La estadificación preoperatoria del cáncer vesical por métodos de imagen presenta serias limitaciones. Se evalúa la exactitud de la resonancia magnética abdominal balanceada con difusión (MRI-DW) para predecir invasión muscular residual, afectación perivesical y/o ganglionar en el espécimen de cistectomía.
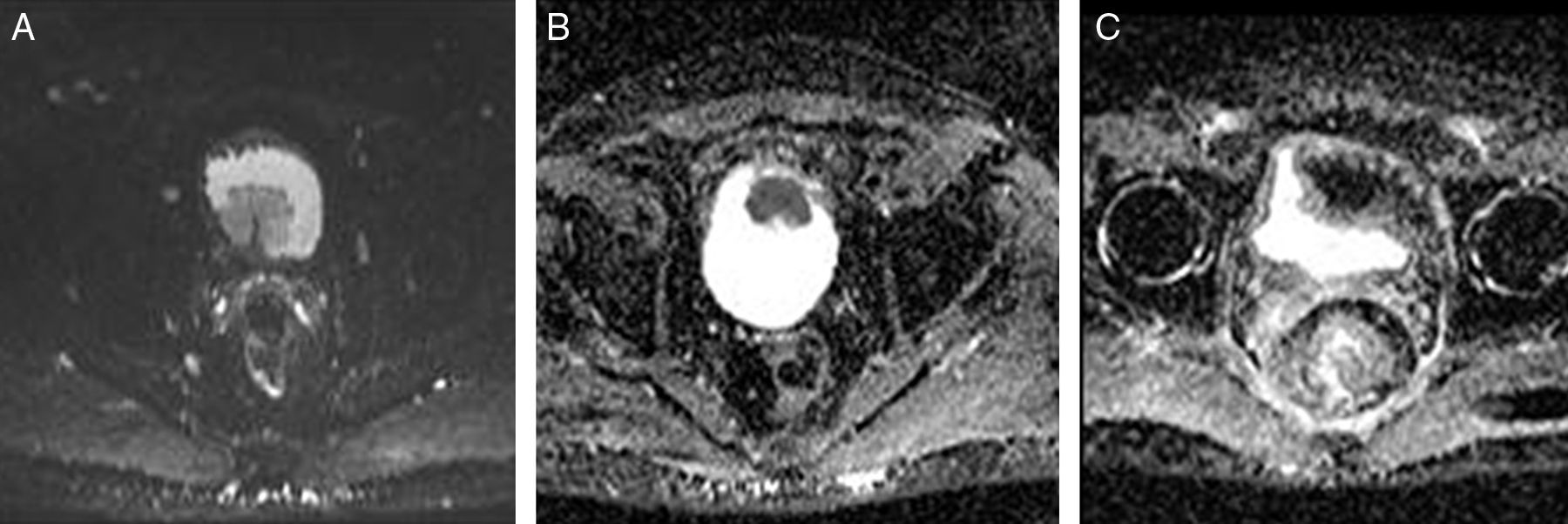
Material y métodosEstudio prospectivo sobre 20 pacientes con cáncer de vejiga músculo-invasivo de alto grado que recibieron RTU vesical en un plazo menor de un mes. Se realizó MRI-DW antes de cistectomía radical y el radiólogo predijo invasión muscular, afectación extravesical y afectación ganglionar de manera ciega al estudio histopatológico. Se analizó sensibilidad (S), especificidad (E), valor predictivo positivo (VPP), valor predictivo negativo (VPN) y exactitud (Ex) de la prueba. Se compararon medianas de valor ADC (Mann-Whitney) y se llevó a cabo estudio de curvas ROC para MRI-DW y ADC.
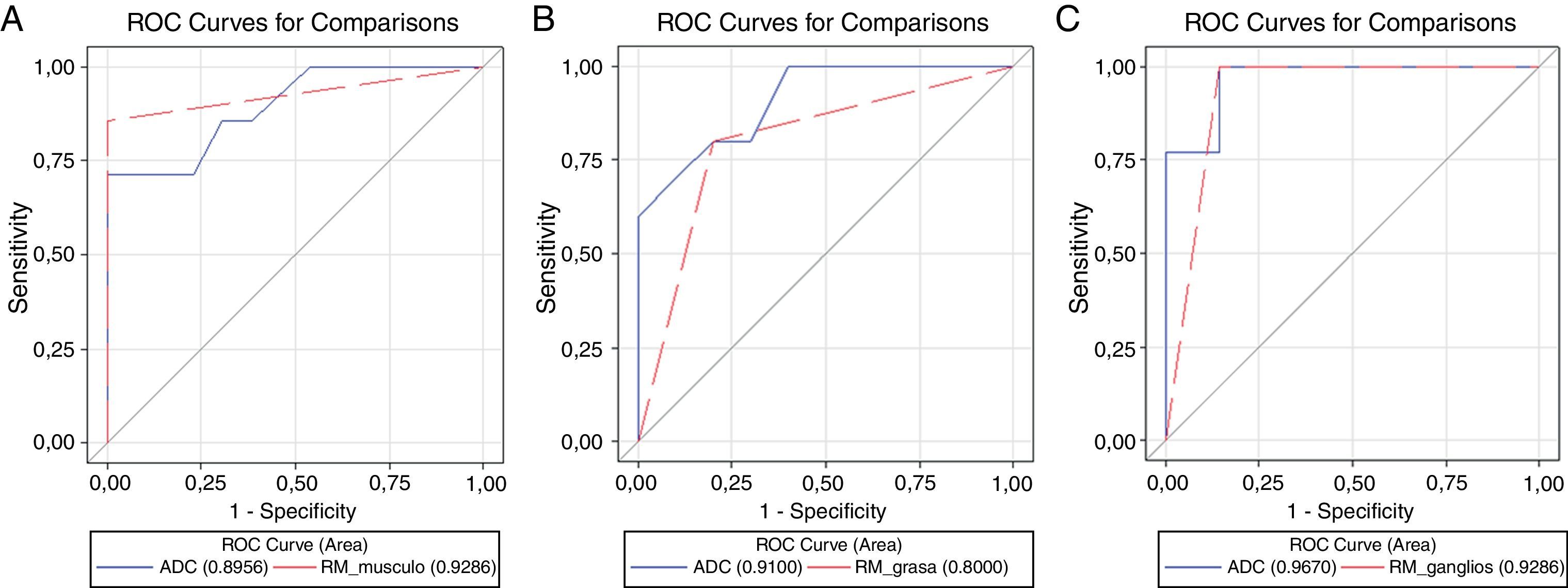
ResultadosLa distribución por categorías fue: pT0 1(5%), pT1 6(30%), pT2 2(10%), pT3 8(40%) y pT4 3(15%). Existió acuerdo en la asignación T-pT en 17 (85%). En 7 (35%) hubo afectación ganglionar (pN1-2). La consistencia de MRI-DW para afectación muscular fue k=0,89 (IC 0,67-1; S=1,0, E=0,86, VPP=0,93, VPN=1,0, Ex=0,95), para afectación de grasa perivesical k=0,6 (IC 0,25-0,95; S=0,8, E=0,8, VPP=0,8, VPN=0,8, Ex=0,8) y para afectación ganglionar k=0,89 (IC 0,67-1; S=0,86, E=1,0, VPP=1,0, VPN=0,93, Ex=0,95). La media de valor de ADC fue mayor en tumores G2 (OMS 1987) frente a G3 (p=0,08). La evaluación por imagen de MRI-DW y el valor numérico ADC mostraron áreas bajo la curva equivalentes para afectación muscular (0,93 y 0,9; Z=0,7), grasa (0,8 y 0,91; Z=0,31) y ganglionar (0,93 y 0,97; Z=0,36), respectivamente.
ConclusionesMRI-DW permite una buena evaluación preoperatoria del paciente candidato a cistectomía, especialmente para la predicción de afectación muscular (<pT2 vs ≥pT2) y/o ganglionar (N0 vs N1-2), ambos puntos clave para elegir la actitud terapéutica después de RTU vesical. Además, el coeficiente ADC predice también el grado de diferenciación tumoral.
Preoperative staging of bladder cancer using imaging methods has serious limitations. The accuracy of the abdominal diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance (DW-MRI) to predict residual muscle invasion, perivesical and/or lymph node affectation in the cystectomy specimen is evaluated.
Material and methodsA prospective study was performed on 20 patients with high grade muscle invasive bladder cancer who received transurethral resection of the bladder (TURB) in a period of <1 month. The DW-MRI was performed before the radical cystectomy and the radiologist predicted muscle invasion, extravesical affectation and lymph node affectation, being blind to the histopathological study. Sensitivity (S), specificity (sp), positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV) and accuracy (Ac) of the test were analyzed. The medians of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value (Mann-Whitney) were compared and the ROC curves study for DW-MRI and ADC was carried out.
ResultsDistribution by categories was: pT0 1(5%), pT1 6(30%), pT2 2(10%), pT3 8(40%) and pT4 3(15%). There was agreement in the T-pT assignment in 17(85%). In 7(35%) there was lymph node affectation (pN1-2). Consistency of the DW-MRI for muscle affectation was k=.89 (CI .67-1; S=1.0, Sp=,86, PPV=.93, NPV=1.0, Ac=.95), for perivesical fat affectation k=.6 (CI .25-.95; S=.8, Sp=.8, PPV=.8, NPV=.8, Ac=.8) and for lymph node affectation k=.89 (CI .67-1; S=.86, Sp=1.0, PPV=1.0, NPV=.93, Ac=.95). Mean value of ADC was greater in G2 tumors (OMS1987) compared to G3 (p=.08). Evaluation of DW-MRI imaging and ADC numerical value showed equivalent areas under the curve for muscle (.93 and .9; Z=.7), fat (.8 and .91; Z=.31) and lymph node (.93 and .97; Z=.36) affectation, respectively.
ConclusionsDW-MRI allows for good pre-operative evaluation of the patient who is a candidate for cystectomy, especially for the prediction of muscle (<pT2 vs ≥pT2) and/or lymph node (N0 vs N1-2) affectation. Both are key points to choice the therapeutic attitude after the bladder TURB. Furthermore, the ADC coefficient also predicts tumor differentiation grade.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora