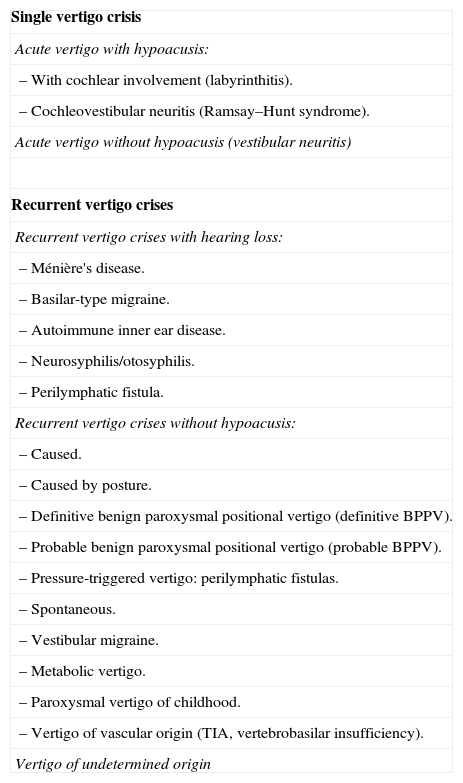
In 2008, the Otoneurology committee of the SEORL-PCF published a classification of peripheral vertigo, based on clinical criteria. The objective of this study was to validate this classification through analysing the diagnostic agreement among several medical assessors.
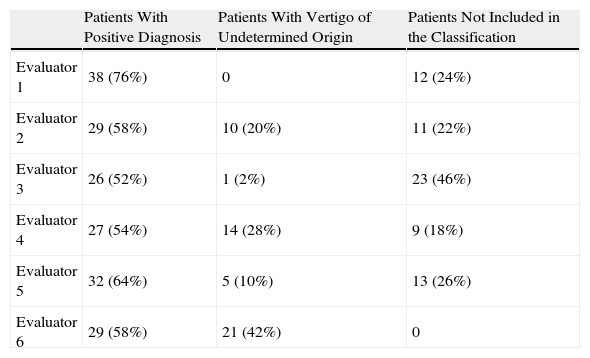
MethodsSeven medical assessors, all with clinical experience, from 6 different hospitals, participated in the study. One of them selected the clinical histories of 50 consecutive patients who had consulted as a result of balance disorders (24 men and 26 women) with an average age of 53.5 years. These clinical histories – without any information that would identify the patient, the diagnosis established and the treatment – were sent to another 6 assessors. Each of these investigators established their own diagnosis, trying to adjust it to the epigraphs of the classification.
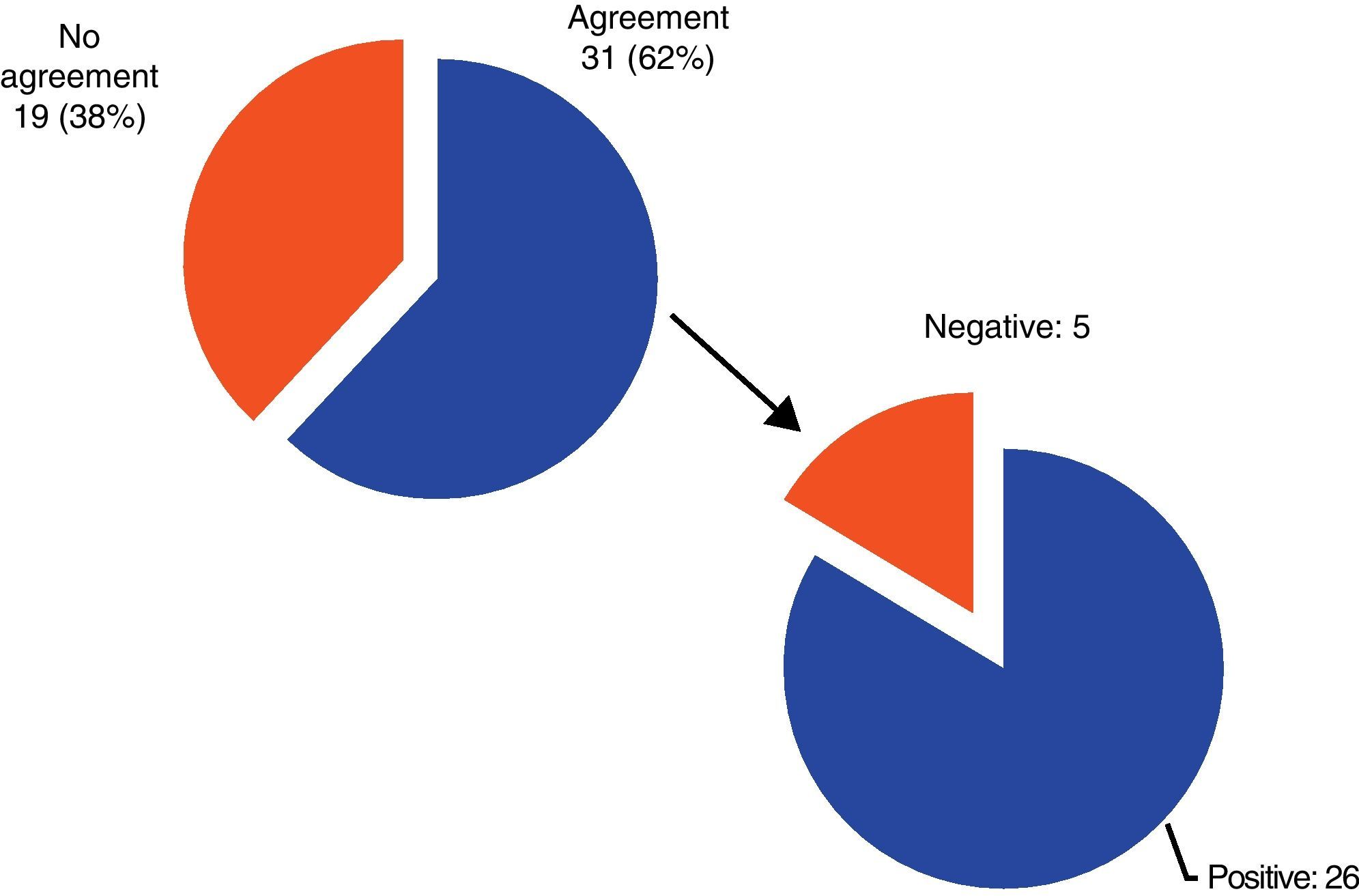
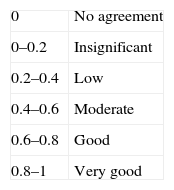
ResultsOf the 50 patients, there was substantial agreement in the diagnosis (4 or more evaluators indicated the same one) in 31 cases (26 with a positive diagnosis and 5 with a negative one, which could not be included in any epigraph). The kappa index, which measures the level of accordance between 2 or more assessors, was 0.4198 (moderate level of agreement). Unanimity was achieved in only 7 cases (4 BPPV, 2 Ménière's disease and 1 vertigo associated with migraine).
ConclusionsThe current classification, with the included criteria it includes, allows labelling with an acceptable consensus to only 62% of the patients. Therefore, a modification in the classification is proposed in relation with the probable BPPV epigraph, as well as a revision of the entries for vertigo-migraine and vertigo associated with migraine.
La Comisión de Otoneurología de la SEORL-PCF publicó en 2008 una clasificación de los vértigos periféricos, basada en criterios clínicos. El objetivo de este estudio es validar esta clasificación mediante el análisis de la concordancia diagnóstica entre múltiples evaluadores.
MétodosParticiparon 7 evaluadores con experiencia clínica en el diagnóstico de afección vestibular, pertenecientes a 6 centros diferentes. Uno de ellos seleccionó las historias clínicas de 50 pacientes consecutivos que consultaron por alteraciones del equilibrio (24 varones y 26 mujeres; edad media: 53,5 años). Estas historias, suprimidos los datos que permitiesen identificar a los pacientes, el diagnóstico establecido y el tratamiento pautado, fueron remitidas a los otros 6 investigadores. Cada uno de ellos estableció un diagnóstico, intentando ajustarlo a los epígrafes de la clasificación.
ResultadosDe los 50 pacientes, existió una coincidencia sustancial en el diagnóstico (4 o más evaluadores alcanzaron el mismo) en 31 (26 con diagnóstico positivo y 5 negativo: no podía ser incluido en ningún epígrafe). El índice kappa, que mide el nivel de concordancia entre tres o más observadores, fue de 0,4198 (lo que indica un grado de acuerdo moderado). La unanimidad solo se alcanzó en 7 pacientes (4 VPPB, dos enfermedades de Ménière y un vértigo asociado a migraña).
ConclusionesLa actual clasificación, con los criterios que incluye, solo permite etiquetar con un consenso aceptable al 62% de los pacientes. Se propone una modificación de la clasificación, incluyendo el epígrafe de VPPB probable, y revisando los de vértigo-migraña y vértigo asociado a migraña.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora