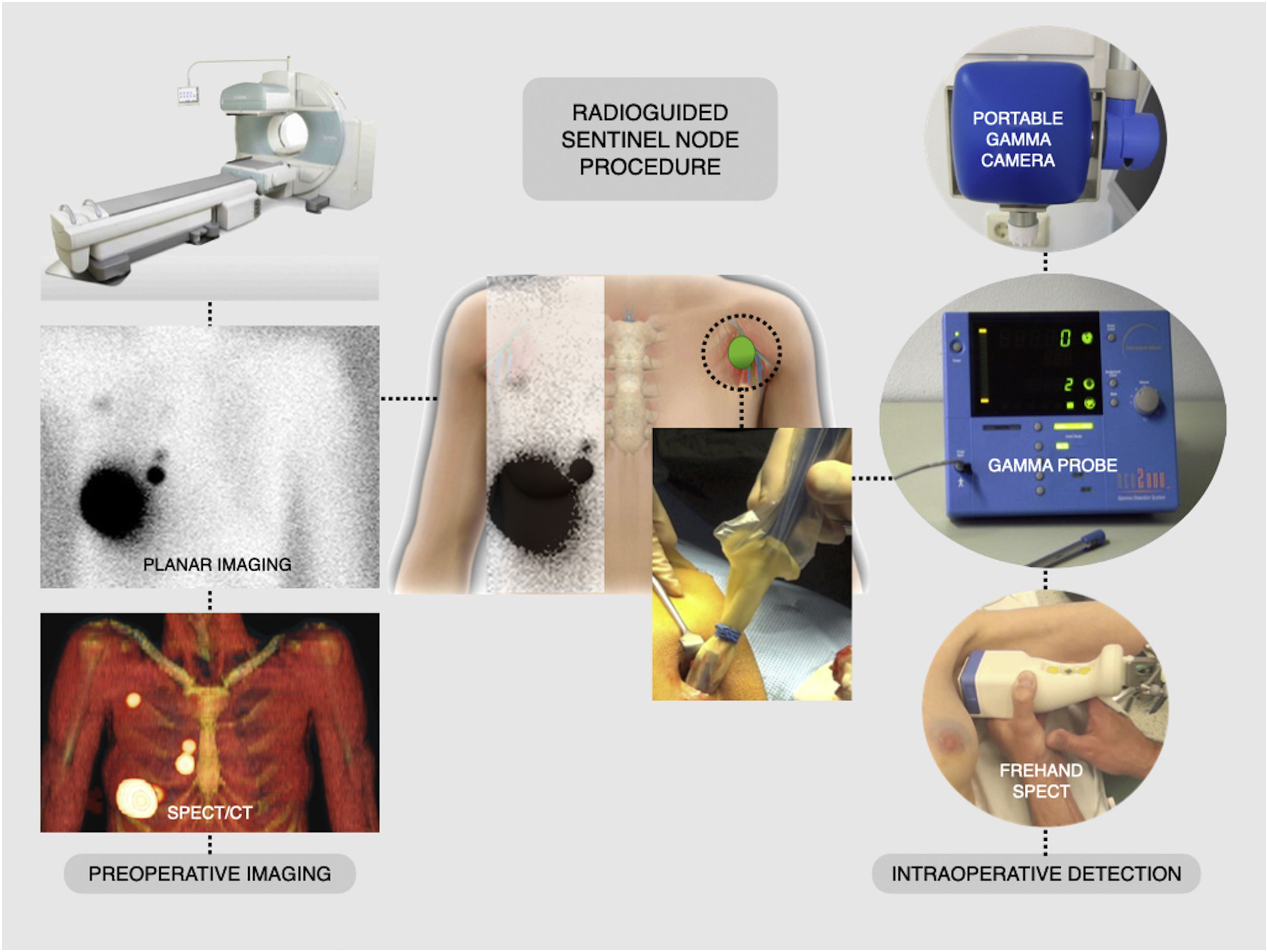
Nuclear medicine has significantly contributed to precision surgery in breast cancer in the past decades. Radioguided surgery (RGS) has enabled sentinel node (SN) biopsy in assessing regional nodal involvement modifying the management of patients with early breast cancer. For the axilla the SN procedure has resulted in fewer complications and better quality of life when compared with axillary lymph node dissection. Originally, SN biopsy principally concerned cT 1-2 tumours without evidence of axillary lymph node metastases. However, in last years SN biopsy is also being offered to patients with large or multifocal tumours, ductal carcinoma in situ, ipsilateral breast cancer relapse, and to patients receiving neoadjuvant systemic treatment (NST) for breast sparing surgery. Parallel to this evolution various scientific associations are trying to homogenise issues such as radiotracer choice, breast injection site, preoperative imaging standardisation and SN biopsy timing in relation to NST as well as management of non-axillary SN metastasis (e.g. internal mammary chain). Additionally, RGS is currently used to accomplish primary breast tumour excision either by intralesional radiocolloid injection or by radioactive iodine seed implantation which is also employed to target metastatic axillary lymph nodes. This latter procedure contributes to manage the node-positive axilla in combination with 18F-FDG PET/CT in an effort to tailor systemic and loco regional treatment.
La medicina nuclear ha contribuido significativamente en la cirugía de precisión en el cáncer de mama en las últimas décadas. La cirugía radioguiada (CRG) ha permitido la biopsia del ganglio centinela (GC) en la evaluación de la infiltración ganglionar regional modificando el manejo de pacientes con cáncer de mama precoz. Para la axila, el procedimiento de la biopsia del GC ha significado un decremento de complicaciones y una mejor calidad de vida en comparación con la disección de los ganglios linfáticos axilares. Originalmente, la biopsia del GC se indicó principalmente en tumores cT 1-2 sin evidencia de metástasis en los ganglios linfáticos axilares. Sin embargo, en los últimos años la biopsia del GC también se está ofreciendo a pacientes con tumores grandes o multifocales, carcinoma ductal in situ, recidiva del cáncer de mama ipsilateral y a pacientes que reciben tratamiento sistémico neoadyuvante (TSN) para cirugía conservadora de mama. Paralelamente a esta evolución, varias asociaciones científicas están tratando de homogeneizar cuestiones como la elección del radiotrazador, el lugar de inyección de la mama, la estandarización de las imágenes preoperatorias y el momento de la biopsia del GC en relación con la NST, así como el manejo de la metástasis del GC no axilar (p. ej., cadena mamaria interna). Además, la CRG se usa actualmente para lograr la extirpación de tumores de mama primarios mediante inyección de radiocoloides intralesionalmente o mediante implantación de semillas de yodo radiactivo que también se emplean para marcar los ganglios linfáticos axilares metastásicos. Este último procedimiento contribuye a manejar la axila con ganglios positivos en combinación con la 18F-FDG PET/CT en un esfuerzo por adaptar el tratamiento sistémico y locorregional.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)