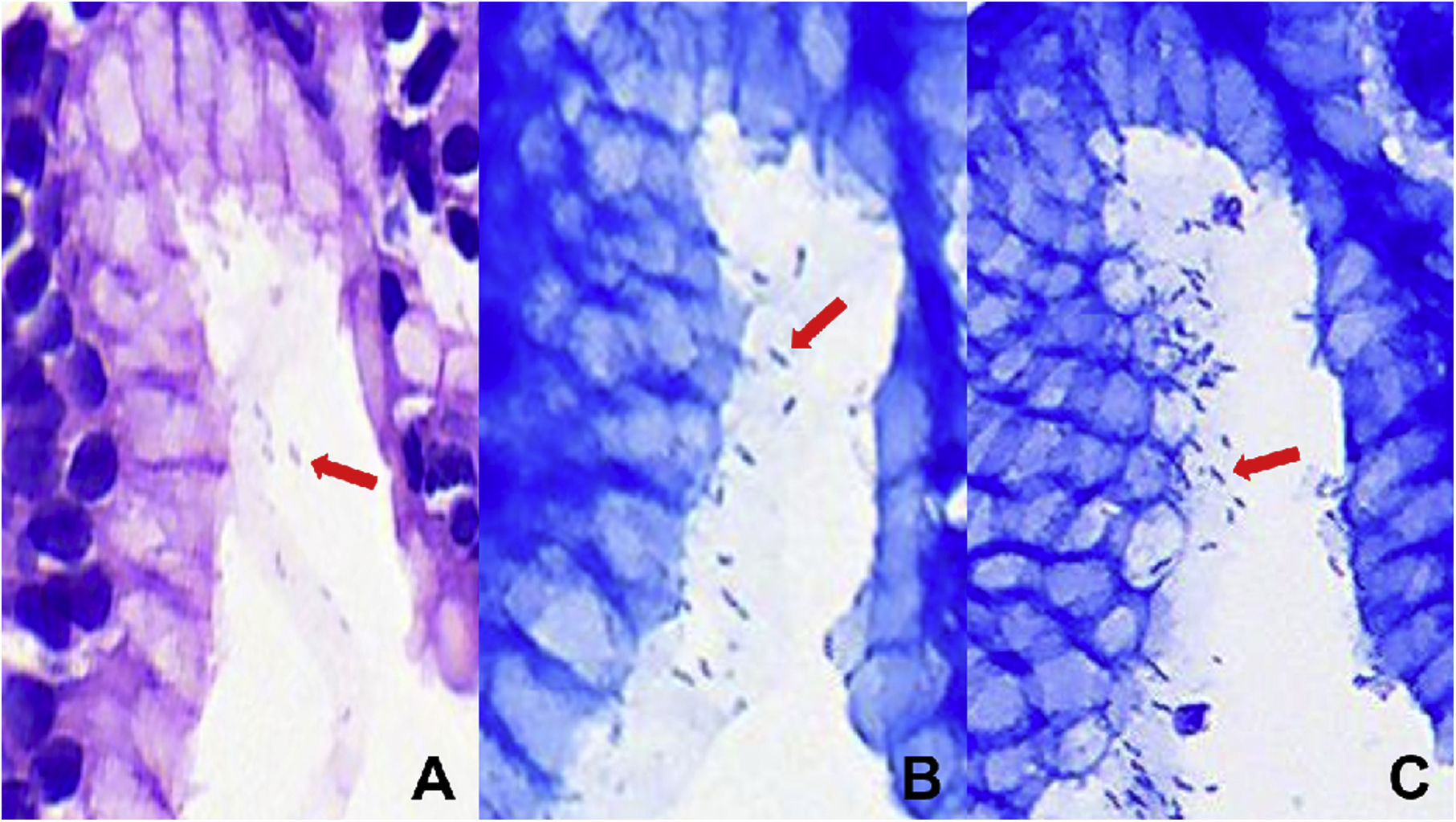
The histopathological identification of Helicobacter pylori using the routine method (haematoxylin–eosin) is not only very difficult but also has low sensitivity. Giemsa staining is often used in addition, but different protocols do not produce homogeneous results. Furthermore, the Gold Standard recommended by the European Helicobacter Pylori Study Group has been applied in very few studies, thus resulting in uncertain outcomes. Therefore, a new staining method is required to overcome these limitations. The aim of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic capacity and inter-observer agreement of “Gissell's stain”.
Material and MethodsA cross-sectional study evaluated 99 gastric paraffin blocks from a private laboratory. Three sections were prepared from each block, and haematoxylin–eosin (HE), Giemsa and “Gissell's stain” methods were applied. The kappa statistics, sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values were calculated.
Results“Gissell's stain” obtained the highest inter-observer agreement (kappa=0.87) compared to the other two methods (HE, kappa=0.51; Giemsa, kappa=0.83). It also obtained the best sensitivity and negative predictive value (97.1% and 98.3%, respectively) compared with the other two methods (HE: 68.6% and 85.1%, respectively; Giemsa: 88.6% and 93.9%, respectively).
ConclusionsGiven its unique characteristics (fast, cheap, accessible, and easy to use), in addition to its statistical reliability, “Gissell's stain” has great potential for routine use in the identification of H. pylori.
La identificación histopatológica del Helicobacter pylori, utilizando hematoxilina-eosina (HE) como método de rutina es frecuentemente dificultosa y con una baja sensibilidad. El método de Giemsa es usado a veces de modo adicional, pero diferentes protocolos no producen resultados homogéneos. Además, el método recomendado por el grupo europeo de estudio de Helicobacter pylori ha sido empleado en pocos estudios, resultando en datos discrepantes. Por tanto, un método alternativo eficaz podría superar estas limitaciones. El presente estudio valora la agudeza diagnostica y el acuerdo interobservador en la aplicación del método de Gissell.
Material y métodosUn estudio interobservador de 99 biopsias gástricas provenientes de la practica privada. De cada caso se prepararon tres muestras teñidas correspondientemente con: HE, Giemsa y Gissell. Se procedió mediante estadística kappa a valorar la sensibilidad, especificidad y valores predictivos.
ResultadosLa técnica de Gissell obtuvo el mayor acuerdo interobservador con un kappa con 0,87, comparado con la HE (kappa = 0,51) y Giemsa (kappa = 0,83). Además, obtuvo la mayor sensibilidad y valor predictivo negativo comparado con los otros dos métodos.
ConclusionesDadas sus características prácticas, tales como rapidez, economía, accesibilidad y facilidad de uso, además de su fiabilidad estadística, el método de Gissell posee un gran potencial para la identificación rutinaria del Helicobacter pylori.