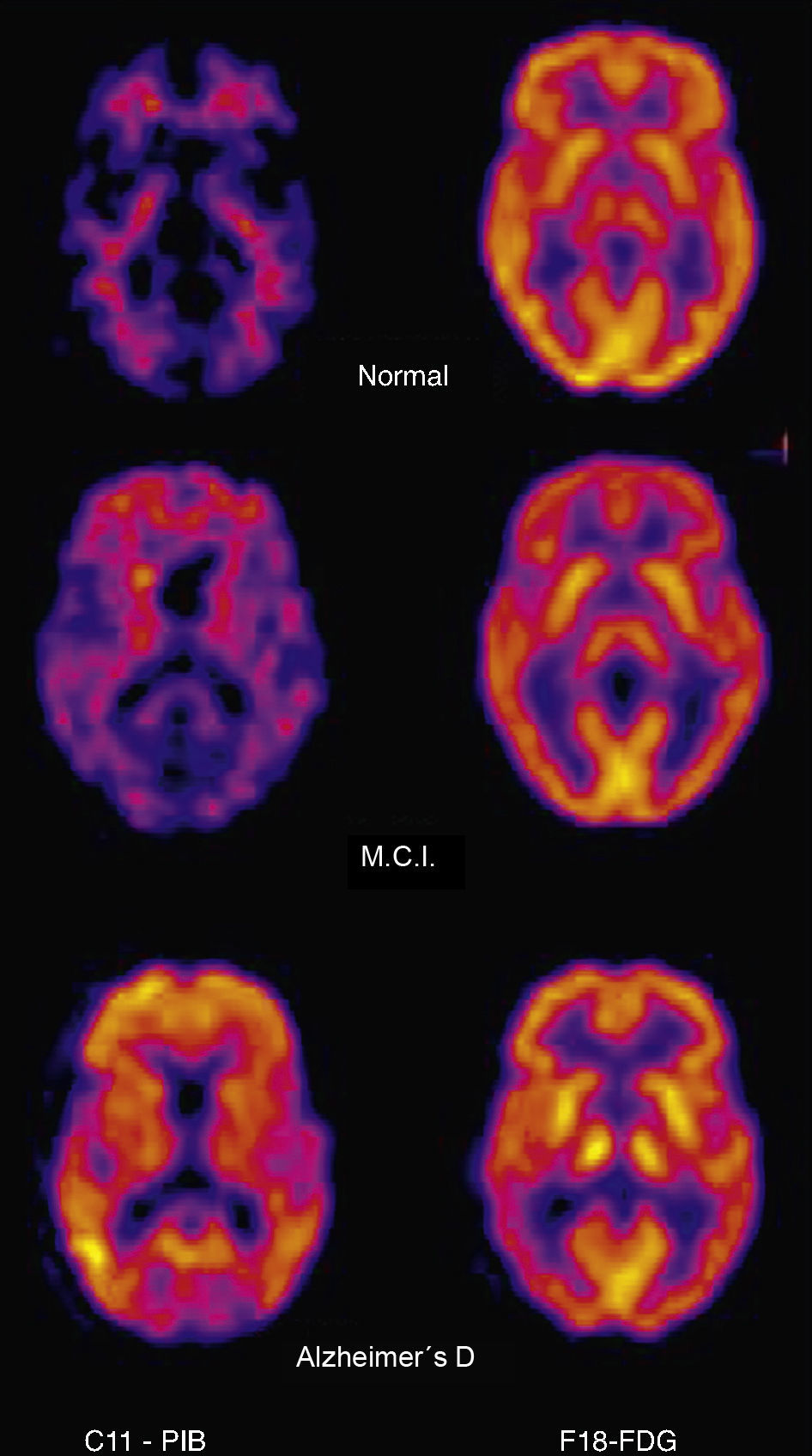
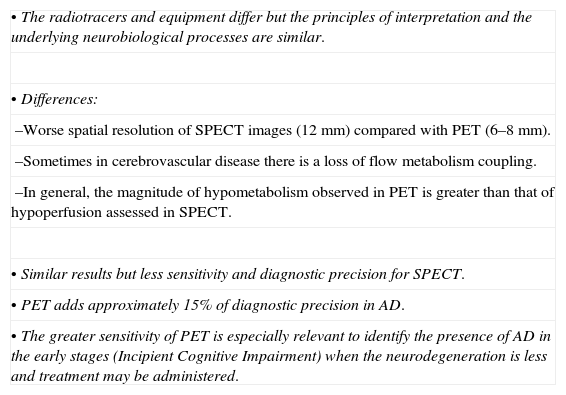
In the context of the limitations of structural imaging, brain perfusion and metabolism using SPECT and PET have provided relevant information for the study of cognitive decline. The introduction of the radiotracers for cerebral amyloid imaging has changed the diagnostic strategy regarding Alzheimer's disease, which is currently considered to be a “continuum.” According to this new paradigm, the increasing amyloid load would be associated to the preclinical phase and mild cognitive impairment. It has been possible to observe “in vivo” images using 11C-PIB and PET scans.
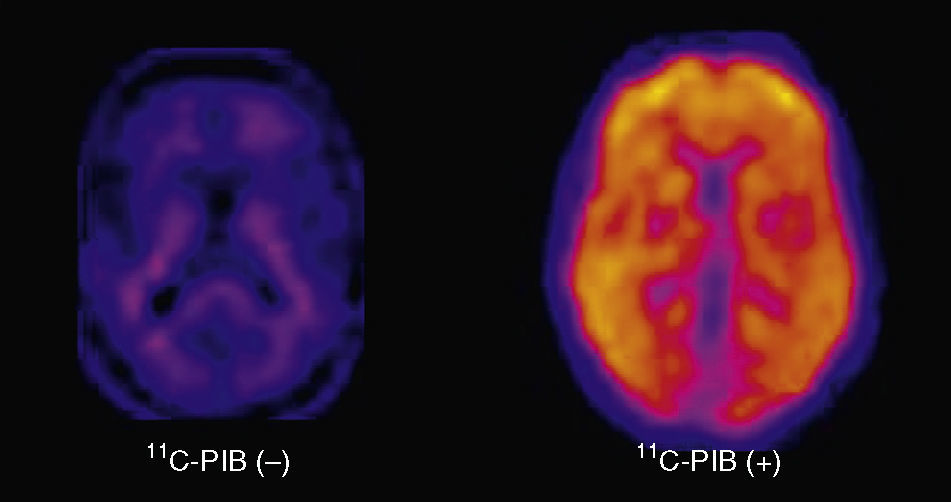
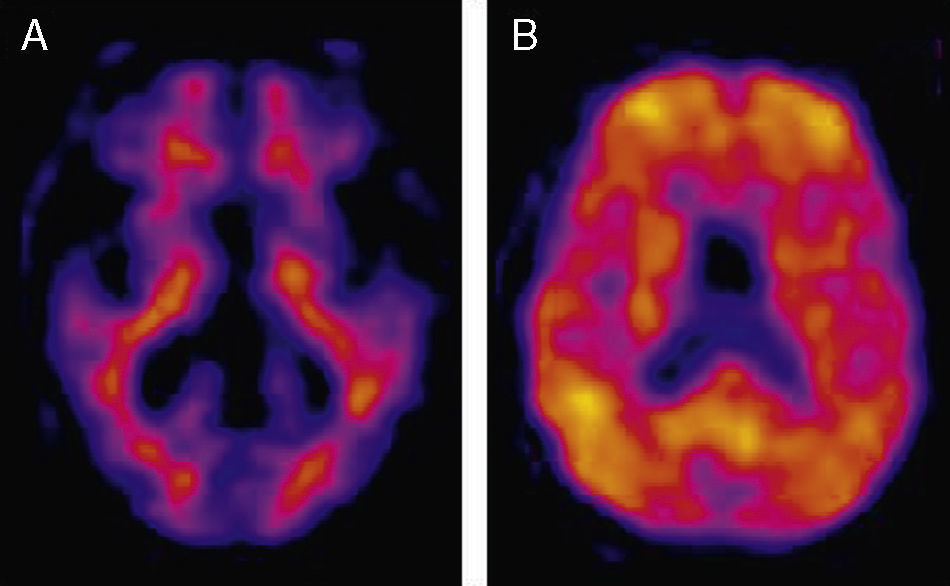
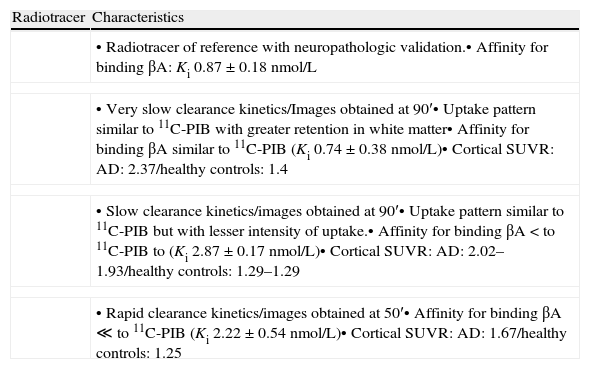
The characteristics of the 11C-PIB image include specific high brain cortical area retention in the positive cases with typical distribution pattern and no retention in the negative cases. This, in combination with 18F-FDG PET, is the basis of molecular neuroimaging as a biomarker. At present, its prognostic value is being evaluated in longitudinal studies. 11C-PIB-PET has become the reference radiotracer to evaluate the presence of cerebral amyloid. However, its availability is limited due to the need for a nearby cyclotron. Therefore, 18F labeled radiotracers are being introduced. Our experience in the last two years with 11C-PIB, first in the research phase and then as being clinically applied, has shown the utility of the technique in the clinical field, either alone or in combination with FDG. Thus, amyloid image is a useful tool for the differential diagnosis of dementia and it is a potentially useful method for early diagnosis and evaluation of future treatments.
En el contexto de las limitaciones de la imagen estructural, los estudios de perfusión y metabolismo cerebral con SPECT y PET han aportado información relevante en el estudio del deterioro cognitivo. La introducción de radiotrazadores de amiloide cerebral ha replanteado la estrategia diagnóstica en torno a la enfermedad de Alzheimer (EA), considerada actualmente un “continuum”. En este nuevo paradigma, la carga amiloide creciente se asocia al estadio preclínico y de deterioro cognitivo leve de la enfermedad y ha podido ser objetivada en exploraciones “in vivo” gracias a la introducción del 11C-PIB y los tomógrafos PET.
Las características de la imagen 11C-PIB son una elevada retención específica cortical cerebral en los casos positivos, con distribución topográfica característica y no retención en los negativos. Junto al PET con 18F-FDG constituye la base de la neuroimagen molecular como biomarcador y se está valorando su significado pronóstico en estudios longitudinales. El PET con 11C-PIB se ha consolidado como la técnica óptima para valorar la presencia de amiloide cerebral, pero la necesidad de un ciclotrón cercano para su síntesis limita su disponibilidad, por lo que se están introduciendo trazadores análogos marcados con 18F. Nuestra experiencia en los dos últimos años aplicando el 11C-PIB, primero en fase investigadora y después en la clínica, ha constatado la utilidad de la técnica en el campo asistencial, tanto de forma aislada como en combinación con la FDG. Así pues, la imagen de amiloide ha demostrado ser una herramienta útil en el diagnóstico diferencial de la demencia y un método prometedor de diagnóstico precoz y evaluación de tratamientos futuros.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)