Rapid vaccination is the only way to fight against COVID-19.Vaccine hesitancy is the major barrier against this strategy. The main objective of this cross-sectional study was to analyze COVID-19 vaccine acceptance in the general population of West Bengal (India), as well as to investigate the factors that were independently associated with people's desire to receive the vaccine.
MethodsAn online questionnaire was distributed by email, Whatsapp, and other social media platforms, and the responses were analyzed using the SPSS (Version 20) software.
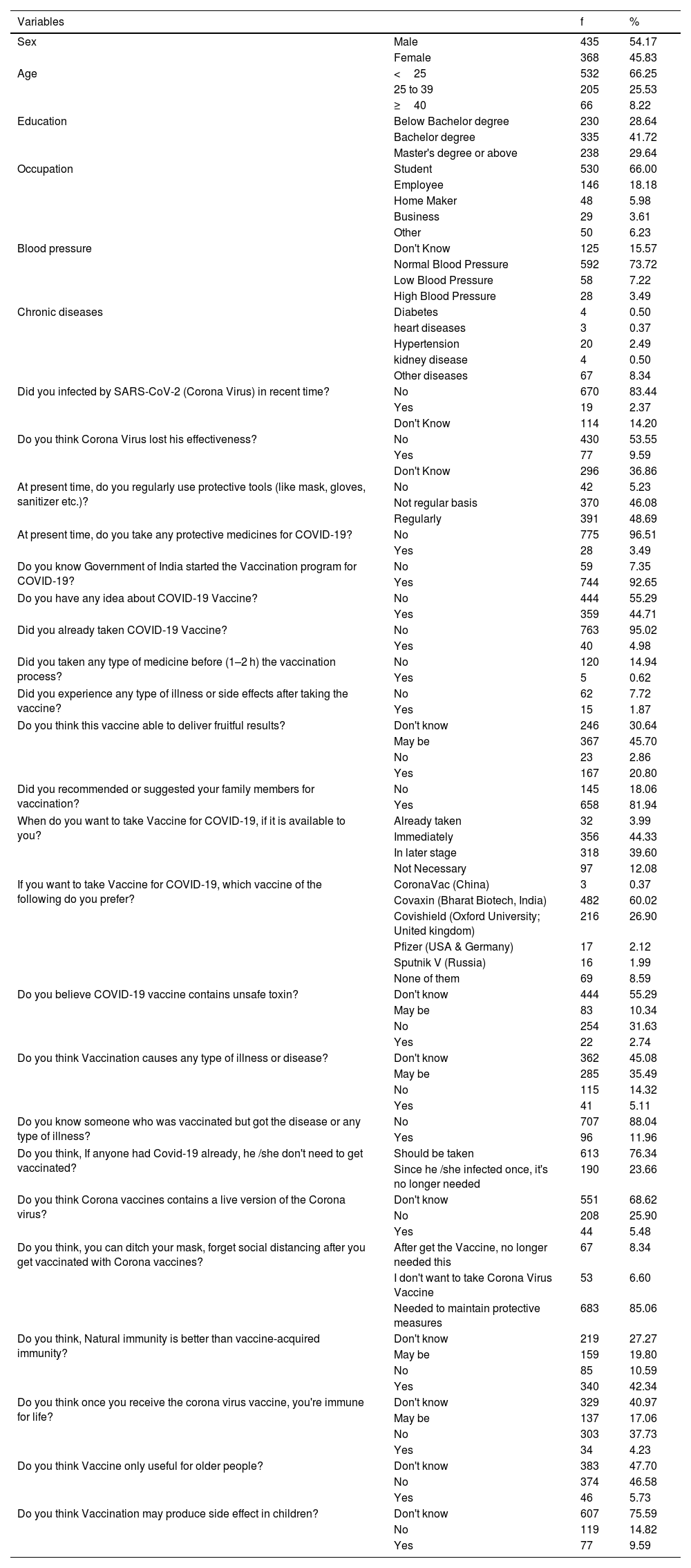
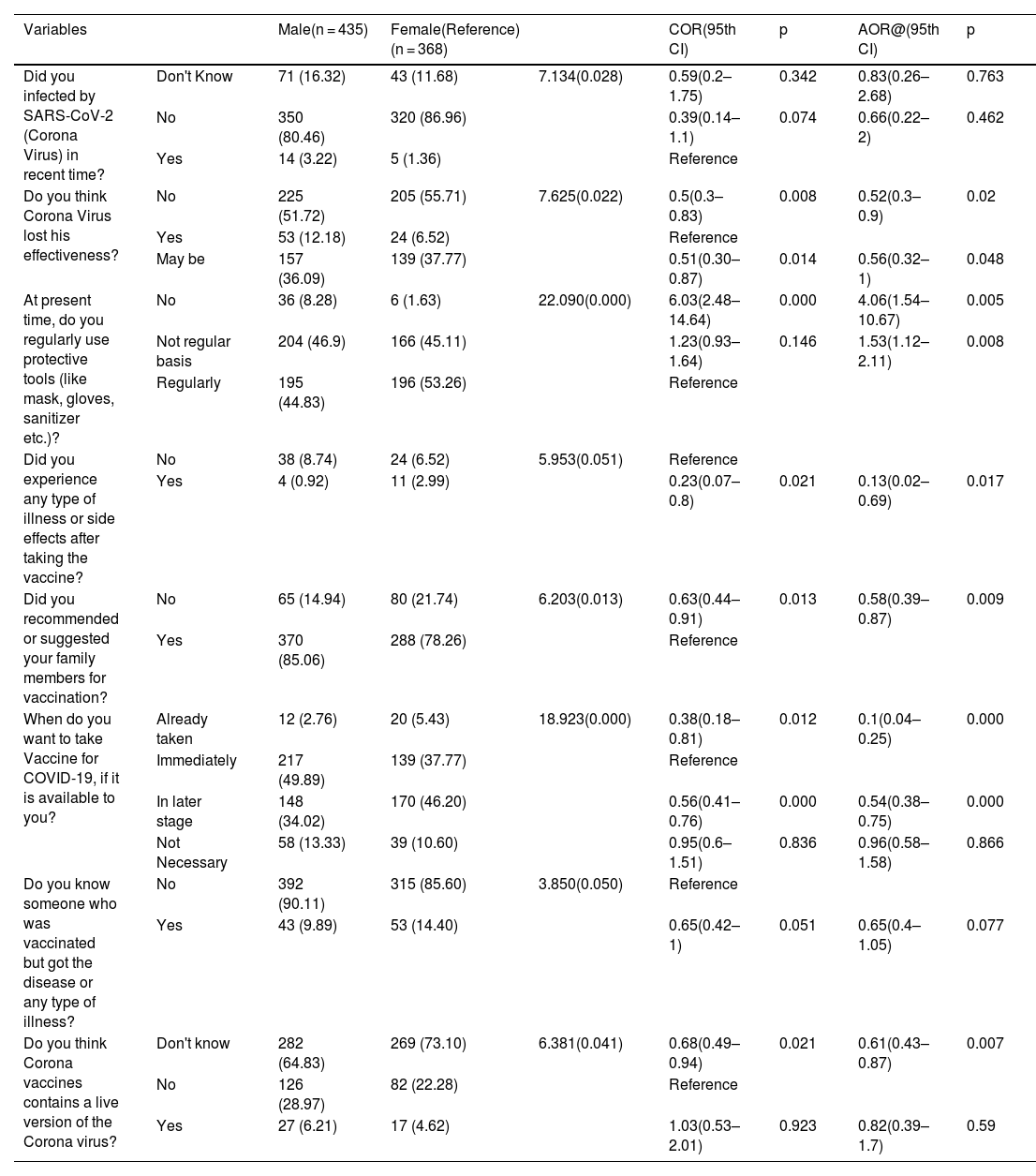
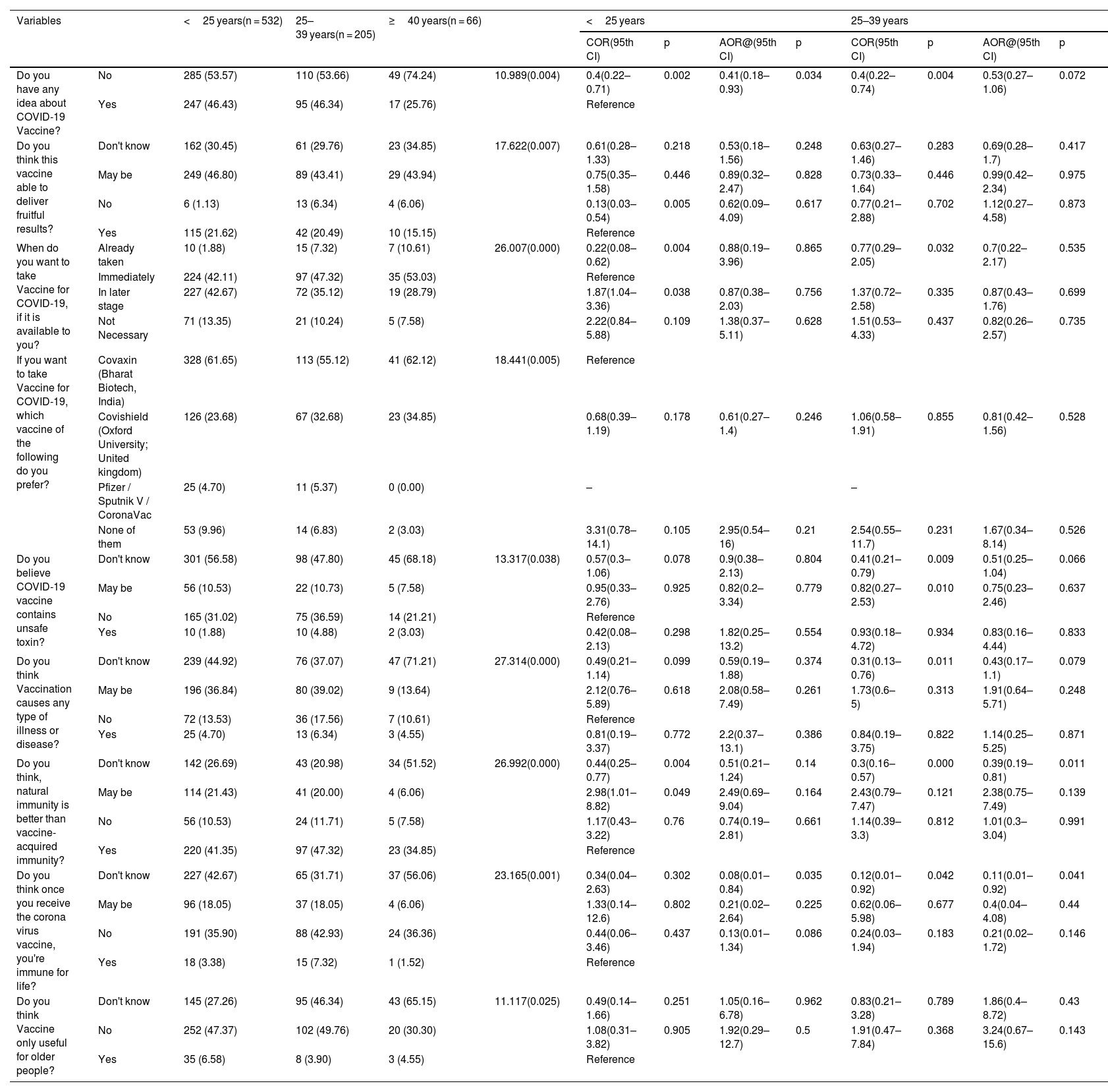
ResultsWe conducted a web-based survey in West Bengal, India (N = 803), and accumulated information on individuals' desire to adopt vaccine against COVID-19, views about the virus's effectiveness, and many knowledge-based socio-demographic factors that potentially impact the overall vaccination efforts. We found that, 12.08% of participants do not believe that vaccination against COVID-19 is necessary, but among the rest of the population, 44.33% of individuals are willing to be vaccinated once the vaccine is available, whereas 39.60% of the population responded that they will not be vaccinated immediately but will do so later.
ConclusionsDespite the participants' strong vaccine willingness, our findings revealed a troubling degree of lake of awareness and insignificant scientific knowledge about the COVID-19 pandemic and its associated vaccination programme. Vaccination hesitancy is not a barrier in this survey region, but poor vaccine availability and a lack of awareness campaigns may instill unfavorable beliefs in those who refuse to be vaccinated.