Patient safety is paramount in providing quality healthcare and constitutes a global concern for healthcare systems. Radioiodine treatment to patients with well-differentiated thyroid cancer is not without risks. The aim of this study is to identify, evaluate and mitigate the risks associated with this procedure.
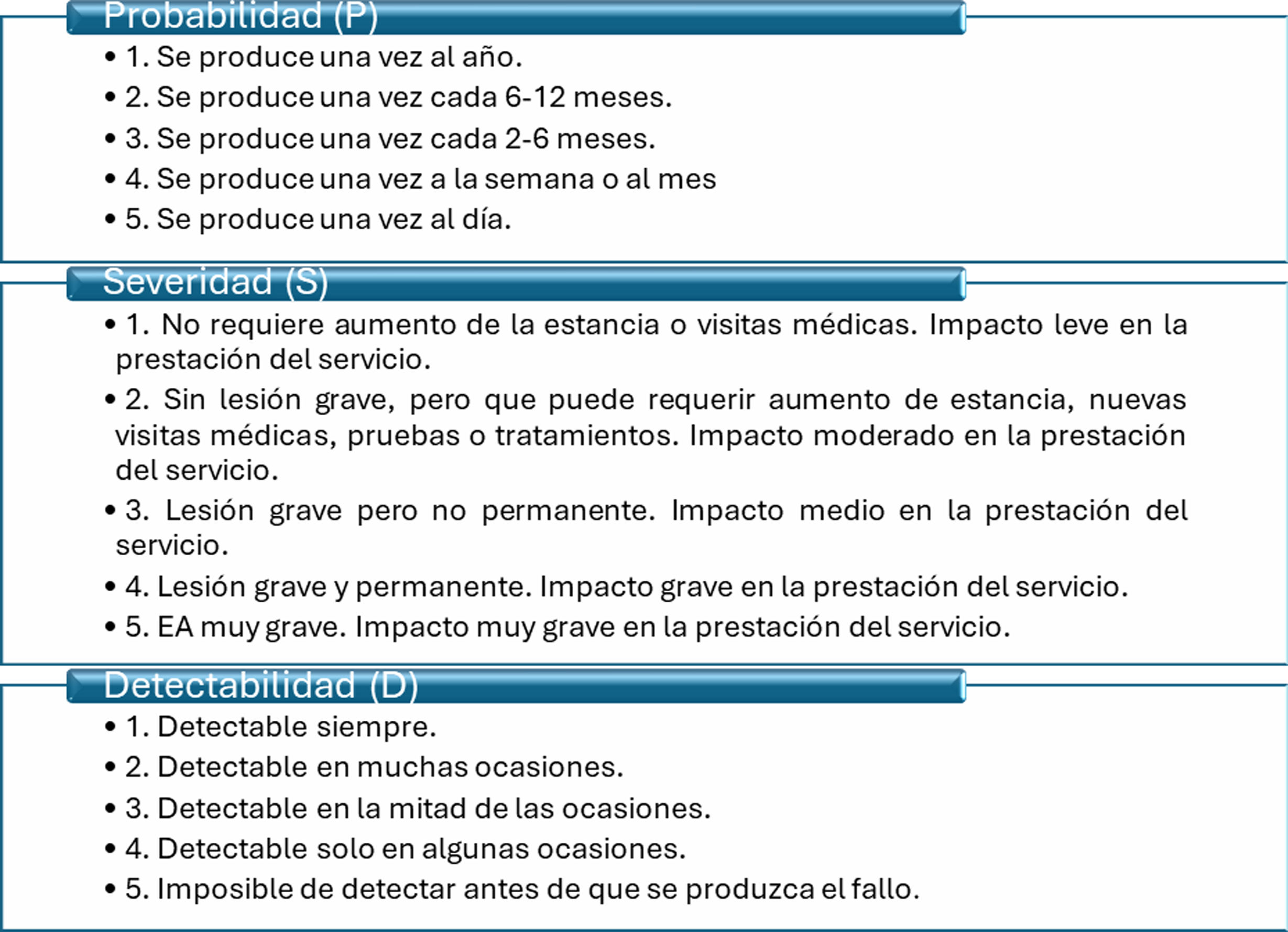
Materials and methodsA single-centre descriptive study was conducted in which risk management was carried out by establishing a risk map using FMEA methodology.
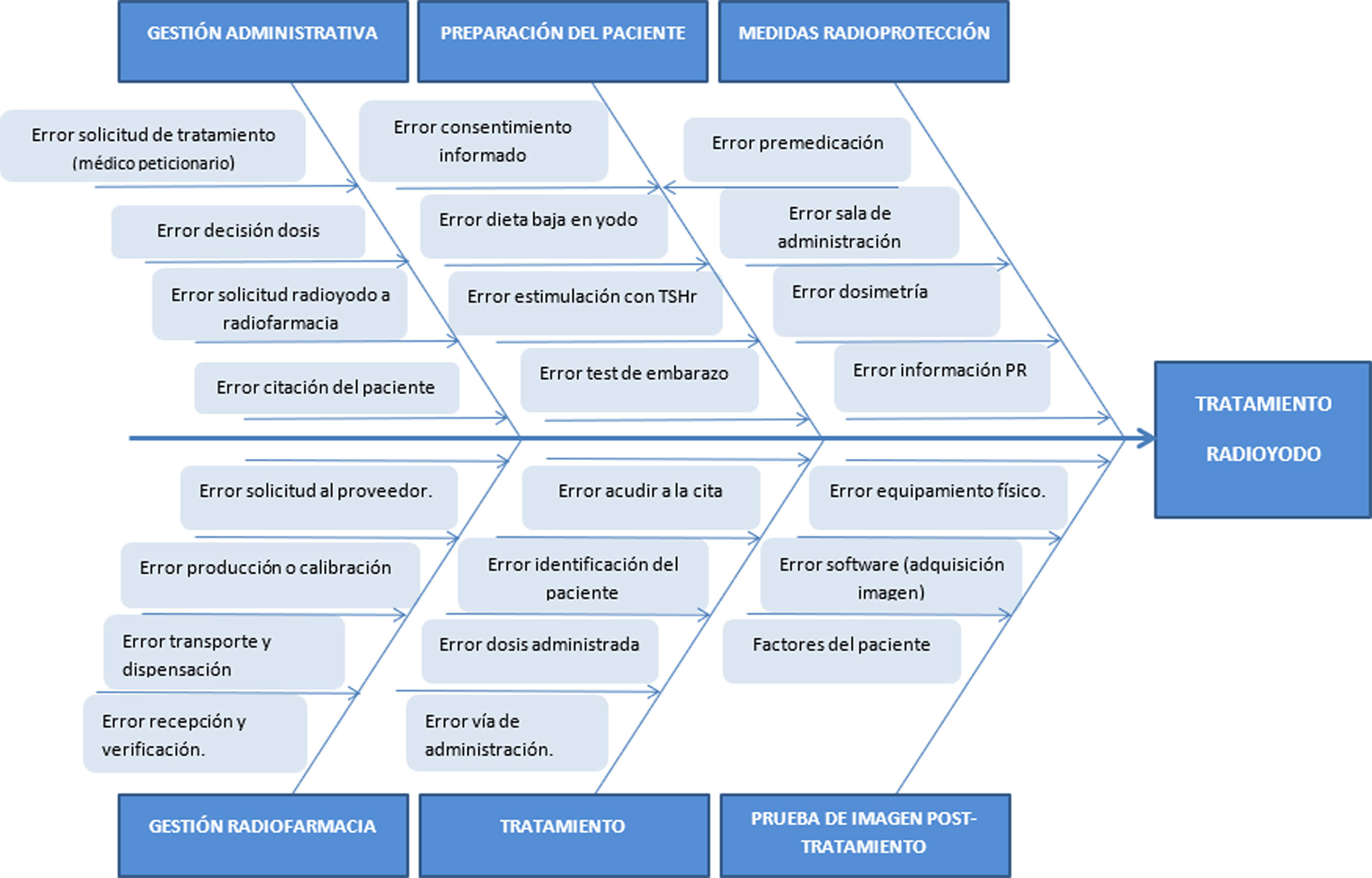
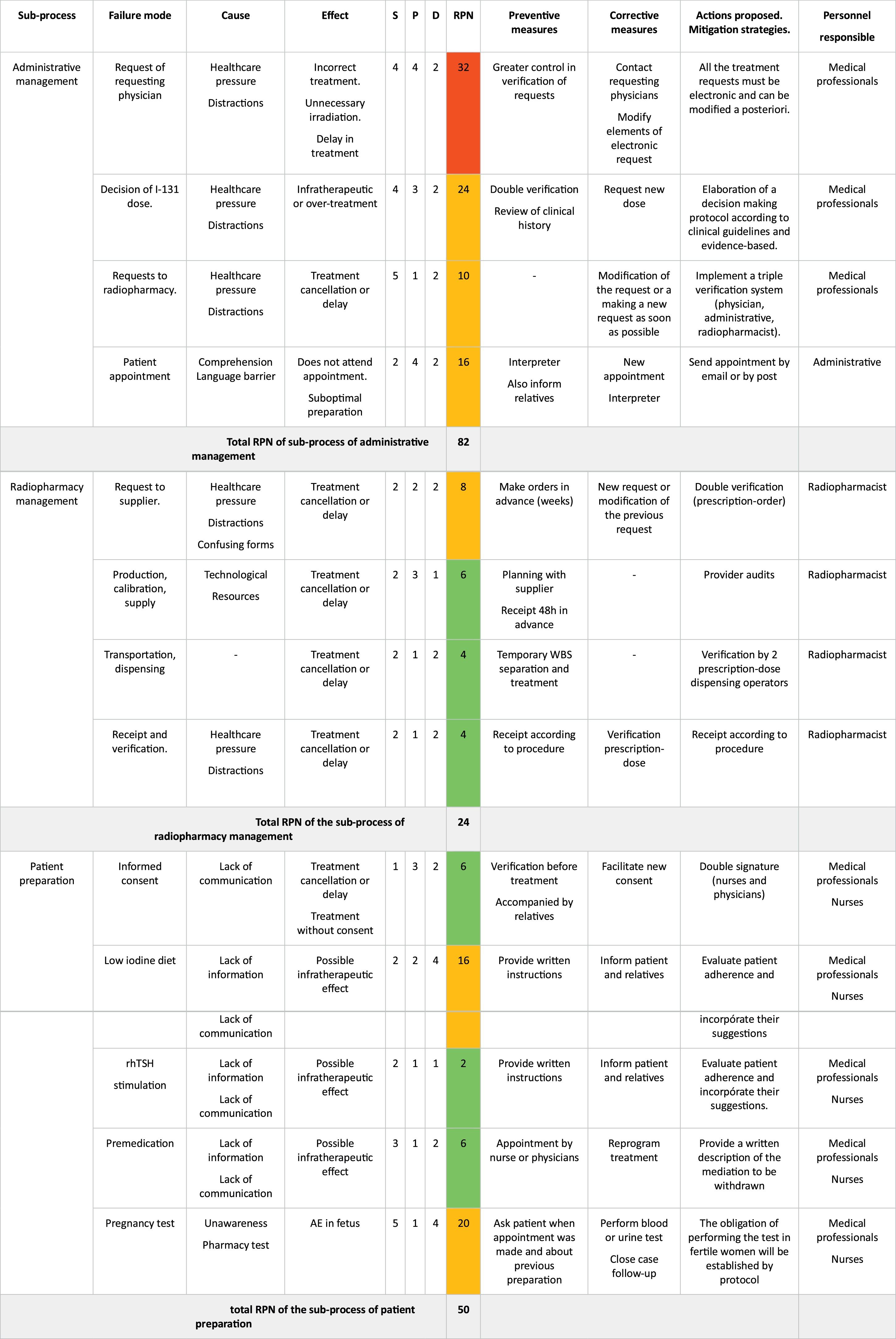
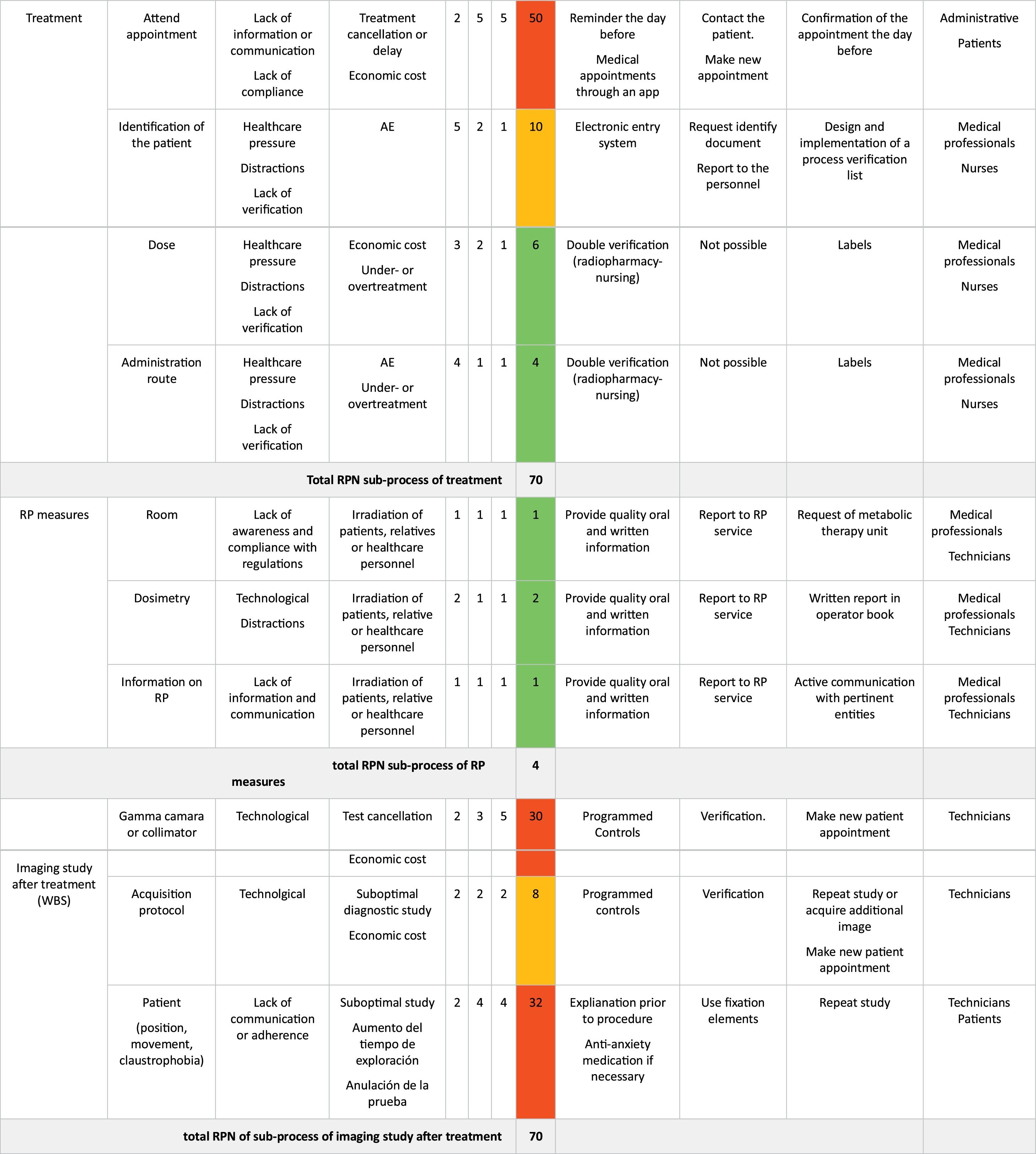
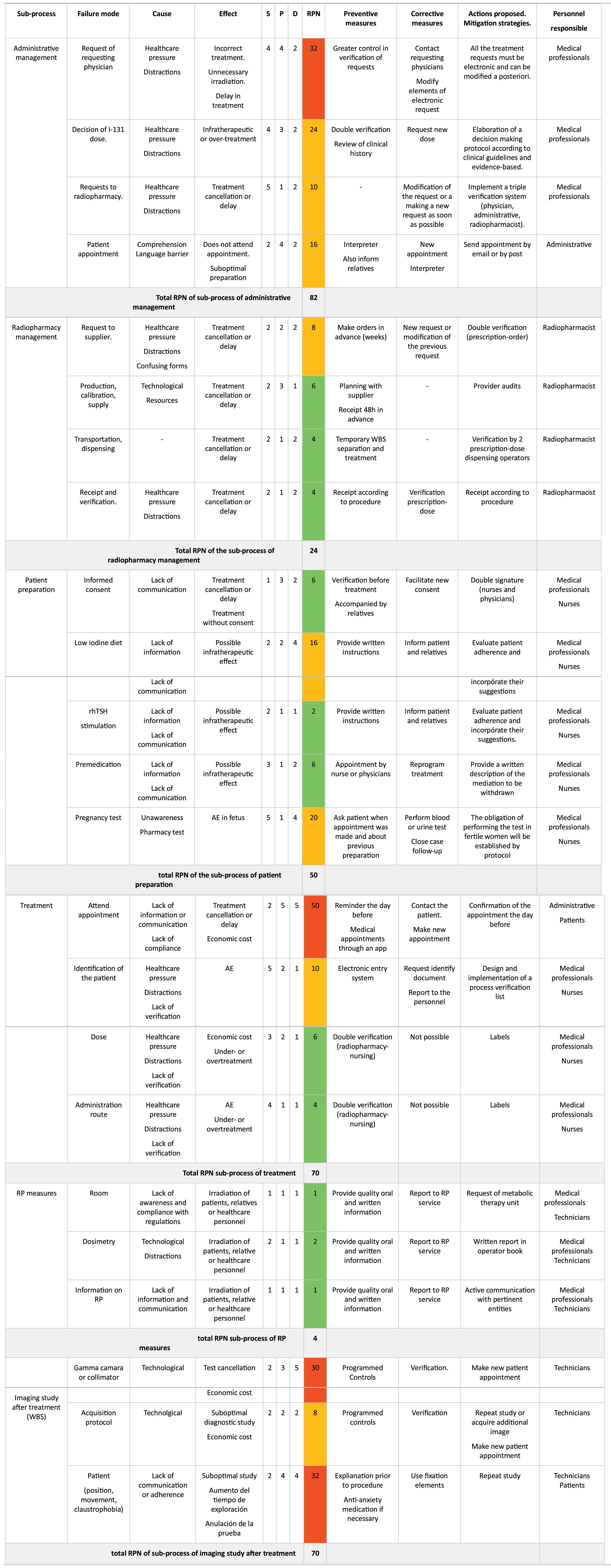
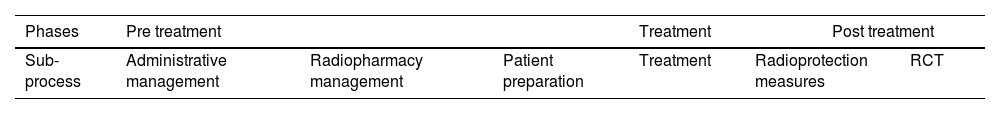
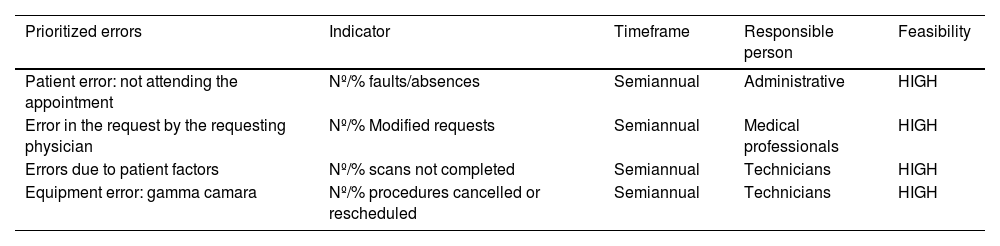
ResultsBased on the process map 6 sub-processes and 23 failure modes in the three phases of the treatment process were analysed. According to risk priority number (RPN), the sub-process with the highest risk was administrative management (RPN 82), followed by treatment per se and post-treatment imaging (both with RPN 70). An overall process RPN of 300 (156 pre-treatment, 74 treatment and 70 post-treatment) was obtained. Failures directly related to the patient pose a high risk. The implementation of verification systems, performing tasks earlier and providing quality medical information are the most relevant preventive measures to be implemented.
ConclusionsThe application of the FMEA methodology in the risk management for radioiodine treatment is a valuable tool for improving the quality and safety of this process. The risk map has been able to identify failures at different stages, assess their causes and effects, prioritise the risks identified and implement preventive and corrective measures that can be monitored, ensuring the effectiveness of the actions taken.
La seguridad del paciente es fundamental en una atención médica de calidad y constituye una preocupación global para los sistemas de salud. El tratamiento con radioyodo de pacientes con cáncer diferenciado de tiroides no está exento de riesgos. El objetivo de este estudio es conocer, evaluar y mitigar los riesgos asociados con este procedimiento.
Materiales y métodosEstudio unicéntrico descriptivo en el que se realiza una gestión de riesgo estableciendo un mapa de riesgo mediante la metodología AMFE.
ResultadosA partir del mapa de proceso, se analizaron 6 subprocesos y 23 modos de fallo en las tres fases del proceso de tratamiento. Acorde al número prioritario de riesgo (NPR), el subproceso con mayor riesgo fue la gestión administrativa (NPR 82), seguidos del tratamiento per se y de la prueba de imagen post-tratamiento (ambos con NPR 70). Se obtuvo un NPR global del proceso de 300 (156 pre-tratamiento, 74 tratamiento y 70 post-tratamiento). Los fallos relacionados directamente con el paciente suponen un riesgo alto. La implantación de sistemas de verificación, realizar las tareas con mayor antelación y aportar información médica de calidad constituyen las medidas preventivas más relevantes que debemos implementar.
ConclusionesLa aplicación de la metodología AMFE en la gestión de riesgos del tratamiento con radioyodo es una herramienta valiosa para mejorar la calidad y seguridad de este proceso. El mapa de riesgo ha logrado identificar fallos en sus diferentes etapas, evaluar sus causas y efectos, priorizar los riesgos identificados e implementar medidas preventivas y correctoras que podrán monitorizarse, asegurando la efectividad de las acciones tomadas.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)