Comparar, en términos de eficacia y seguridad, los resultados del tratamiento endoscópico del reflujo vesicoureteral (RVU) en dos cohortes diferentes de RVU primario tratadas con Dexell y Vantris.
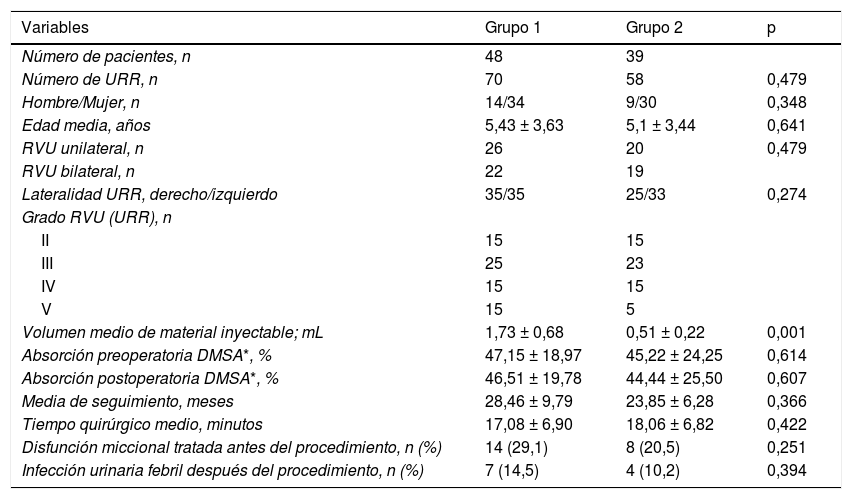
PacientesEl estudio incluyó 128 unidades de reflujo renal (URR) en 87 pacientes con RVU primario (64 mujeres, 23 hombres). Se excluyeron los pacientes con RVU secundario y disfunción vesical e intestinal severa. Un total de 22 niños mayores ya continentes, con disfunción vesico-intestinal leve, fueron sometidos a entrenamiento vesico-intestinal previo a la implantación. Todos los procedimientos se realizaron en presencia de orina estéril mediante la técnica convencional de inyección transuretral subureteral.
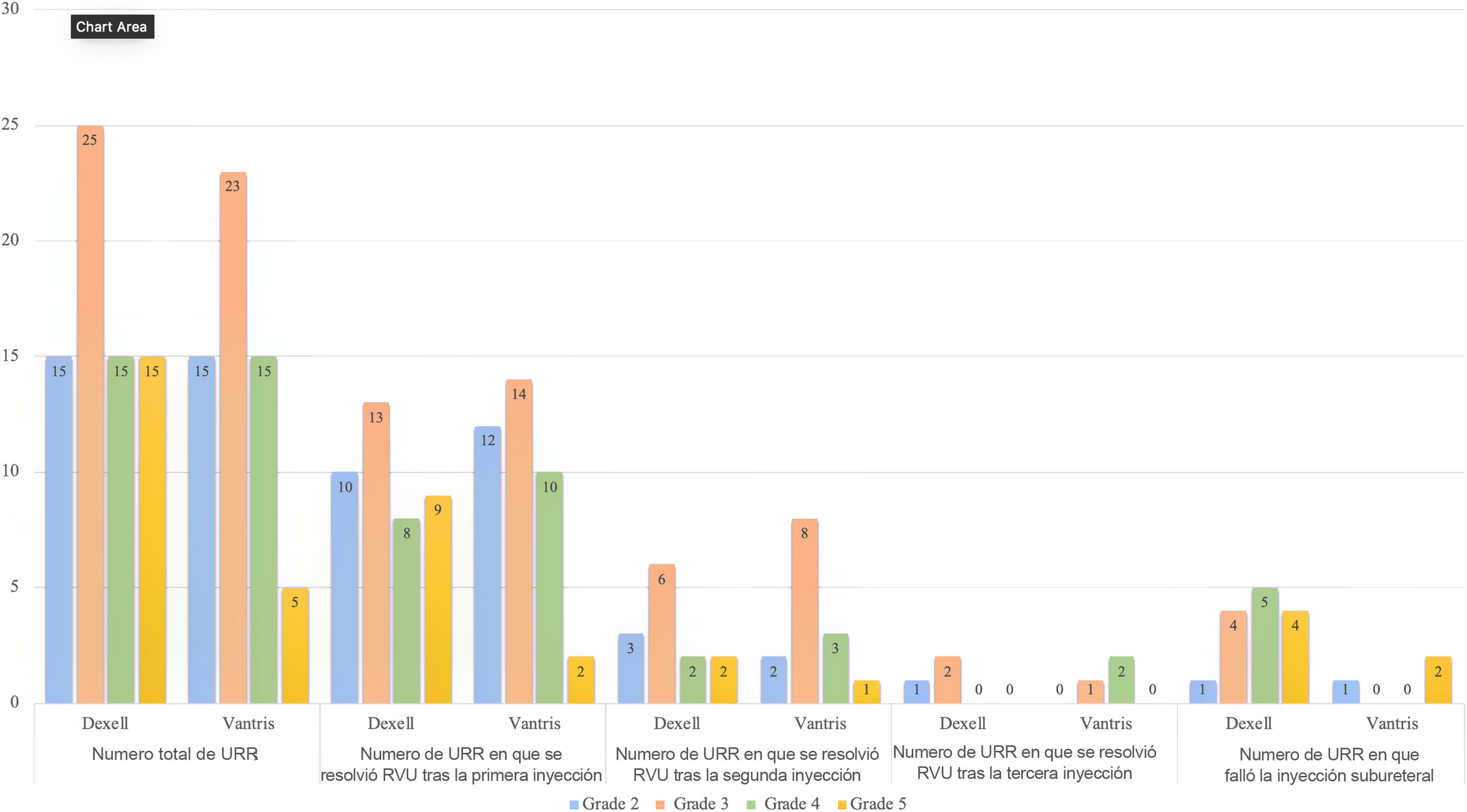
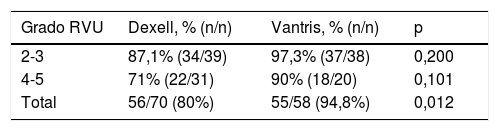
ResultadosNo hubo diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre los dos grupos en cuanto a media de edad, sexo, lateralidad de la URR, captación de 99mTc-DMSA y grado de reflujo. Las tasas de resolución global con base en el número de URR con hasta tres tratamientos endoscópicos fueron del 80% (56/70) en el grupo Dexell y del 94,8% (55/58) en el grupo Vantris (p = 0,012). No se observaron recidivas ni obstrucciones de la unión vesicoureteral en el postoperatorio en ningún grupo.
ConclusionesDexell y Vantris proporcionaron un tratamiento endoscópico eficaz y seguro en el seguimiento a corto y medio plazo del RVU primario en niños. Se requieren más estudios para evaluar la eficacia de estas sustancias, cuyo efecto de volumen depende del tamaño de sus partículas, en la resolución segura del RVU.
To compare the results in terms of efficacy and safety of the endoscopic management for vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) in two different standardized primary VUR cohorts treated with Dexell and Vantris.
Patients128 refluxing renal units (RRU) in 87 patients with primary VUR (64 females, 23 males). Patients with secondary VUR and severe bladder and bowel dysfunction were excluded. A total of 22 continent children with mild bladder-bowel dysfunction underwent bladder-bowel training before the implantation. All procedures were performed in the presence of sterile urine using a conventional subureteral transurethral injection technique.
ResultsThere were no statistically significant differences between groups in terms of mean age, sex, RRU side, 99mTc-DMSA uptake, and reflux grade. The overall resolution rates based on the number of RRUs for up to three endoscopic treatments were 80% (56/70) in Dexell group and 94.8% (55/58) in Vantris group (p = 0.012). No postoperative recurrences or vesicoureteral junction obstructions were seen in any group.
ConclusionsDexell and Vantris provided an effective and safe endoscopic VUR treatment in the early and mid-term follow up of children with primary VUR. The effectiveness of these substances, which can produce different mass effects with different particle sizes, in safe VUR resolution, needs further investigations.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora