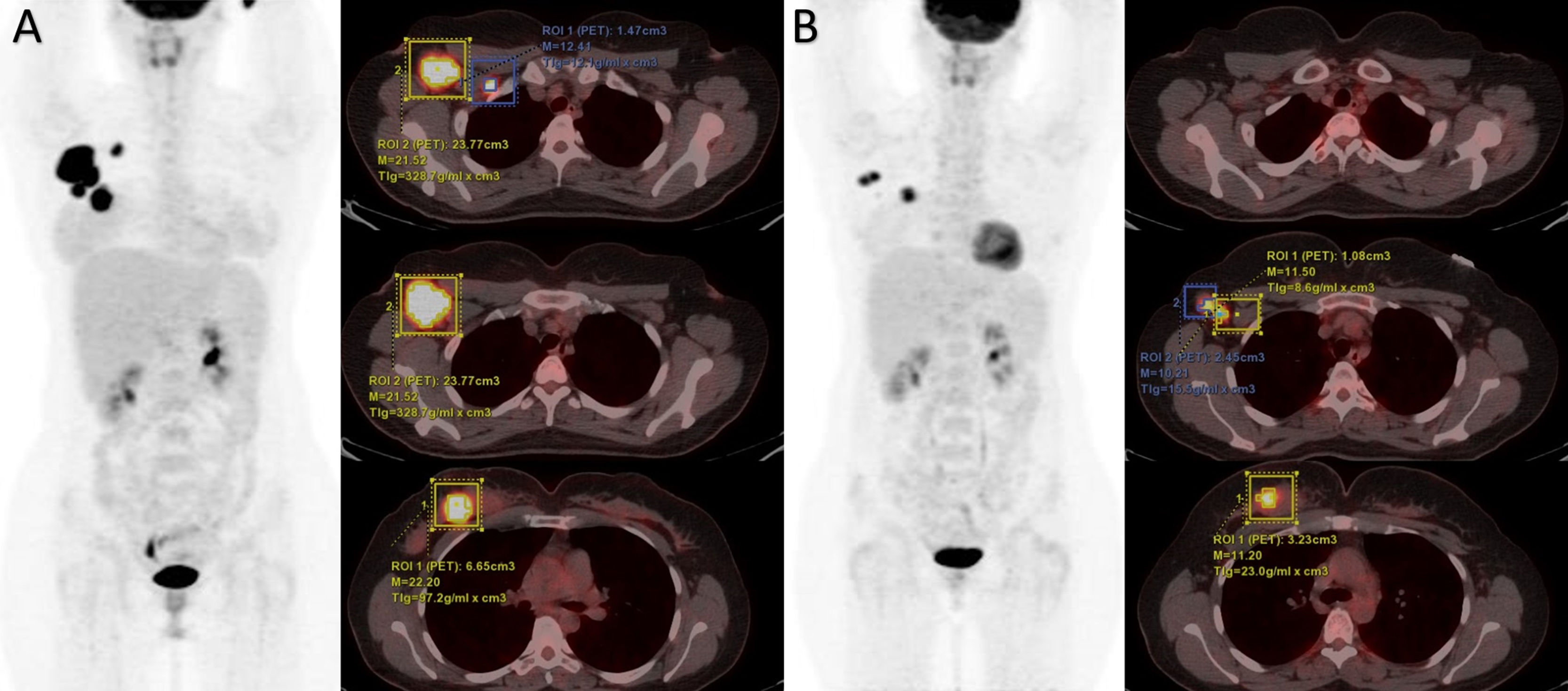
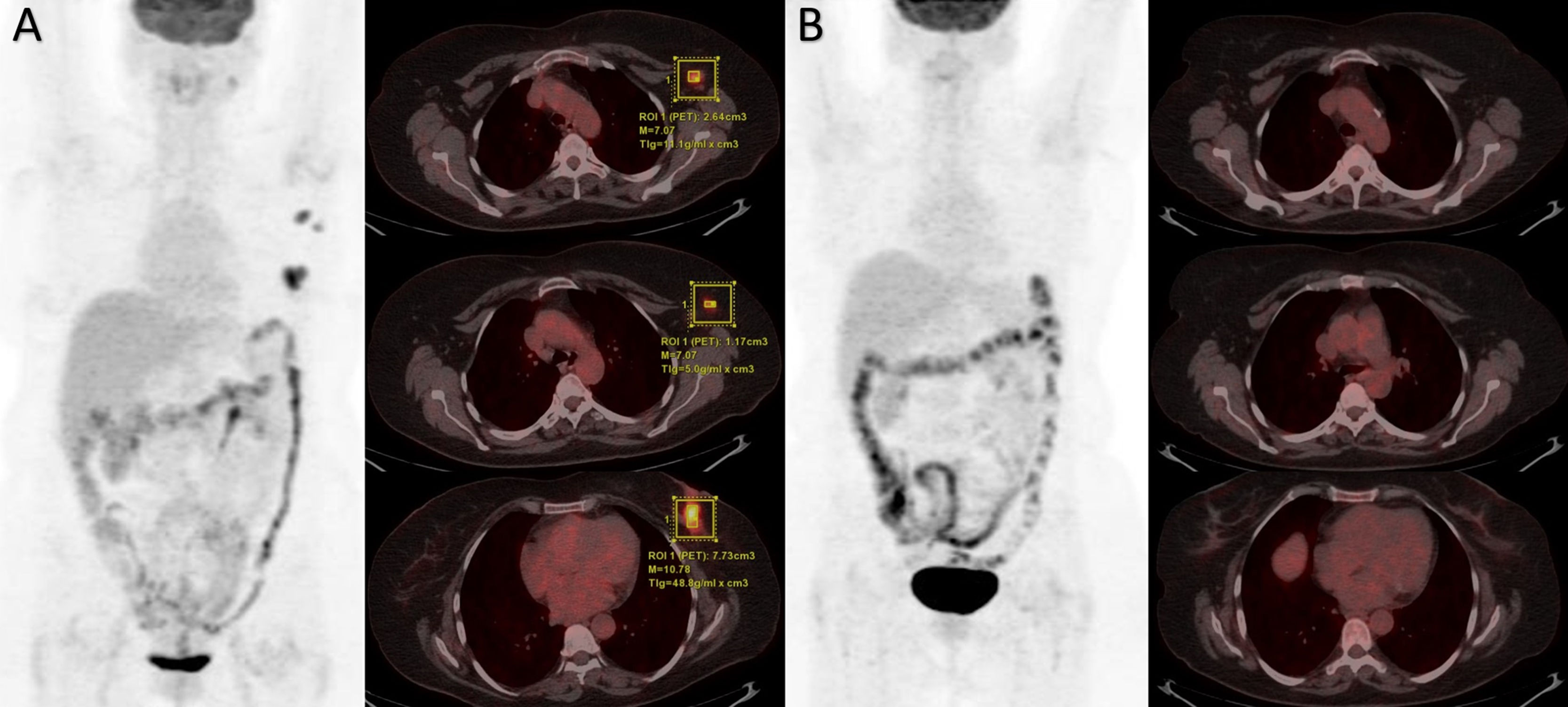
We investigated the correlation between 18F-FDG PET/CT indices and pathological response in breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) which was scored with Residual Cancer Burden (RCB) system after surgery. Our aim is to detect extensive residual cancer burden earlier by using PET/CT indices.
MethodsCharacteristics of patients were retrieved retrospectively. Baseline maximum Standart Uptake Value (SUVmax), Metabolic Tumor Volume (MTV) and Total Lesion Glycolysis (TLG) indices and reduction rate (RR) between baseline and interim evaluation were calculated with FDG PET/CT scan. All patients were evaluated according to RCB scores after surgery. Pathological responses and PET/CT measurement results were analyzed with demographic and clinical parameters.
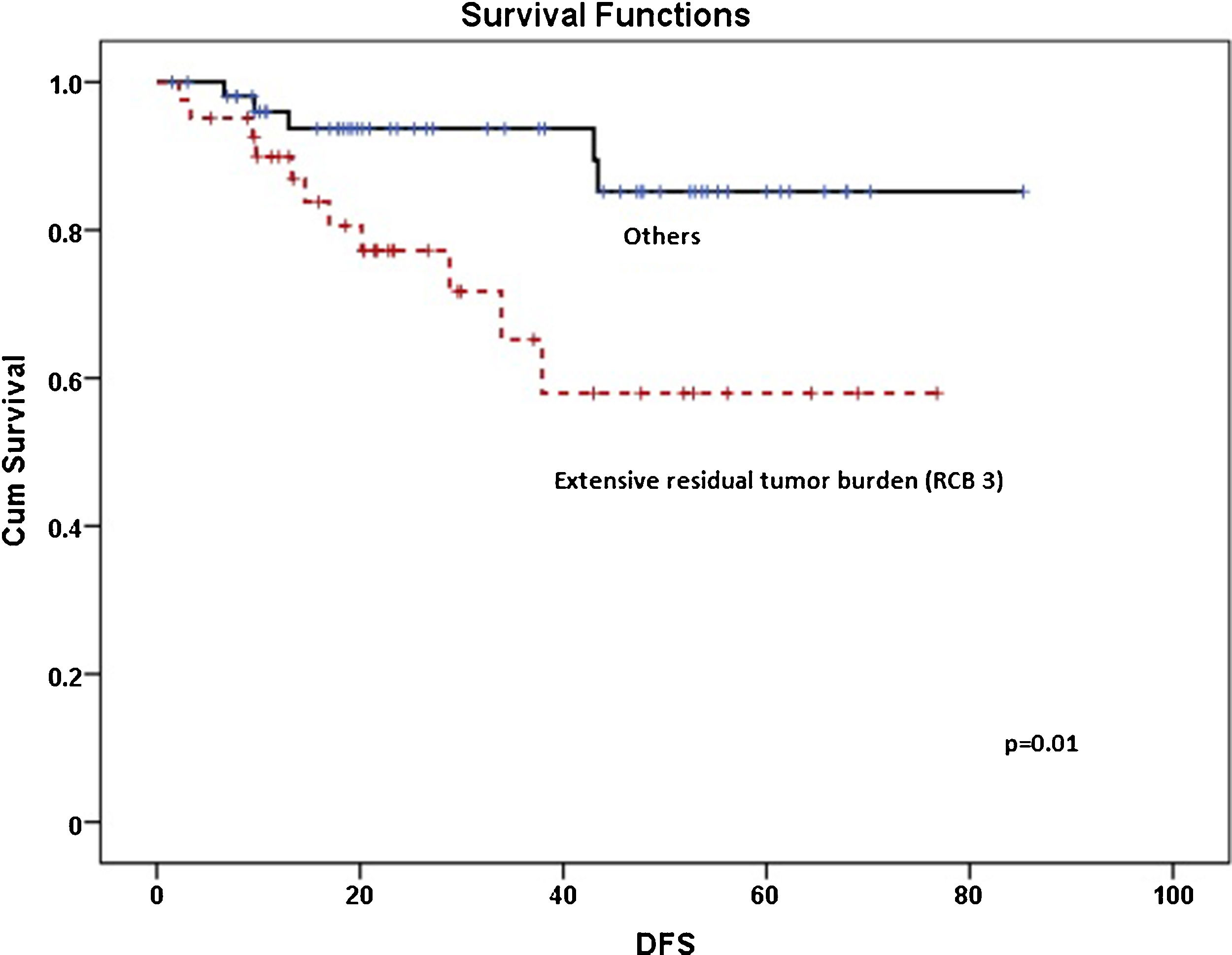
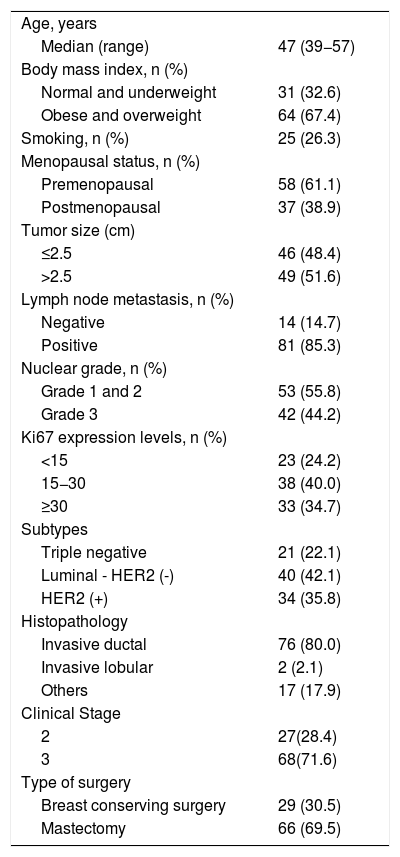
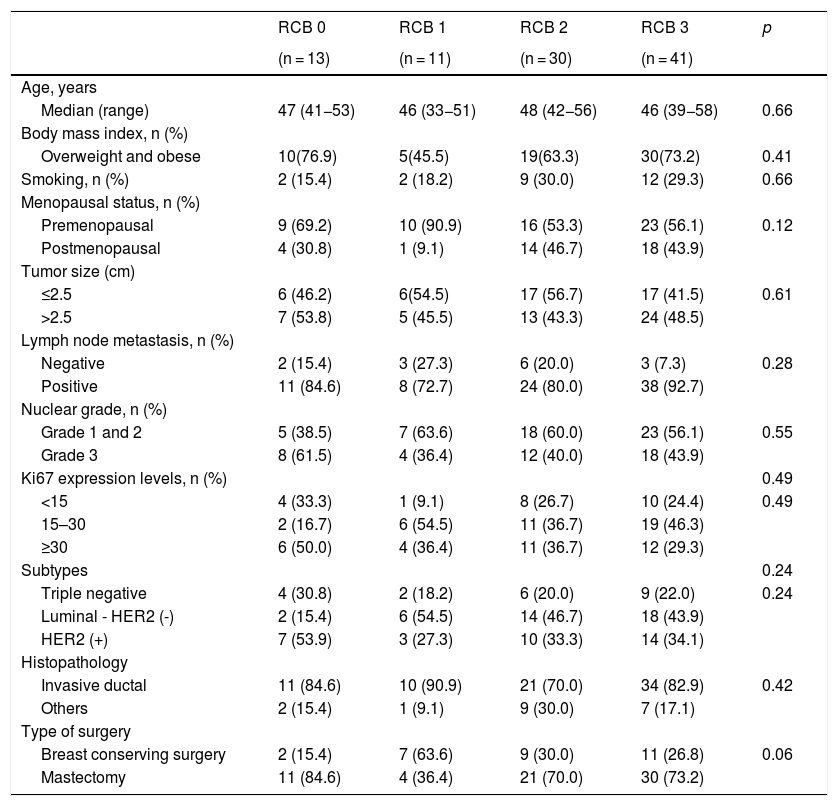
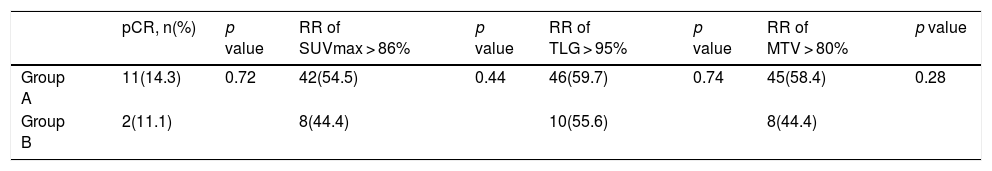
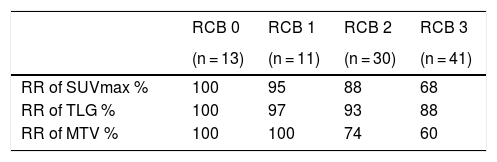
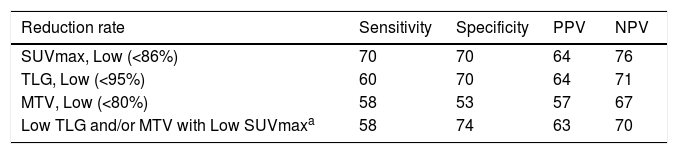
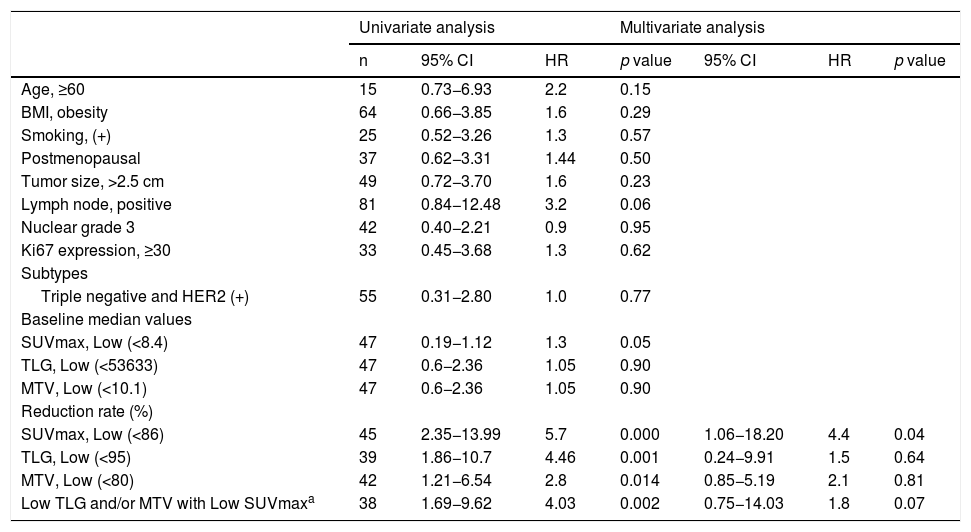
ResultsA total of 95 patients were included in the study. According to pathological responses, the distribution of RCB -0, -1, -2, -3 were 13 (13.7%), 11 (11.6%), 30 (31.6%), 41 (43.2%), respectively. Disease-free survival was significantly lower in the RCB3 group compared to the pathological responder group (p = 0.01). According to multivariate analysis, RR of SUVmax was determined as an independent variable predicting extensive residual cancer burden with an optimal cut-off value of 86% (p < 0.05).
ConclusionsWe determined RR of SUVmax as an independent factor for predicting extensive residual tumor burden. We believe that RR of SUVmax is sufficient to predict pathological response in daily practice. In addition, MTV and TLG measurements do not contribute additionally to SUVmax alone and can cause unnecessary labor loss.
Investigamos la correlación entre los índices de PET/TC con 18F-FDG y la respuesta patológica en el cáncer de mama tratado con quimioterapia neoadyuvante (NACT), que se puntuó con el sistema de carga de cáncer residual (RCB) después de la cirugía. Nuestro objetivo es detectar antes una carga extensa de cáncer residual mediante el uso de los índices de PET/TC.
MétodosSe registraron las características de las pacientes de forma retrospectiva. Se calculó el valor máximo de captación estándar (SUVmáx), el volumen metabólico del tumor (MTV) y los índices de glucólisis total de la lesión (TLG), así como la tasa de reducción (RR) entre la línea de base y la evaluación intermedia, con la exploración FDG PET/TC. Todos los pacientes fueron evaluados según las puntuaciones RCB después de la cirugía. Las respuestas patológicas y los resultados de las mediciones de PET/TC se analizaron con parámetros demográficos y clínicos.
ResultadosUn total de 95 pacientes fueron incluidos en el estudio. Según las respuestas patológicas, la distribución de RCB -0, -1, -2, -3 fue de 13 (13,7%), 11 (11,6%), 30 (31,6%), 41 (43,2%), respectivamente. La supervivencia libre de enfermedad fue significativamente menor en el grupo RCB3 en comparación con el grupo de respuesta patológica (p = 0,01). Según el análisis multivariante, se determinó que el RR del SUVmax era una variable independiente que predecía la carga de cáncer residual extensa con un valor de corte óptimo del 86% (p < 0,05).
ConclusionesDeterminamos el RR de SUVmax como un factor independiente para predecir la carga tumoral residual extensa. Creemos que el RR de SUVmax es suficiente para predecir la respuesta patológica en la práctica diaria. Además, las mediciones de MTV y TLG no contribuyen adicionalmente al SUVmax por sí solas y pueden causar una pérdida de trabajo innecesaria.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)