Hasta la fecha no existe un tratamiento efectivo para la nefropatía inducida por contraste (CIN). Recientemente, la N-acetilcisteína (NAC) ha dado algunos resultados prometedores en la prevención de CIN. En este estudio se analizó los efectos estructurales de la NAC en la CIN.
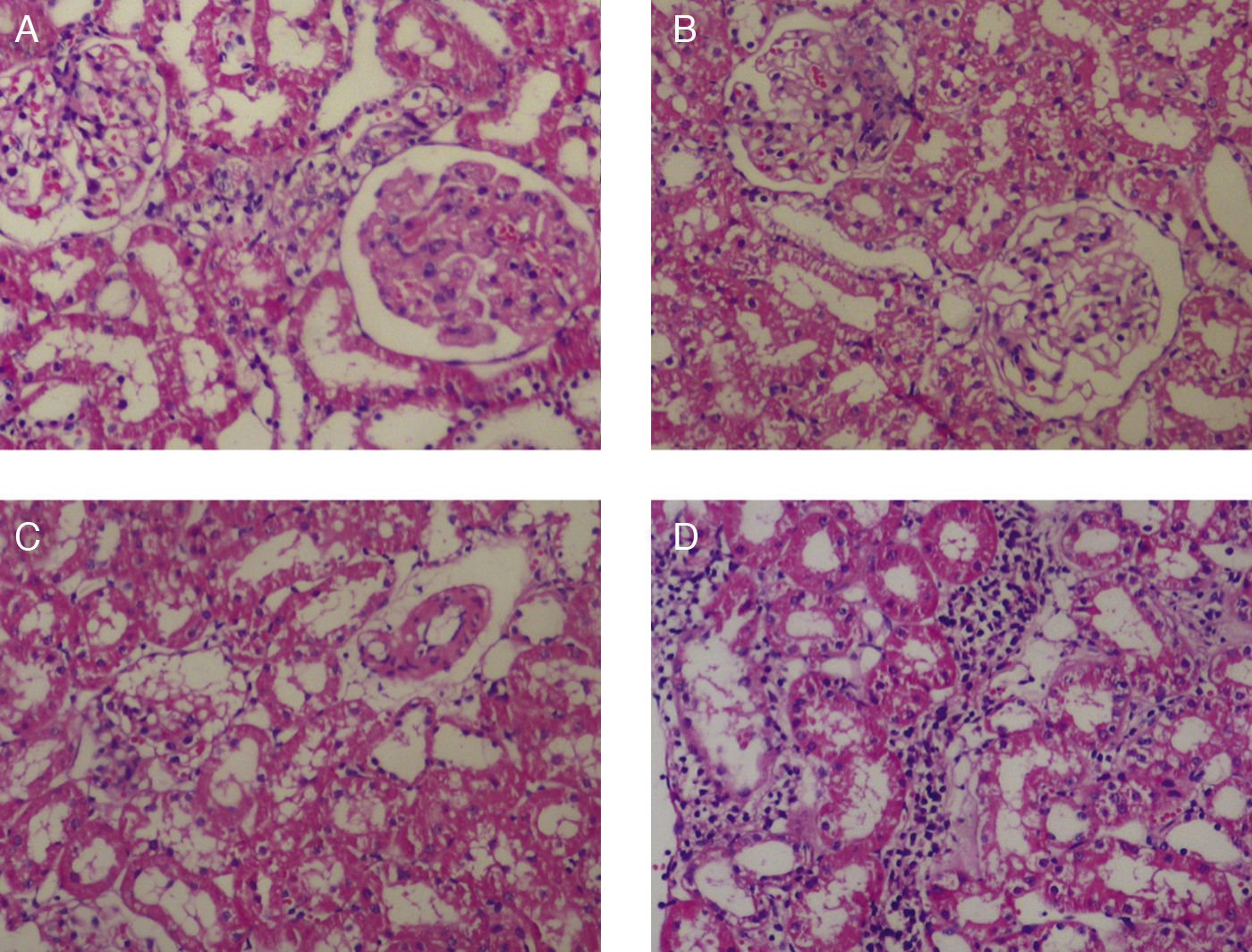
Material y métodosSe asignó 40 ratas albinas Wistar macho de manera aleatoria en 4 grupos: el grupo 1 (n=9) que recibía solo agua destilada, el grupo 2 (n=10) que recibió medio de contraste (CM), el grupo 3 (n=8), que recibió contraste más NAC y el último grupo (n=10) que recibió solo NAC. Al final del tercer día se extrajo los riñones izquierdo y derecho y se les realizó un examen histopatológico. Todas las secciones de tejido fueron examinadas con un microscopio óptico por el mismo histopatólogo buscando alteraciones sin conocer el tratamiento recibido. Se calcularon las puntuaciones de daño glomerular, las de daño arteriolar y las de daño tubulointersticial.
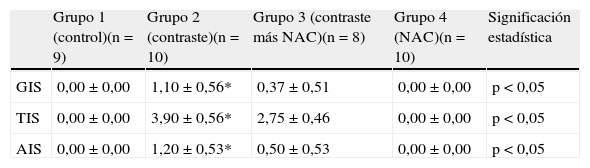
ResultadosHubo diferencias significativas entre las puntuaciones de daño glomerular, arteriolar y tubulointersticial en todos los grupos (p<0,05). las puntuaciones de daño glomerular, arteriolar y tubulointersticial de los grupos 1 y 4 no fueron significativamente diferentes entre sí (p>0,05). Las puntuaciones de daño renal en el grupo 3 fueron mayores que en grupo 1 y en el grupo 4, pero significativamente menores que las puntuaciones del grupo 2 (p<0,05).
ConclusiónLa NAC podría ser útil para evitar el daño tisular renal por CIN, especialmente en pacientes de alto riesgo.
To date, there is no effective treatment of contrast induced nephropathy (CIN). N-acetylcysteine (NAC) has yielded some promising results recently in the prevention of CIN. In this study, the structural effects of NAC on CIN were analyzed.
Material and methodsFourty adult Wistar albino male rats were randomly allocated to four groups. The first group was the control group (n=9) which received only distilled water; second group was the contrast group (n=10) which received CM; the third group was the contrast plus NAC group (n=8) which received CM and was treated with NAC; and the last group was NAC group (n=10) which received only NAC. At the end of the 3rd day, the right and left kidneys were removed and reserved for histopathological examination. All tissue sections were examined with light microscope looking for histopathological changes by the same experienced renal pathologist, without knowledge of the prior treatment. Histopathological examination was conducted in a blinded fashion, and glomerular injury scores, arteriolar injury scores and tubulointerstitial injury scores were calculated.
ResultsThere was a significant difference among the scores of glomerular injury, arteriolar injury and tubulointerstitial injury in all groups (p<0.05). The scores of glomerular, arteriolar and tubulointerstitial injury of the group-1 and group-4 were not significantly different from each other (p<0.05). Renal injury scores in group-3 group were higher than in group-1 and-4, but significantly lower than the scores of the Group-2 (p<0.05).
ConclusionNAC could be useful to prevent the renal tissue from CIN, especially in high-risk patients.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora