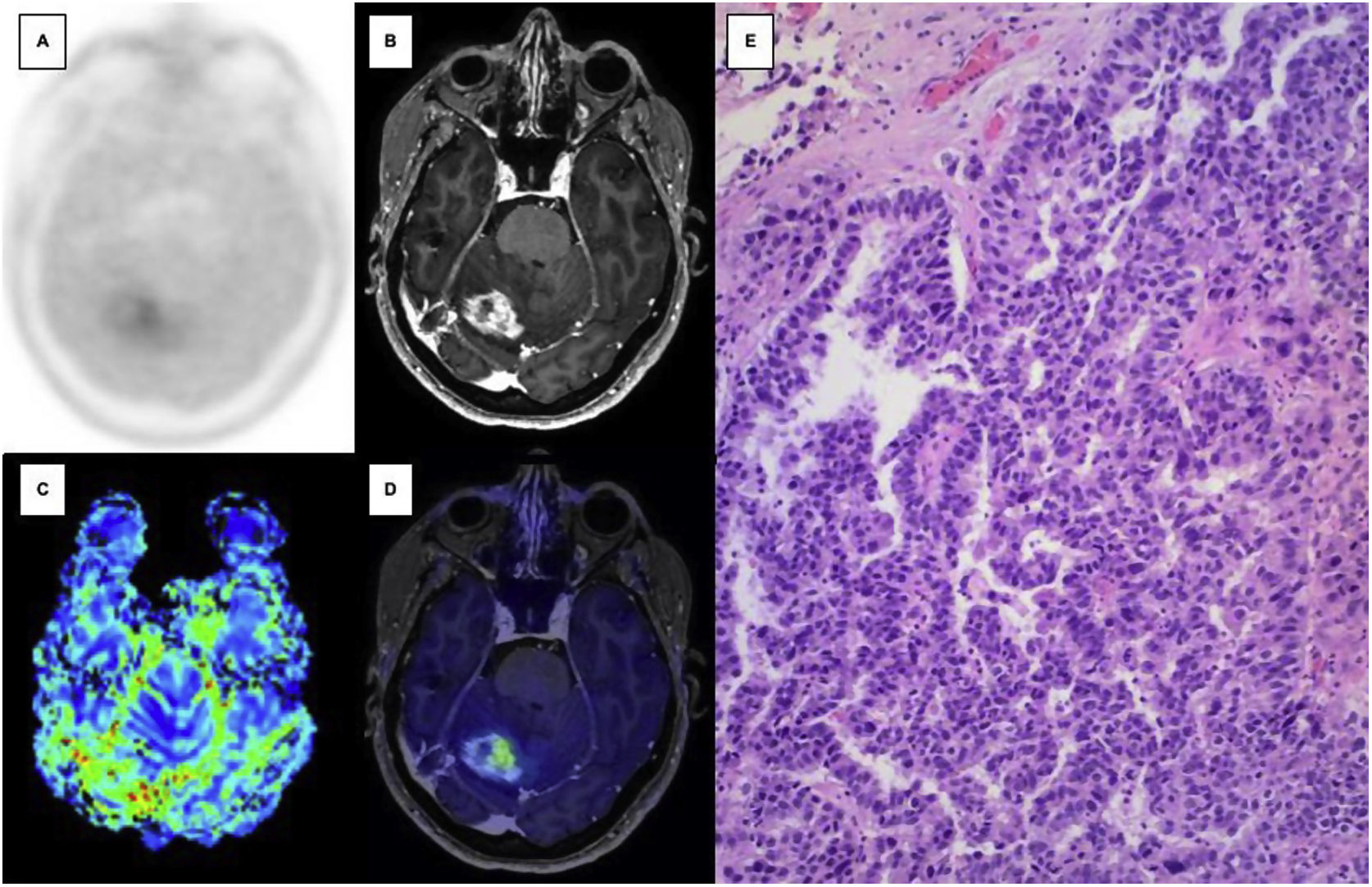
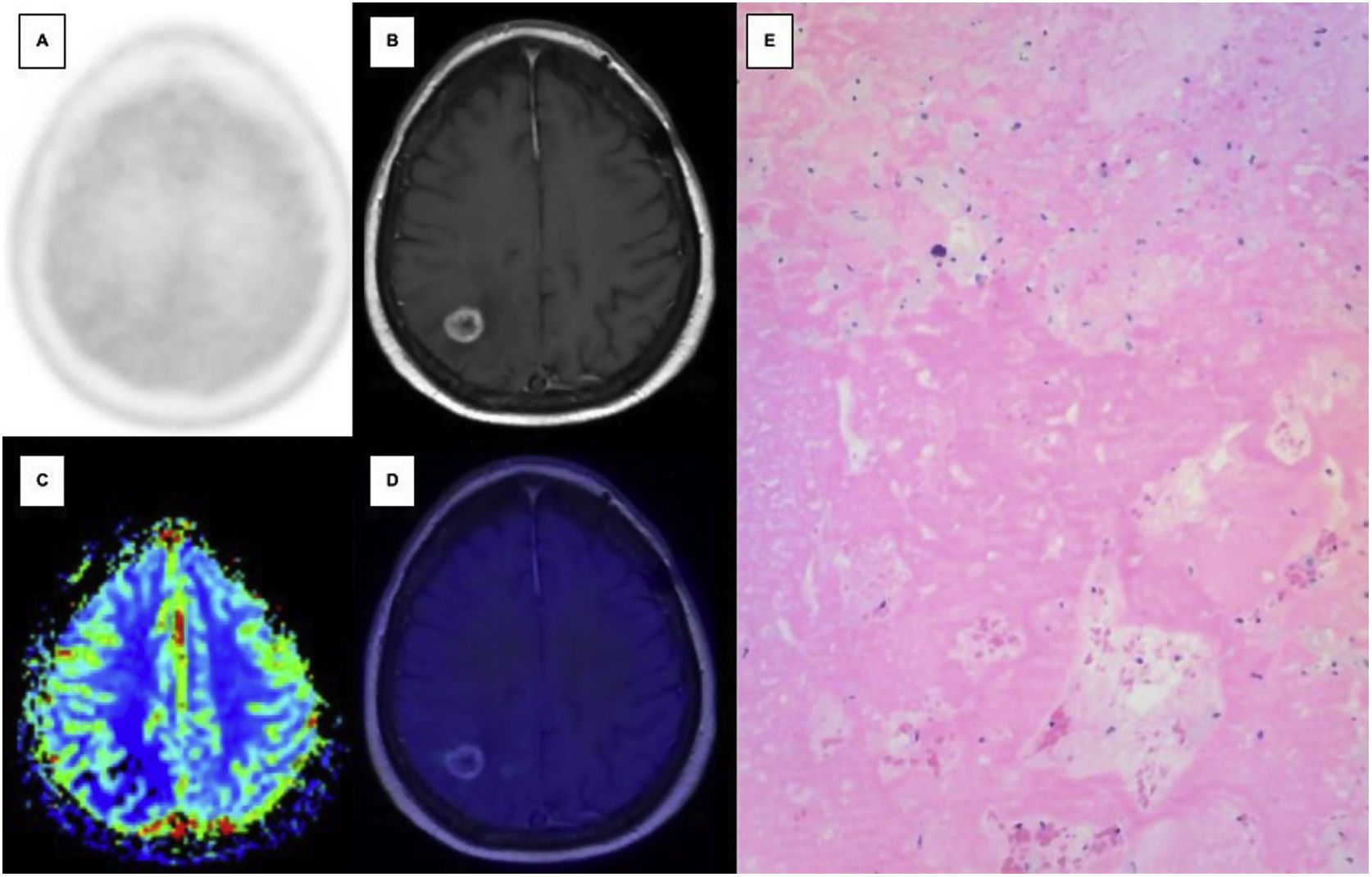
Amino acid PET is a tool recommended by the main neuroimaging societies in the differential diagnosis between radionecrosis (RNC) and umour recurrence (TR) in brain tumours, but its use in our country is still limited. The aim of this work is to present our experience with 6-[18F]FDOPA PET/CT (FDOPA) in brain tumours (primary and M1), comparing these results with other published results.
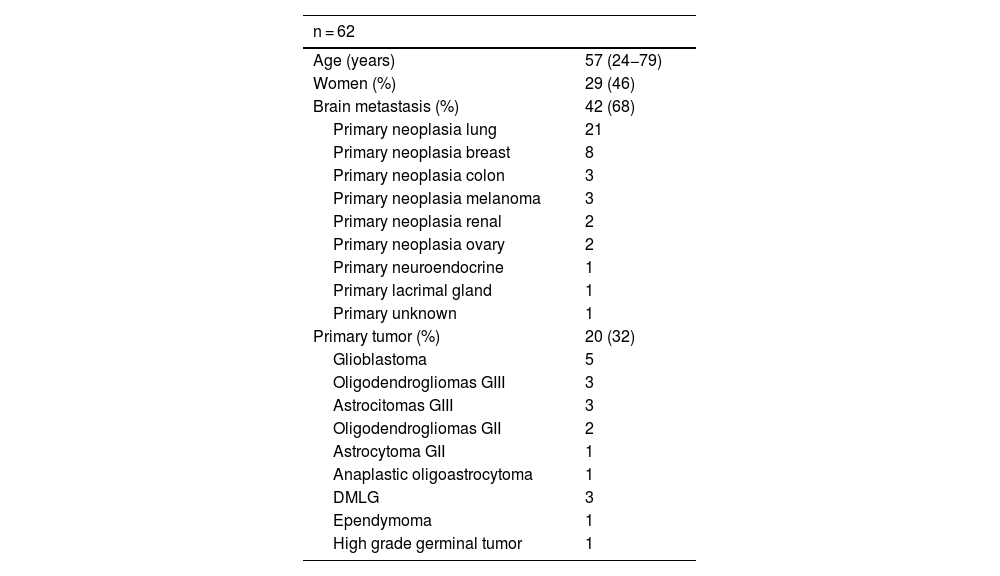
Material and methodsRetrospective study of 62 patients with suspected tumour recurrence (TR): 42 brain metastases (M1) and 20 primary, who underwent FDOPA. Images were analysed visually and semi-quantitatively, obtaining SUVmax and SUVmaxlesion/SUVmaxstriatum (L/S) and SUVmaxlesion/SUVmaxcortex (L/C) ratios. The diagnostic validity of PET was analysed and the best performing cut-off points were calculated. PET results were compared with clinical-radiological follow-up and/or histopathology.
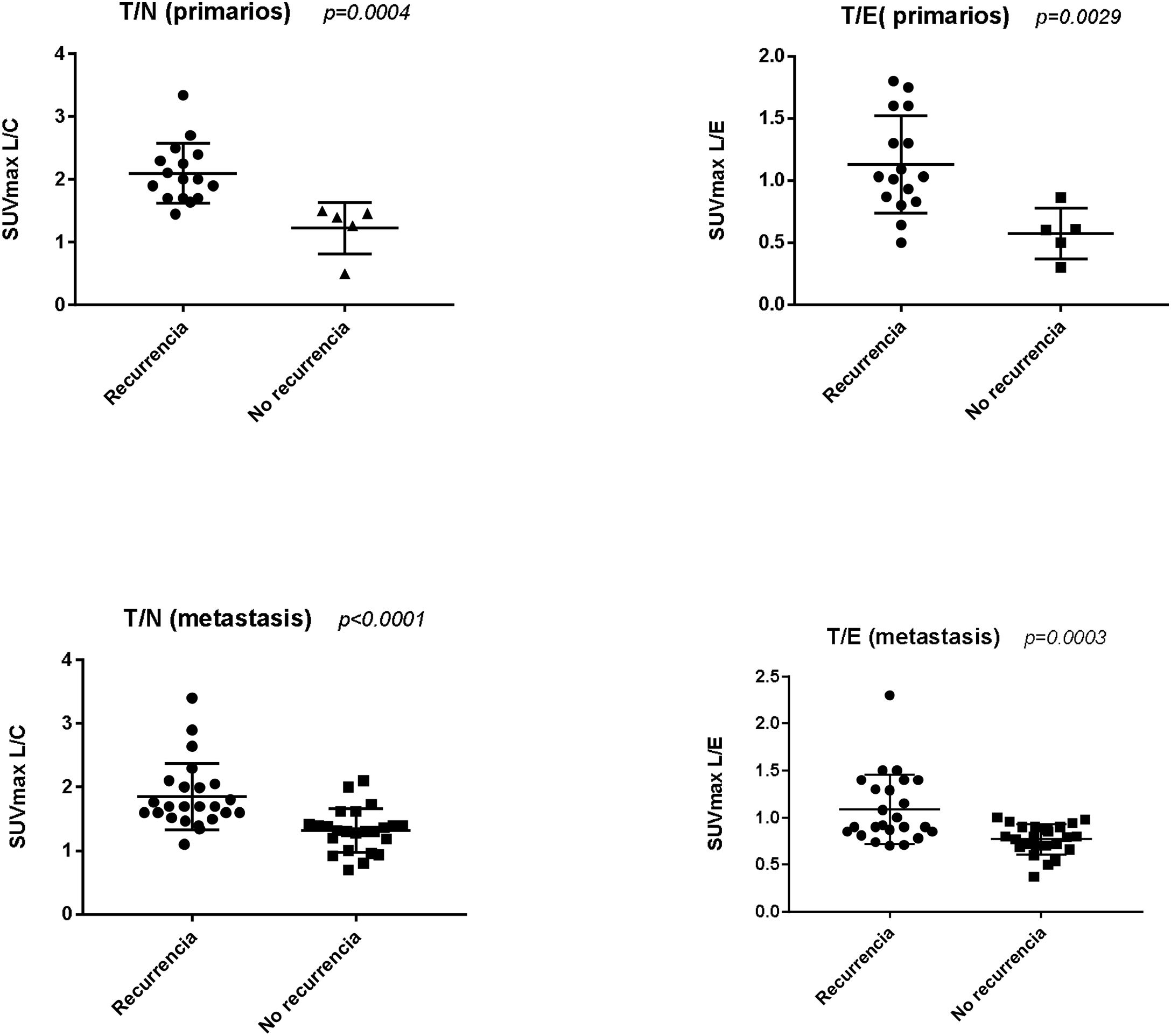
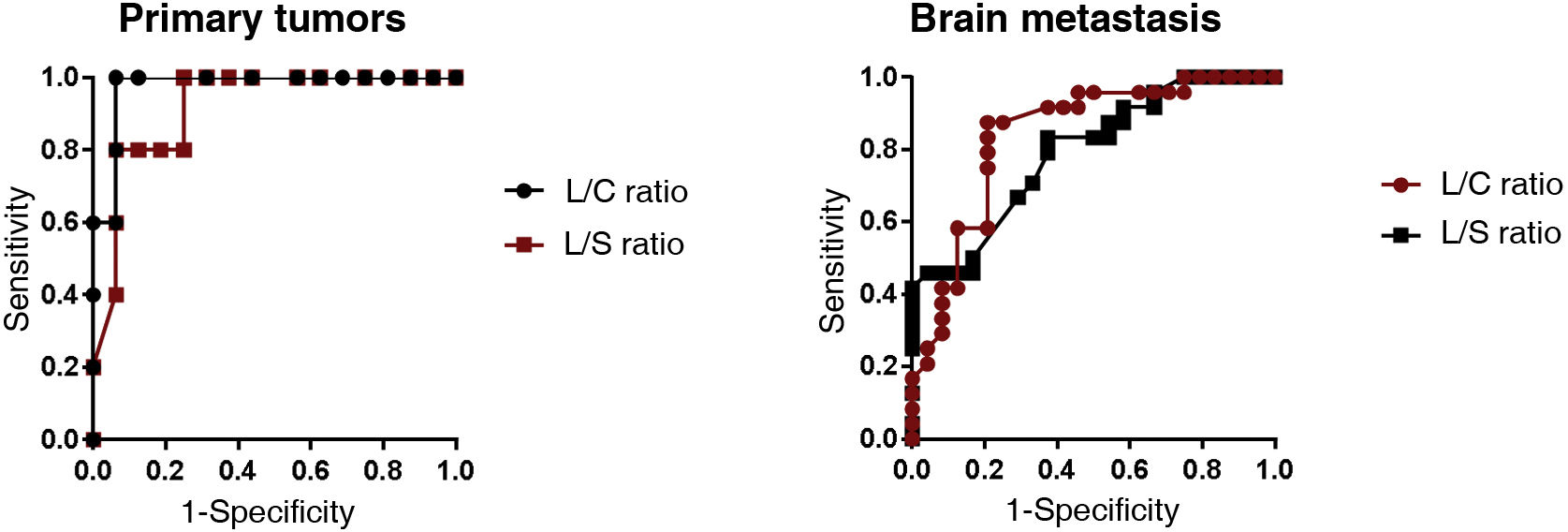
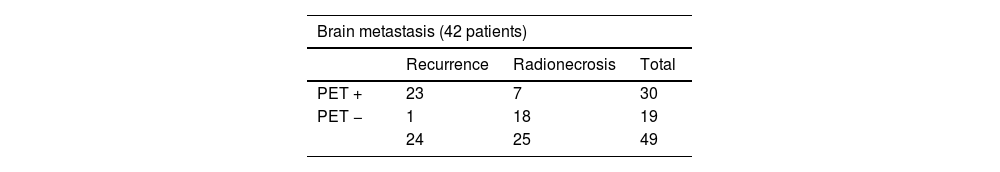
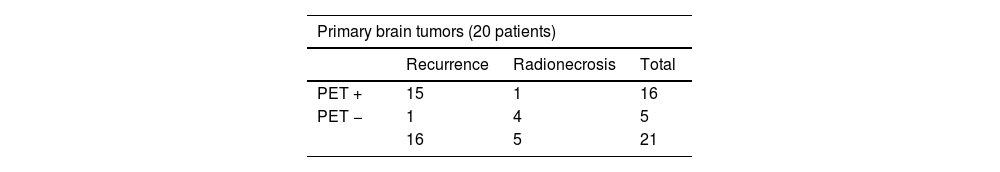
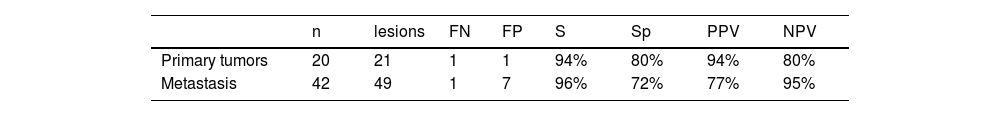
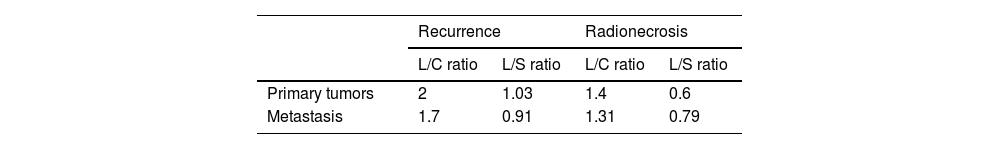
ResultsTR was identified in 49% of M1 and 76% of brain primaries. The best performing FDOPA interpretation was visual and semi-quantitative, with a sensitivity and specificity in primaries of 94% and 80% and in M1s of 96% and 72% respectively. The cut-off points with the best diagnostic performance were L/C1.44 in M1 and L/C1.55 in primaries. There are discrepant results with other published results.
ConclusionFDOPA PET/CT is a useful tool in the differential diagnosis between recurrence and RNC in brain tumours. It is needed a standardization to contribute to homogenise FDOPA results a inter-centre level.
El PET con aminoácidos es una herramienta recomendada por las principales sociedades de neuroimagen, en el diagnóstico diferencial entre radionecrosis (RNC) y recurrencial tumoral (RT) en tumores cerebrales, sin embargo su uso en nuestro pais aún es limitado. El objetivo de este trabajo es presentar nuestra experiencia con 6-[18F]FDOPA PET/TC (FDOPA) en tumores cerebrales (primarios y M1), comparando estos resultados con otros publicados.
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de 62 pacientes con sospecha de recurrencia tumoral (RT): 42 metástasis cerebrales (M1) y 20 primarios, a los que se les realizó una FDOPA. Las imágenes fueron analizadas visual y semicuantitativamente, obteniendo el SUVmax y los ratios SUVmaxlesión/SUVmaxestriado (L/E) y SUVmaxlesión/SUVmaxcortex (L/C). Se analizó la validez diagnóstica del PET y se calcularon los puntos de corte con mayor rendimiento. Los resultados del PET se compararon con la evolución clínico-radiológica y/o con la histopatología.
ResultadosSe identificó RT en el 49% de las M1 y en el 76% de los primarios cerebrales. La interpretación de la FDOPA con mejores resultados fue la conjunta; visual y semicuantitativa, con una sensibilidad y especificidad en los primarios del 94 y 80% y en las M1 del 96 y 72% respectivamente. Los puntos de corte con mejor rendimiento diagnóstico fueron L/C1.44 en M1 y L/C1.55 en primarios. Existen resultados discrepantes con otros publicados.
ConclusiónLa FDOPA PET/TC es una herramienta útil en el diagnóstico diferencial entre recurrencia y RNC en tumores cerebrales. Es necesario una estandarización que contribuya a homogeneizar los resultados de la FDOPA a nivel intercentro.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)