Interplay of Factor XIIIa (FXIIIa), a transglutaminase, responsible for cross-linking of matrix proteins, Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), a gelatinase, and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), an angiogenic inducer, were studied in relation to fibrogenesis and disease progression in oral submucous fibrosis (OSMF).
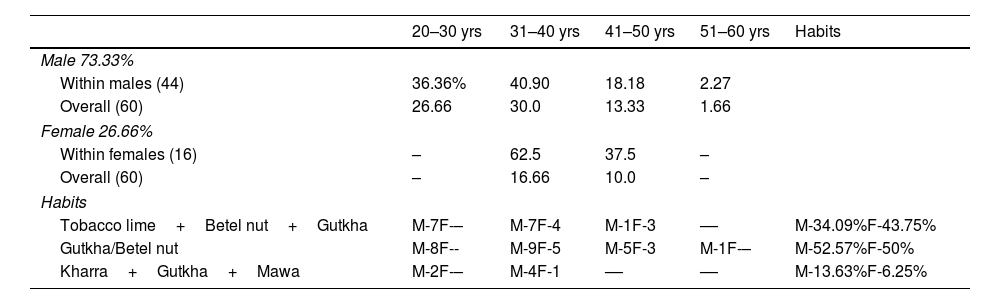
Material and methodsImmunohistochemical expression of markers was studied in 60 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue blocks of OSMF and 20 normal oral mucosal tissues. FXIIIa was studied quantitatively while MMP-9 and VEGF were assessed semi-quantitatively. Expression was compared with histopathological grades of OSMF.
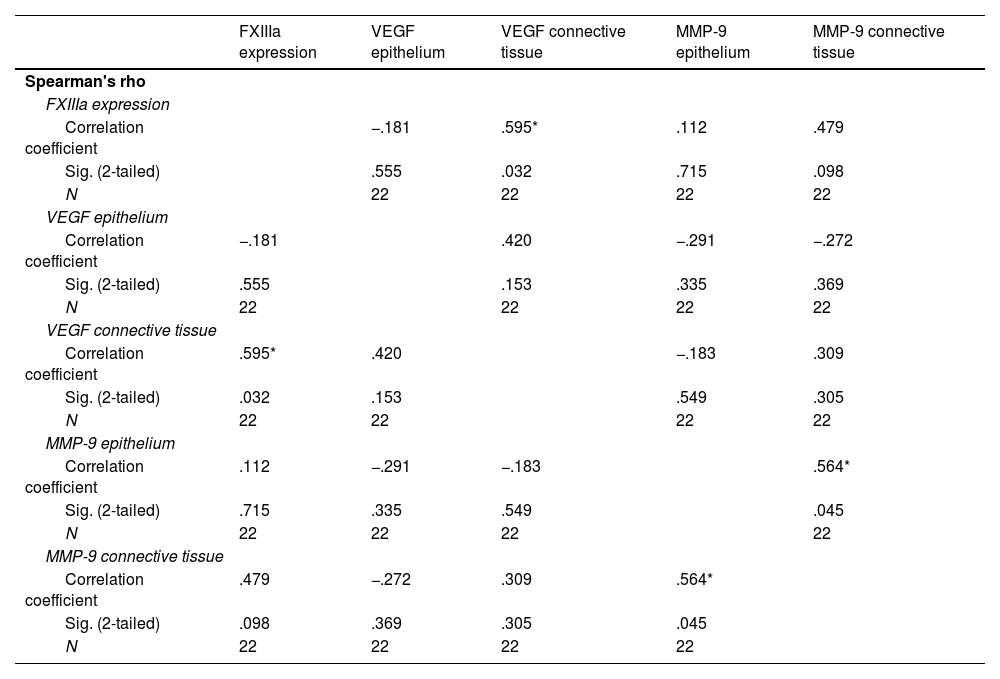
ResultsFXIIIa expression significantly increased in OSMF (p-value 0.000). However, expression decreased and cells became quiescent with increasing grades (p-value 0.000). MMP-9 (p-value epithelium 0.011, p-value connective tissue 0.000) and VEGF expression (p-value epithelium 0.000, connective tissue 0.000) increased in OSMF. A negative correlation between FXIIIa and MMP-9 (−0.653) in early grade (p-value of 0.021) and a positive correlation between FXIIIa and VEGF (0.595) (p-value of 0.032) was found in the moderate grade OSMF. Regression analysis showed a significant association (p<0.01) of FXIIIa in OSMF and with increasing grades of OSMF.
ConclusionFXIIIa may play a crucial role in initiation of fibrosis in OSMF. MMP-9 may have a diverse role to play in OSMF as a regulator of fibrosis. VEGF may show an angio-fibrotic switch and contribute to fibrosis in OSMF. These cytokines may show altered function and can contribute to fibrosis and chronicity of disease due to changes in the microenvironment. Tissue stiffness in OSMF itself creates an environment that enhances the chronicity of the disease.
Se estudió la interacción del factor XIIIa (FXIIIa), una transglutaminasa responsable de los entrecruzamientos de las proteínas de la matriz, la metaloproteinasa de matriz-9 (MMP-9), una gelatinasa y el factor de crecimiento endotelial vascular (VEGF), un inductor angiogénico, en relación con la fibrogénesis y la progresión de la enfermedad en la fibrosis submucosa oral (OSMF).
Material y métodosSe estudió la expresión inmunohistoquímica de marcadores en 60 bloques de tejido de OSMF fijados con formalina e incluidos en parafina y 20 tejidos de mucosa oral normales. FXIIIa se estudió cuantitativamente mientras que MMP-9 y VEGF se evaluaron semicuantitativamente. La expresión se comparó con los grados histopatológicos de OSMF.
ResultadosLa expresión de FXIIIa aumentó significativamente en OSMF (valor de p 0,000). Sin embargo, la expresión disminuyó y las células se volvieron inactivas a medida que aumentaban los grados (valor de p 0,000). MMP-9 (valor de p epitelio 0,011, tejido conectivo valor de p 0,000) y expresión de VEGF (valor de p epitelio 0,000, tejido conectivo 0,000) aumentaron en OSMF. Se encontró una correlación negativa entre FXIIIa y MMP-9 (-0,653) en grado temprano (valor de p de 0,021) y una correlación positiva entre FXIIIa y VEGF (0,595) (valor de p de 0,032) en OSMF de grado moderado. El análisis de regresión mostró una asociación significativa (p<0,01) de FXIIIa en OSMF y con grados crecientes de OSMF.
ConclusiónFXIIIa puede desempeñar un papel crucial en el inicio de la fibrosis en OSMF. MMP-9 puede desempeñar un papel diverso en OSMF como regulador de la fibrosis. VEGF puede mostrar un interruptor angiofibrótico y contribuir a la fibrosis en OSMF. Estas citocinas pueden mostrar una función alterada y pueden contribuir a la fibrosis y la cronicidad de la enfermedad debido a cambios en el microambiente. La rigidez del tejido en el propio OSMF crea un entorno que mejora la cronicidad de la enfermedad.