Spanish figures on Influenza vaccine uptake among health care workers (HCWs) are not well known. For the 2017/18 campaign, the Spanish Ministry of Health established a minimum goal of 40%. HCWs’ uptake at our hospital has not been measured in previous years. During the 2017/2018 season we enhanced the follow up of the vaccination campaign in our hospital.
MethodsWe set up a vaccination registry including working unit and professional profile. We conducted a descriptive and bivariate analysis. We checked whether influenza incidence in the area and the number of influenza patients admitted with influenza in the hospital influenced vaccination. Communication activities were conducted to promote the campaign.
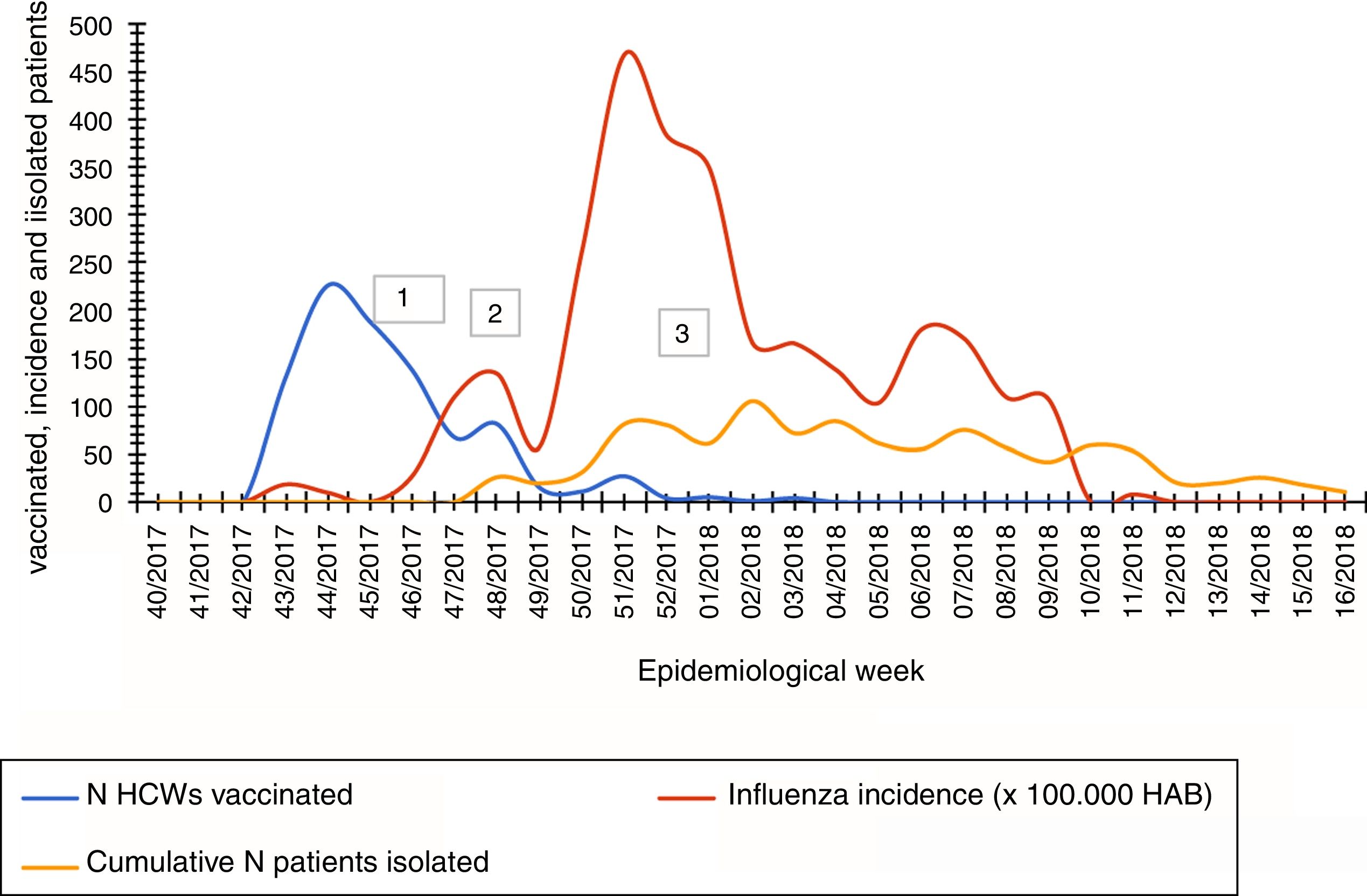
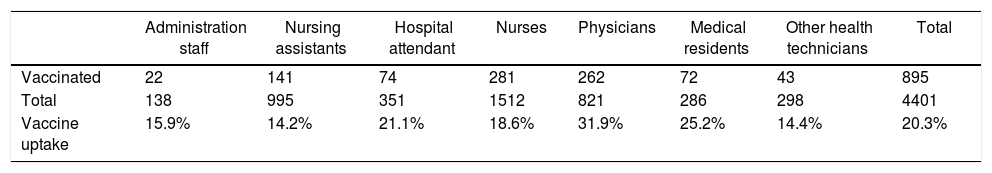
ResultsThe campaign lasted from week 42/2017 to 09/2018. A total of 895/4401 HCWs were vaccinated (20.3%). Only 9% of the units (4/44) exceeded 40% vaccination uptake. The number of administered vaccines peaked on week 44/2017, before the main epidemics wave started. A statistically significant relationship was found between vaccine uptake and working unit and professional profile. Communication strategies during the campaign had no effect in vaccine uptake.
Discussion and conclusionOur registry made feasible a situation analysis of vaccine uptake among HCWs at our hospital and will be useful to measure future trends. HCWs vaccine uptake has been suboptimal during this campaign. The current institutional campaign seems to have a very modest impact. There is a need to develop studies to better understand the reason for the suboptimal vaccination in order to conduct targeted and effective intervention programs.
Las cifras de adherencia a la vacunación antigripal de los profesionales sanitarios en España no son bien conocidas. Para la campaña 2017/18, el Ministerio de Sanidad estableció un objetivo mínimo del 40%. La adherencia de los trabajadores de nuestro hospital no se ha medido en años anteriores. Durante la temporada 2017/2018 fortalecimos el seguimiento de la campaña de vacunación.
MétodosElaboramos un registro de vacunación incluyendo la unidad de procedencia y la categoría profesional. Realizamos un análisis descriptivo y bivariante. Comprobamos si la incidencia de gripe en el área y el número de pacientes con gripe aislados en el hospital influyeron en la vacunación. Se realizaron actividades de promoción de la campaña.
ResultadosLa campaña tuvo lugar entre las semanas 42/2017 y 09/2018. Un total de 895/4.401 profesionales fueron vacunados (20,3%). El 9% de las unidades (4/44) excedió el 40% de la vacunación. El mayor número de vacunaciones ocurrió la semana 44/2017, antes de la ola principal de la epidemia. Se encontró una relación estadísticamente significativa entre vacunación y la unidad de procedencia y categoría profesional. Las estrategias de comunicación no tuvieron efecto.
Discusión y conclusiónNuestro registro hizo posible un análisis de la situación de vacunación de profesionales sanitarios en nuestro hospital. La adherencia ha sido subóptima en la temporada analizada. La campaña institucional actual parece tener un impacto muy modesto. Es necesario desarrollar estudios para comprender mejor el motivo de la vacunación subóptima a fin de llevar a cabo programas de intervención más efectivos.