el empleo de drogas psicoactivas para facilitar una agresión sexual ha adquirido gran relevancia en estos últimos años. El objetivo del presente trabajo es ayudar a visibilizar este tipo de situaciones, estableciendo los criterios diagnósticos y así poder determinar la incidencia real de este tipo de delitos.
Material y métodosse ha realizado un estudio descriptivo retrospectivo de las víctimas de violencia sexual mediante el empleo de sustancias psicoactivas, atendidas por los médicos forenses del Instituto de Medicina Legal y Ciencias Forenses de Alicante, en los años 2016 a 2020.
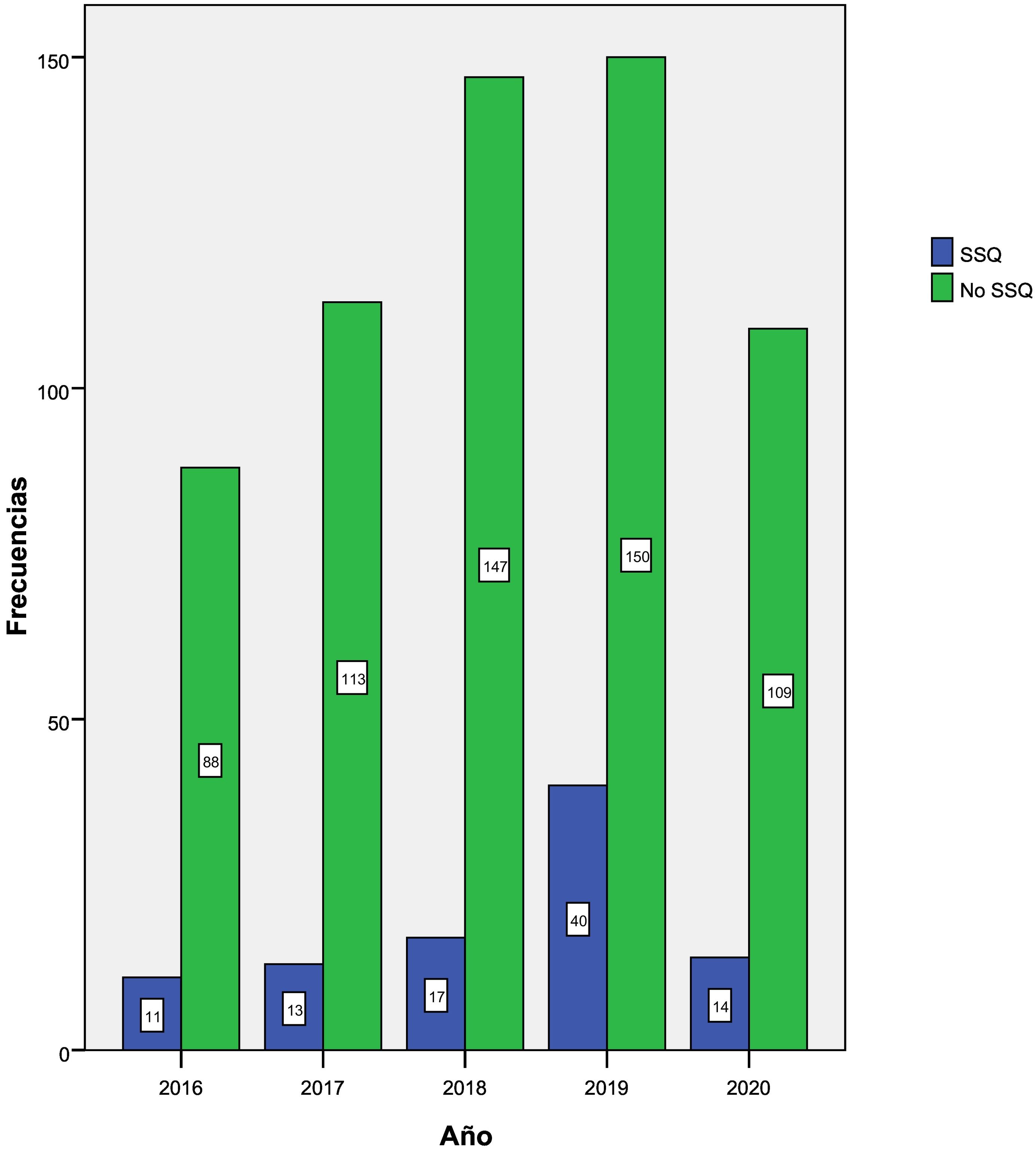
Resultadosde los 702 casos estudiados de víctimas de violencia sexual, en 95 casos (13,5%) se cumplían los criterios de sospecha de sumisión química o delitos facilitados por sustancias psicoactivas.
El perfil de la víctima es mujer (94,7%), de edad media 24,7 años. En la mayoría de los casos la violencia sexual fue cometida por un único agresor (80,6%), varón, conocido o recién conocido por la víctima y generalmente los hechos ocurrieron en fin de semana (54,8%).
La víctima había consumido voluntariamente alcohol solo, o en combinación con drogas y/o medicamentos, inmediatamente antes de los hechos en la mayoría de los casos (88,5%). La situación de vulnerabilidad que genera este consumo puede ser aprovechado por el agresor para agredirla sexualmente (sumisión química oportunista). Los análisis químico-toxicológicos de las muestras analizadas en la sangre y la orina fueron positivos en un 85,3% de los casos. En casi la mitad de los casos fueron positivos a más de una sustancia (46,3%). Las más frecuentes encontradas fueron: alcohol (54,7%), cannabinoides (37,9%), benzodiacepinas (22,1%), cocaína (15,8%) y éxtasis (8,4%).
En la mitad de los casos (50,5%), se obtuvieron hallazgos toxicológicos positivos inesperados de sustancias psicoactivas, que la víctima no admitía haber consumido voluntariamente.
The use of psychoactive drugs to facilitate sexual assault has acquired great relevance in recent years. The objective of this work is to help make this type of situation visible, establishing diagnostic criteria and thus being able to determine the real incidence of this type of crime.
Materials and methodsIn order to determine the frequency and characteristics of victims of sexual assault with suspected chemical submission (SSQ), a retrospective descriptive study of sexual assaults facilitated by psychoactive substances has been carried out at the Institute of Legal Medicine and Forensic Sciences of Alicante in the years 2016-2020.
ResultsAmong 702 cases studied, 95 (13.5%) met the criteria for inclusion in the probable DFSA (drug-facilitated sexual assault) group.
The profile of the victim was a woman (95.4%) around 24 years old. In most cases, the sexual violence was committed by a single male aggressor, recently met or known by the victim, and generally these events happen on weekends. The victim had voluntarily consumed alcohol, drugs or psychotropic drugs immediately before the events in most cases (88,5%). This vulnerable state of the victim was used by the aggressor to sexually assault her (opportunistic DFSA). The toxicological analyses performed on blood and/or urine were positive in 85.3%. In almost half of them (46.3%), there was more than one substance found in the toxicological analyses. The most frequent substance found were: alcohol (54.7%), cannabinoids (37,9%), benzodiazepines (22.1%), cocaine (15.8%) and ecstasy or MDMA (8.4%).
In half of the cases (50.5%), unexpected positive toxicological findings were obtained for psychoactive substances that the victim did not admit to having consumed voluntarily.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora