Evaluar el impacto en la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud (CVRS) y en la función sexual de la hiperplasia benigna de próstata (HBP) y su tratamiento, en pacientes con síntomas urinarios (STUI/HBP) moderados-graves en tratamiento con bloqueadores alfa; estudiar las diferencias asociadas a la edad, la gravedad de síntomas urinarios y el tiempo con tratamiento.
Material y métodosSe reclutaron 1.580 pacientes diagnosticados de HBP y con STUI/HBP en tratamiento con bloqueadores alfa, en consultas de urología de toda España. Se recogieron datos sociodemográficos, clínicos y de gravedad de STUI/HBP (cuestionario IPSS) y las respuestas al cuestionario EQ-5D y el Sexual Function Index (SFI). Se realizó un análisis estadístico descriptivo, contrastes por edad, gravedad de STUI/HBP y tiempo de tratamiento y se ajustaron modelos lineales de regresión múltiple para las respuestas al EQ-5D y SFI.
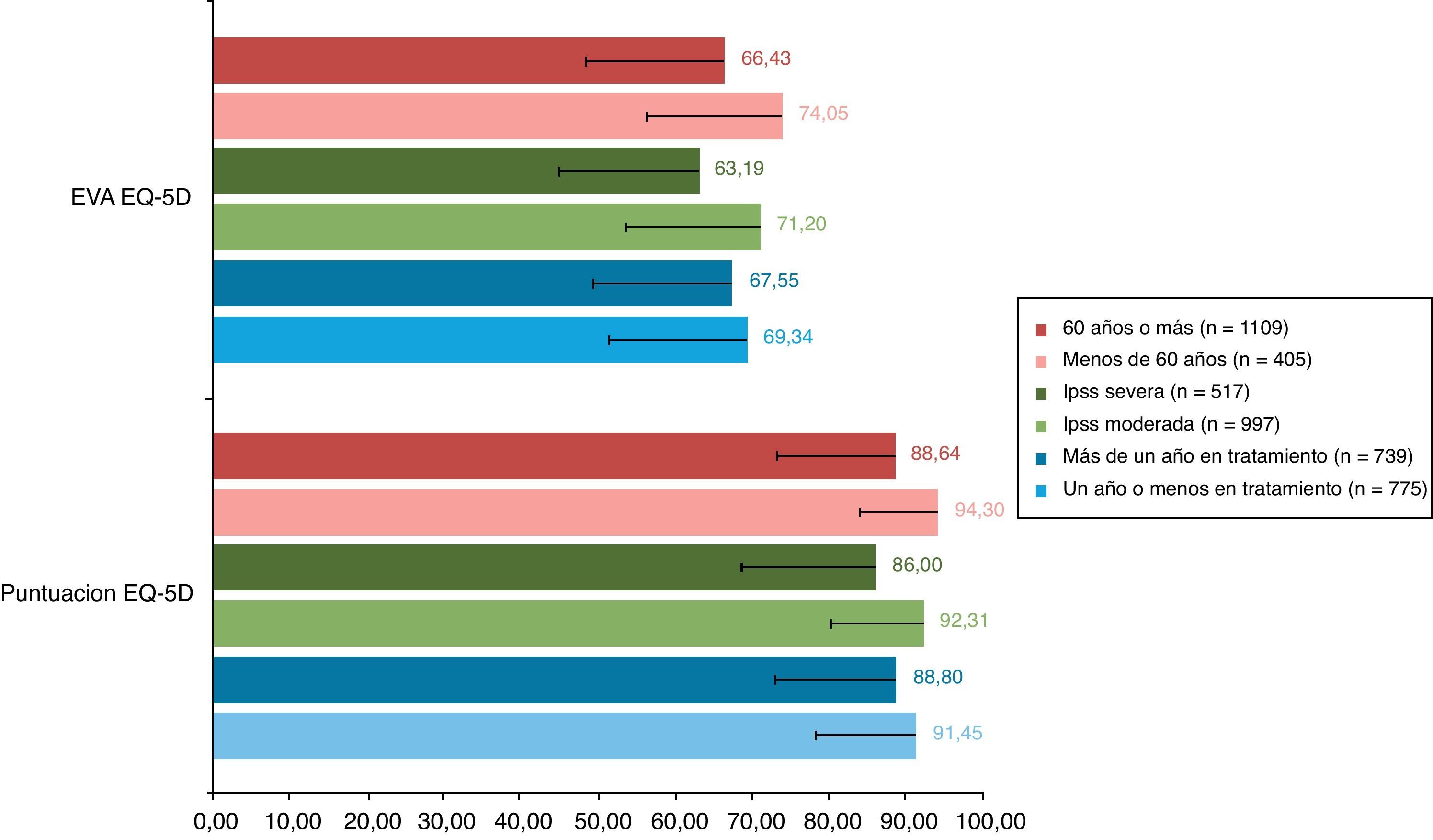
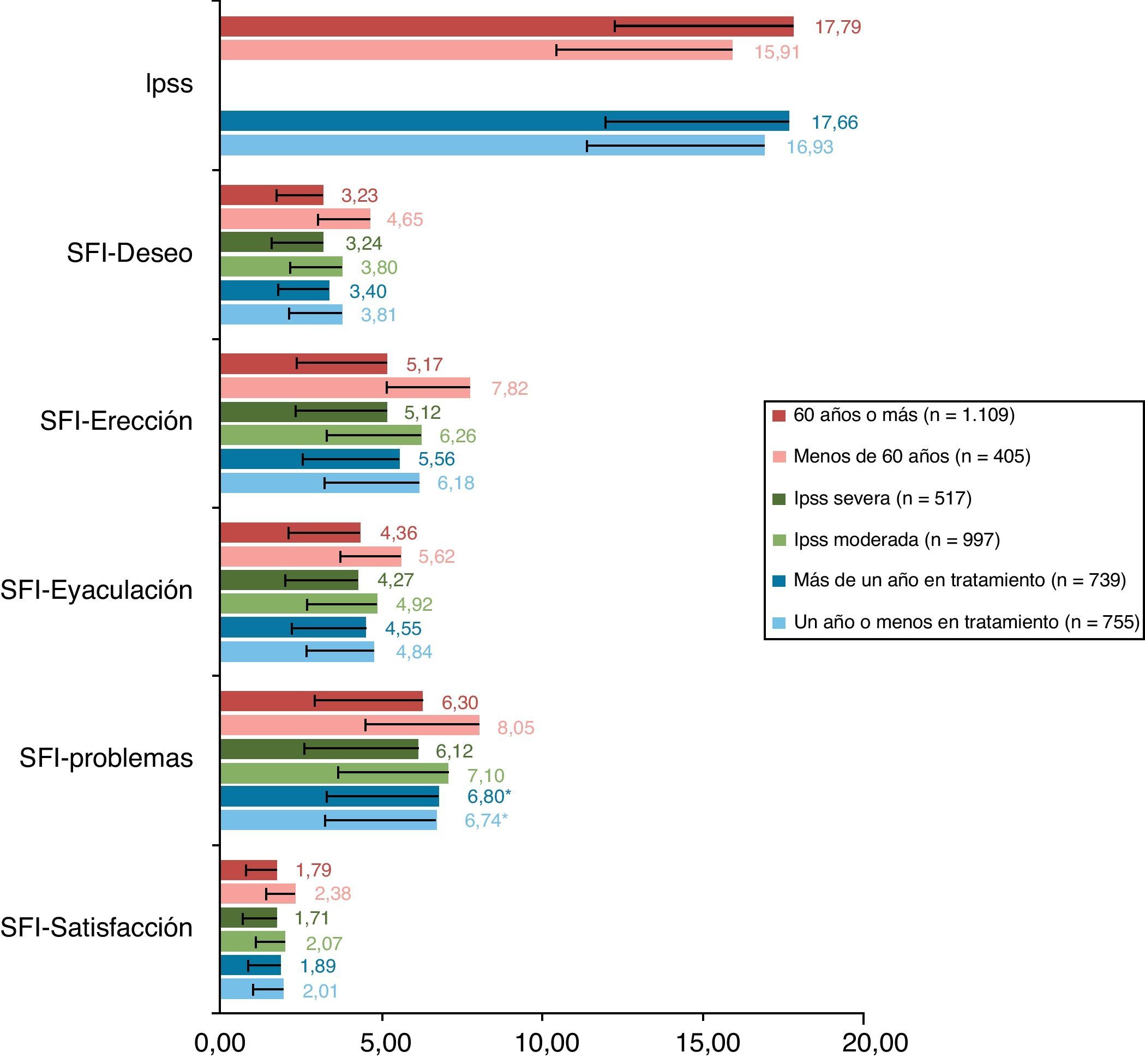
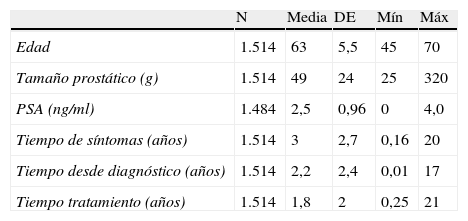
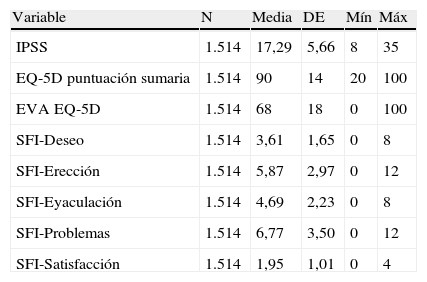
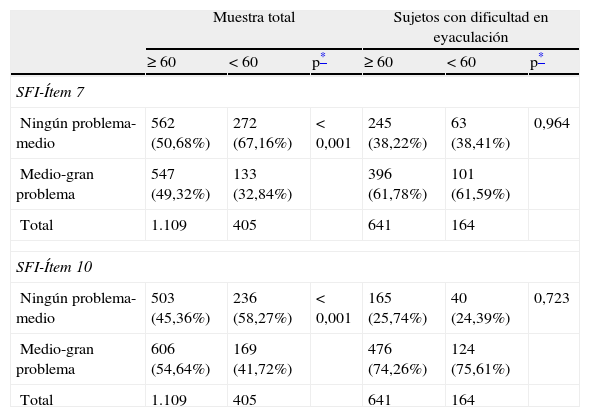
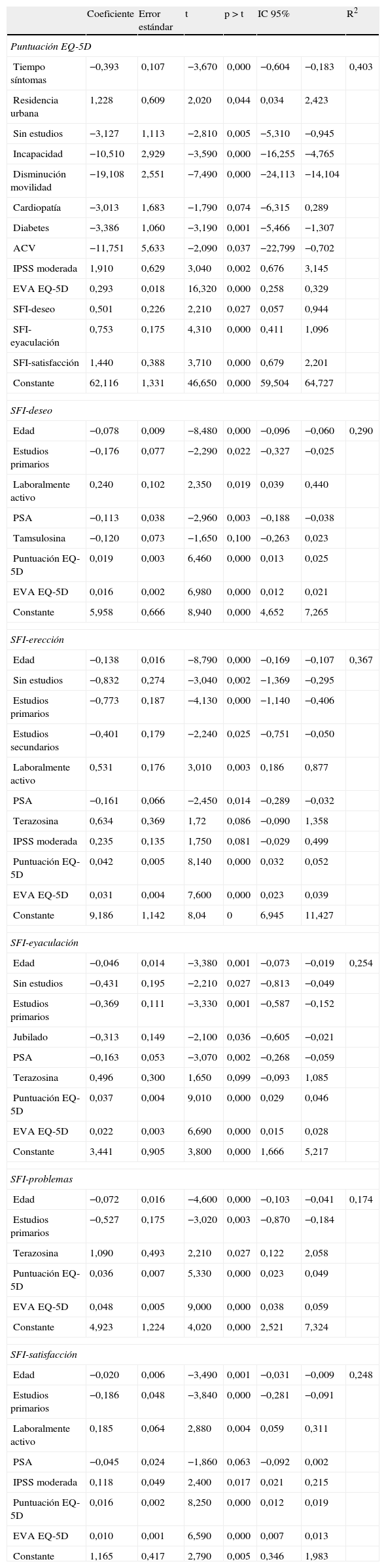
ResultadosSe analizaron datos de 1.514 pacientes. La media (DE) de edad fue 63 (5,5) años (26,75%<60 años), de tiempo de tratamiento 1,8 (2,0) años (51,19%<1 año), para IPSS 17,29 (5,66) puntos (65,85% síntomas moderados), para EQ-5D 90 (14) puntos. Las dimensiones del SFI más dañadas fueron satisfacción y deseo. El 52,58% de los pacientes mostraron afectación en la CVRS (IPSS-ítem 8). Edad, gravedad de síntomas y tiempo en tratamiento mostraron asociación con la CVRS y función sexual.
ConclusionesLa HBP y su tratamiento impactan negativamente en la CVRS y en la función sexual, siendo el deterioro mayor en pacientes con síntomas STU/HBP graves, en los de mayor edad y en los que llevaban más de un año de tratamiento.
To evaluate the impact of bening prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) on health related quality of life (HRQoL) and sexual function, in patients with moderate-severe lower tract urinary symptoms (LUTS/BPH) under treatment with alpha-blockers; to study differences associated to age, urinary symptom severity and time under treatment.
Material and methods1580 patients diagnosed of BPH and LUTS/BPH, and in treatment with alpha-blockers were recruited in urology practices all around Spain. Socio-demographic- and clinic-data together with LUTS/HBP severity assessment (IPSS questionnaire) and responses to EQ-5D and the Sexual Function Index Questionnaire (SFI) were collected. A descriptive statistical analysis was performed, as well as test to contrast the results by age, LUTS/HBP severity and time under treatment; multiple linear regression models were adjusted for the answers to EQ-5D and SFI.
ResultsAnalysis database contained information of 1514 patients. Mean age (SD) was 63 (5.5) years (26.75% under 60 years), mean treatment time 1.8 (2.09) years (51.19% under one year). Mean questionnaire scores were: IPSS 17.29 (5.66) (65.85% moderate symptoms), EQ-5D 90 (14). The SFI-domains with worse scores were satisfaction and sexual drive. 52.58% of patients presented deteriorated HRQoL (IPSS-item 8). Age, symptom severity and time under treatment showed association with HRQoL and sexual function.
ConclusionsBPH and its treatment impact negatively on HRQOL and sexual function, with a more pronounced deterioration in patients with severe LUTS/HBP, in older patients and in patients in treatment over a year.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora