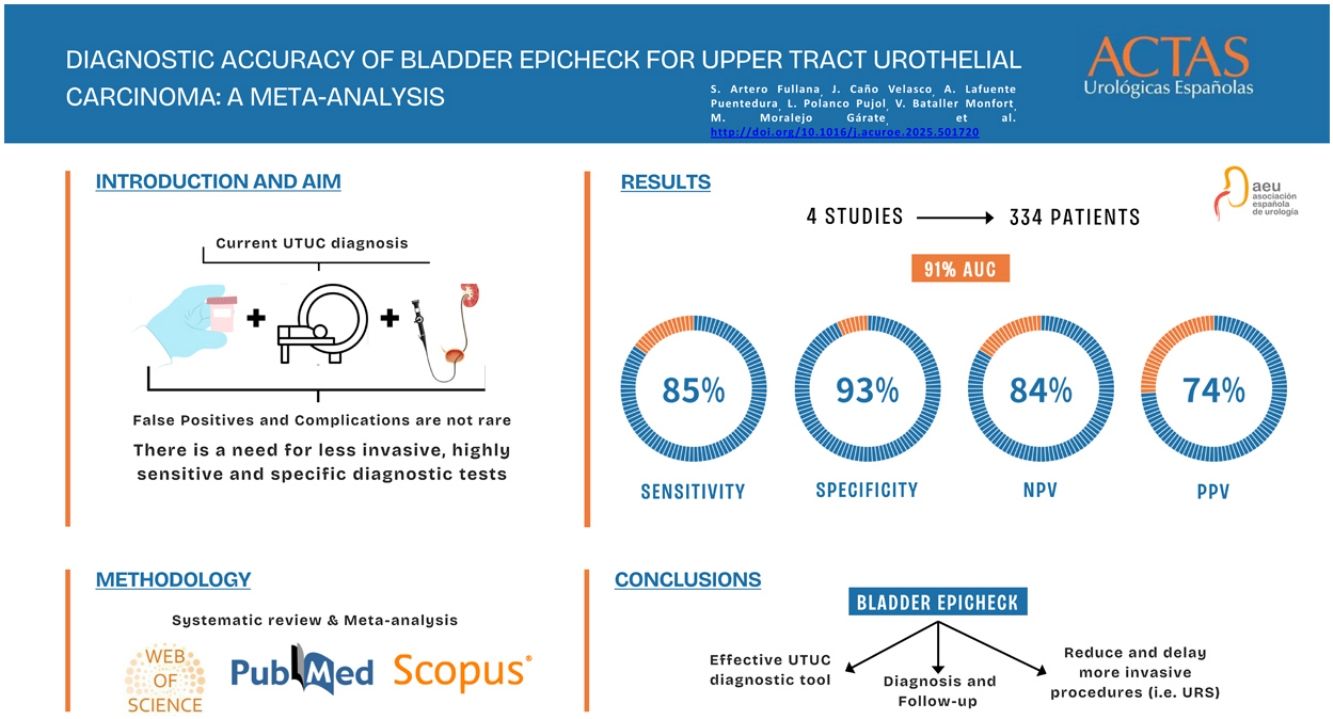
Current upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) diagnosis and disease management rely on the combination of CT Urography (CTU), cytology and ureteroscopy (URS). The limited accuracy and complications associated with these tools have led to the search for non-invasive and reliable biomarkers. Our aim was to review and analyse the existing data on the use of Bladder EpiCheck® to assess its performance as a diagnostic tool for UTUC.
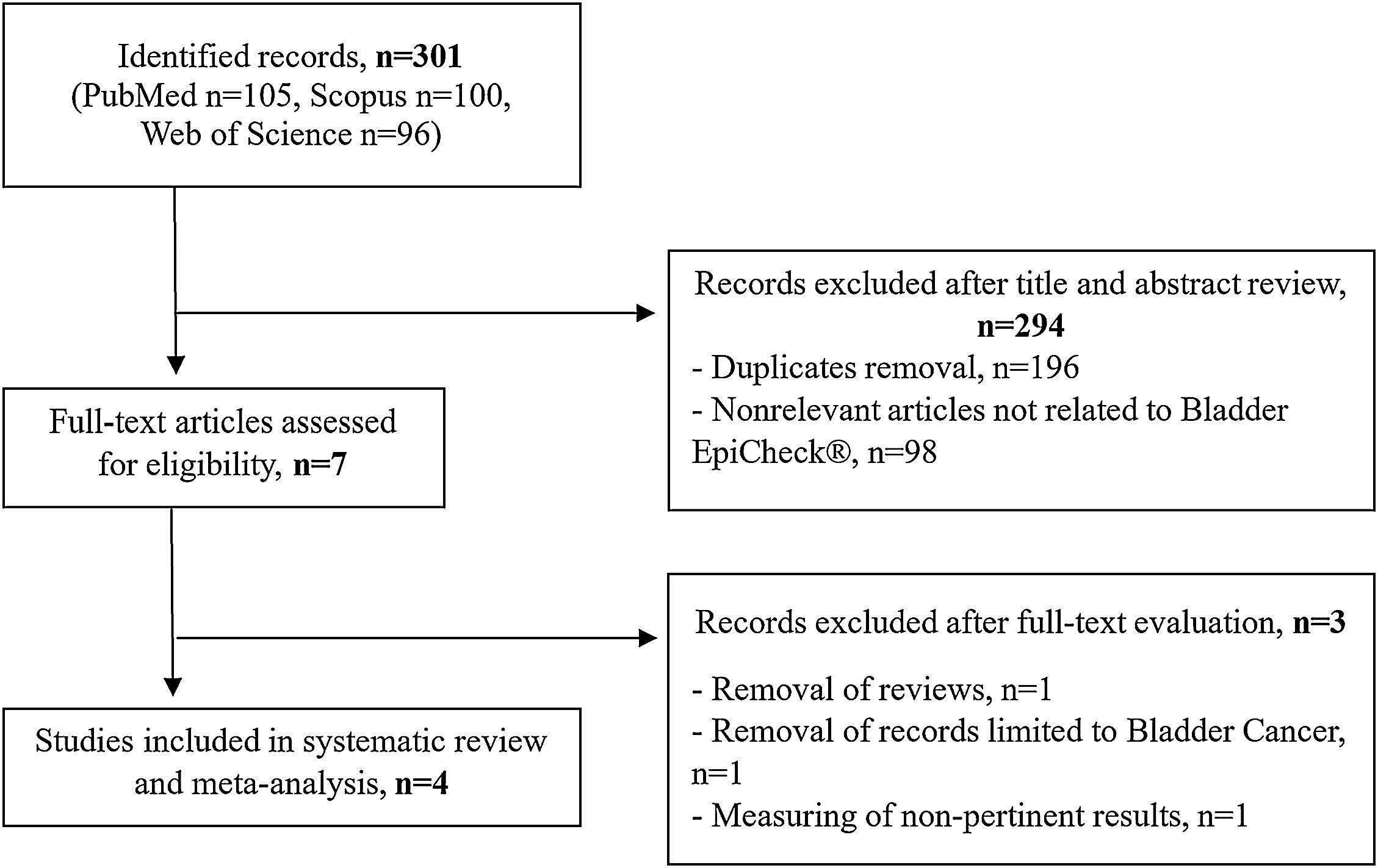
Material and methodsA literature search on the diagnostic value of Bladder EpiCheck® as a urinary biomarker in UTUC was conducted through PubMed, Web of Science and Scopus until February 2024. Pooled sensitivity (Se), specificity (Sp), negative predictive value (NPV) and positive predictive value (PPV) of the biomarker were calculated. Diagnostic performance was assessed through the area under the curve (AUC).
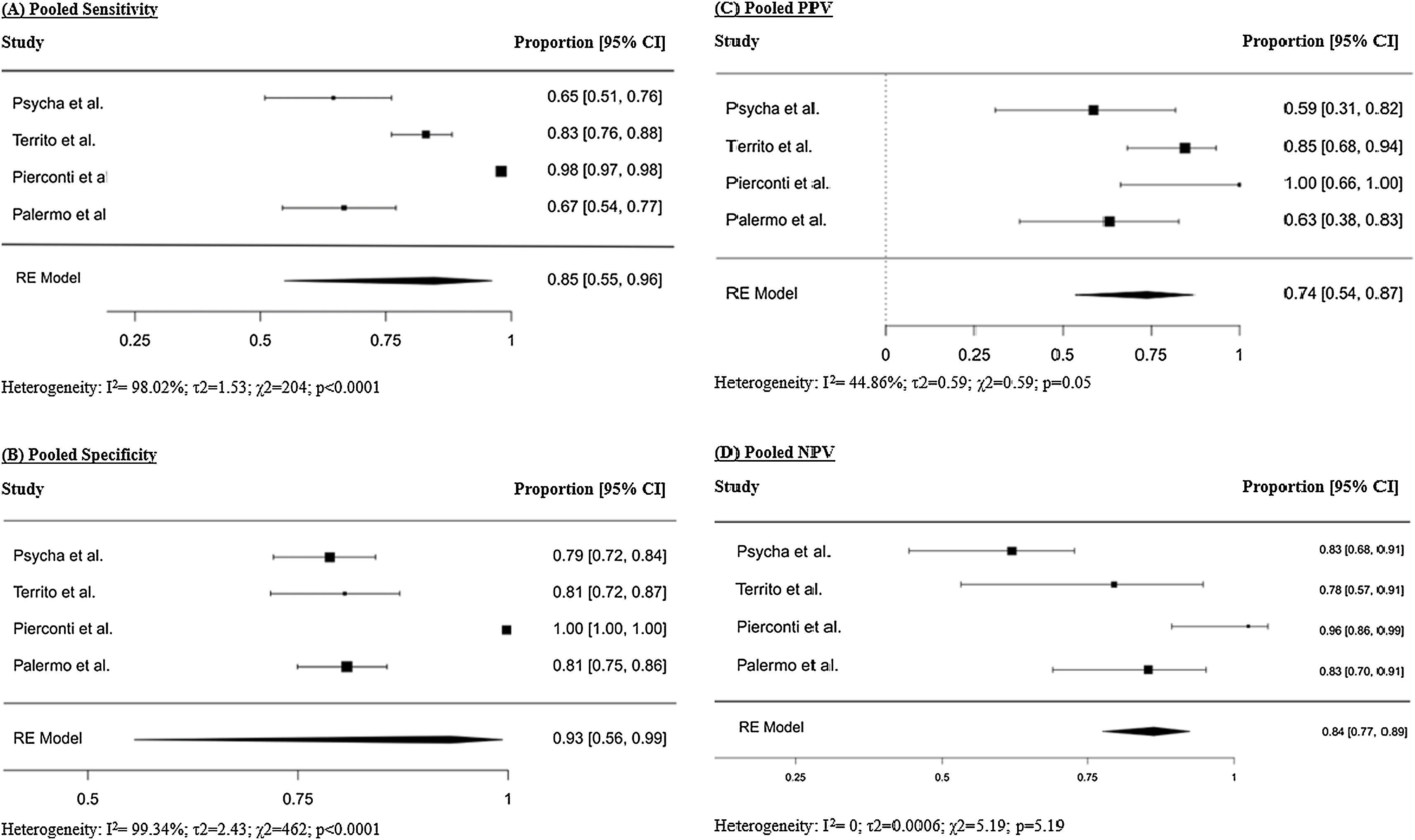
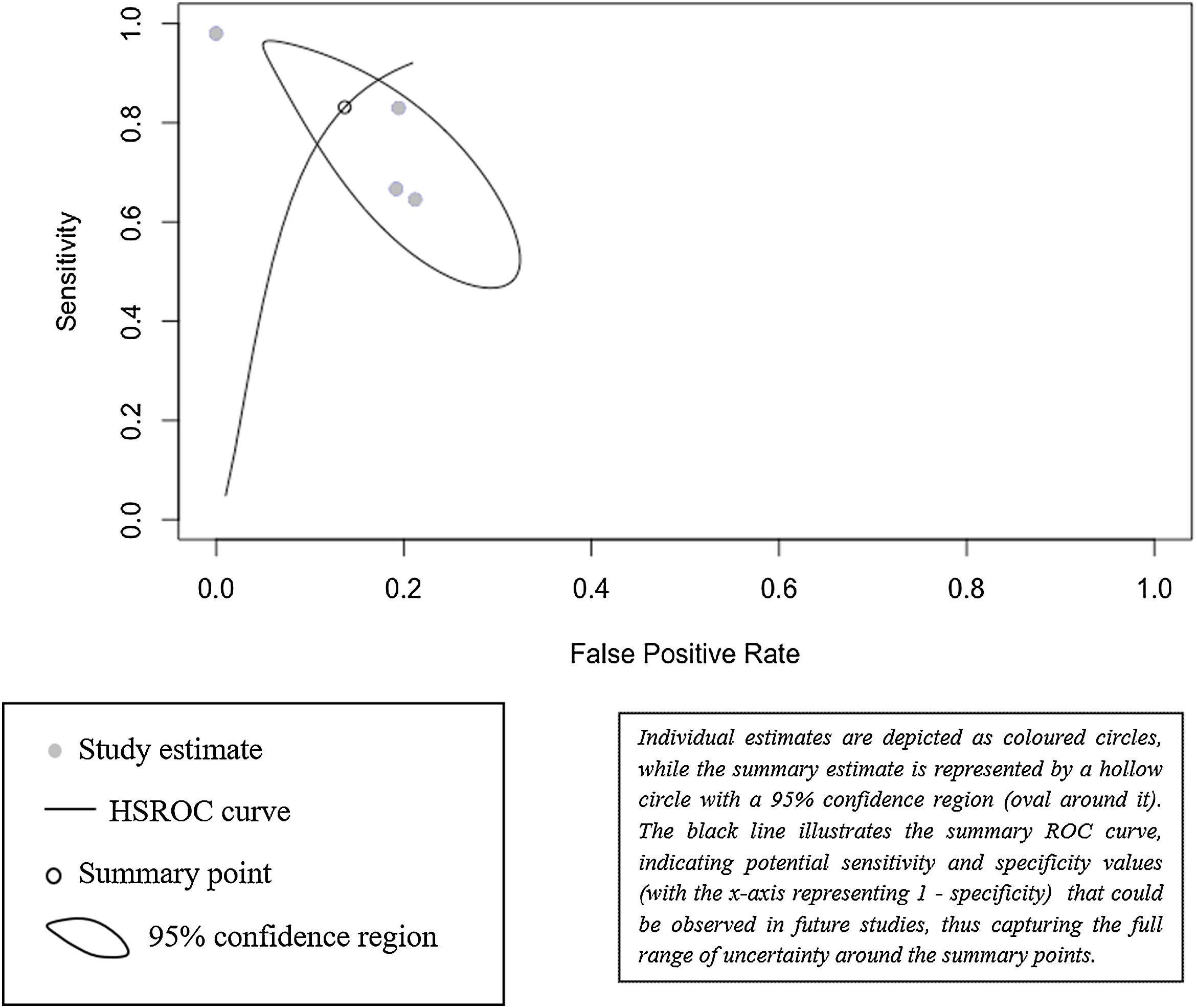
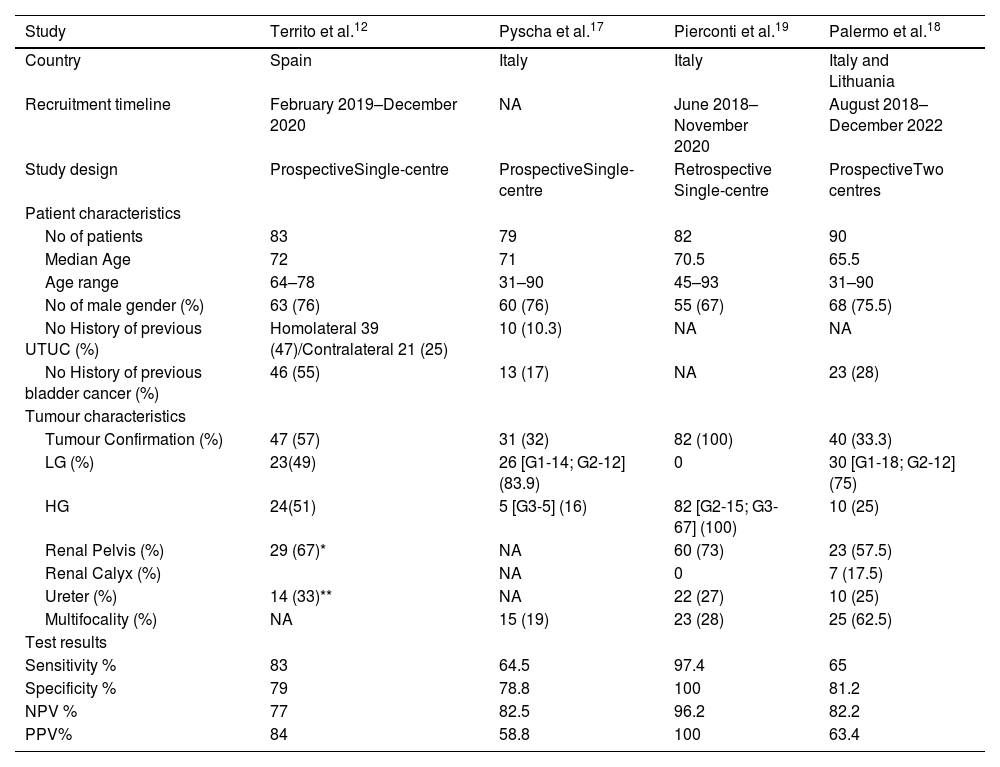
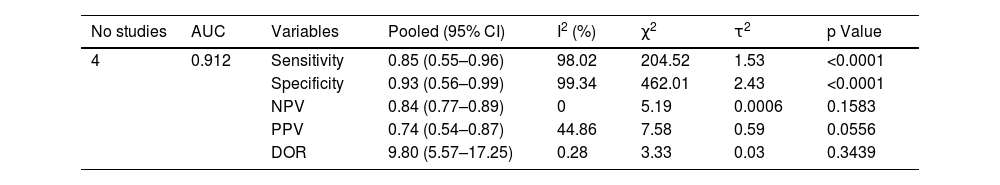
ResultsFour studies, including 334 patients, were included in the quantitative analysis. Bladder EpiCheck® showed promising pooled diagnostic values with Se of 0.85 (95% CI 0.55–0.96), Sp of 0.93 (95% CI 0.56–0.99), PPV of 0.74 (95% CI 0.54–0.87) and NPV of 0.84 (95% CI 0.77–0.89). The exact AUC obtained was 0.912.
ConclusionsBladder EpiCheck® is an effective diagnostic tool in UTUC, showing a promising diagnostic accuracy, with a Se and NPV of 85% and 84%, respectively. Its use in UTUC diagnosis and follow-up could reduce or postpone the need for more invasive procedures, such as URS, thereby reducing the procedure-associated risks and improving patients’ quality of life. Although further research and large prospective studies are needed, the current results indicate that Bladder EpiCheck® is a promising tool in UTUC diagnosis, treatment decision-making, and follow-up.
El diagnóstico y el tratamiento del carcinoma urotelial del tracto superior (CUTS) actualmente se basan en la combinación de la urografía por tomografía computarizada (uro-TAC), la citología y la ureteroscopia (URS). La escasa precisión y las complicaciones asociadas a estas técnicas han motivado el desarrollo de biomarcadores más precisos y no invasivos. El objetivo de este estudio fue revisar y analizar los datos existentes sobre el uso de Bladder EpiCheck® para evaluar su rendimiento en el diagnóstico del CUTS.
Material y métodosSe realizó una búsqueda bibliográfica sobre el valor diagnóstico de Bladder EpiCheck® como biomarcador urinario en el CUTS. Esta búsqueda se realizó en PubMed, Web of Science y Scopus hasta febrero de 2024. Se calcularon los valores agrupados de sensibilidad (S), especificidad (E), valor predictivo negativo (VPN) y valor predictivo positivo (VPP) del biomarcador. El rendimiento diagnóstico se evaluó mediante el área bajo la curva (ABC).
ResultadosEn el análisis cuantitativo se incluyeron cuatro estudios con 334 pacientes. Bladder EpiCheck® mostró valores diagnósticos agrupados prometedores: S de 0,85(IC95% 0,55-0,96), E de 0,93(IC95% 0,56-0,99), VPP de 0,74(IC95% 0,54-0,87) y VPN de 0,84(IC95% 0,77-0,89). El valor exacto del ABC fue de 0,912.
ConclusionesBladder EpiCheck® es una herramienta diagnóstica eficaz en el estudio del CUTS, con una elevada precisión diagnóstica, una S y un VPN del 85% y el 84%, respectivamente. Su uso en el diagnóstico y seguimiento del CUTS podría reducir o posponer procedimientos más invasivos, como la URS, minimizando así los riesgos asociados al procedimiento y mejorando la calidad de vida de los pacientes. Aunque se necesitan más investigaciones y estudios prospectivos a gran escala, los resultados actuales indican que Bladder EpiCheck® es una herramienta prometedora para el diagnóstico, la elección del tratamiento y el seguimiento del CUTS.