Colombia is a country with a high prevalence of hypothyroidism, approximately 18.5% compared to the rest of Latin American countries, which is estimated at 10%. That is why in the ophthalmology consultation we find a large proportion of patients with this disease and who also present symptoms of dry eye. When conducting a search in the medical literature, most publications refer to the clinical presentation of dry eye in hyperthyroidism, which is why the main objective of this study is to evaluate tear function tests in the diagnosis of dry eye in patients with hypothyroidism.
MethodsThis is an observational, cross-sectional study carried out in the period between May and December 2019 in the ocular surface unit of the Ophthalmic Technology Center (CTO) in Bogotá. The tests of: OSDI test (Ocular Surface Disease Index), Schirmer type I, tear meniscus height, NiBUT, Osmolarity, Ferning test, Lisamine Green test of 59 patients with Dry Eye Disease (DED) and history of hypothyroidism.
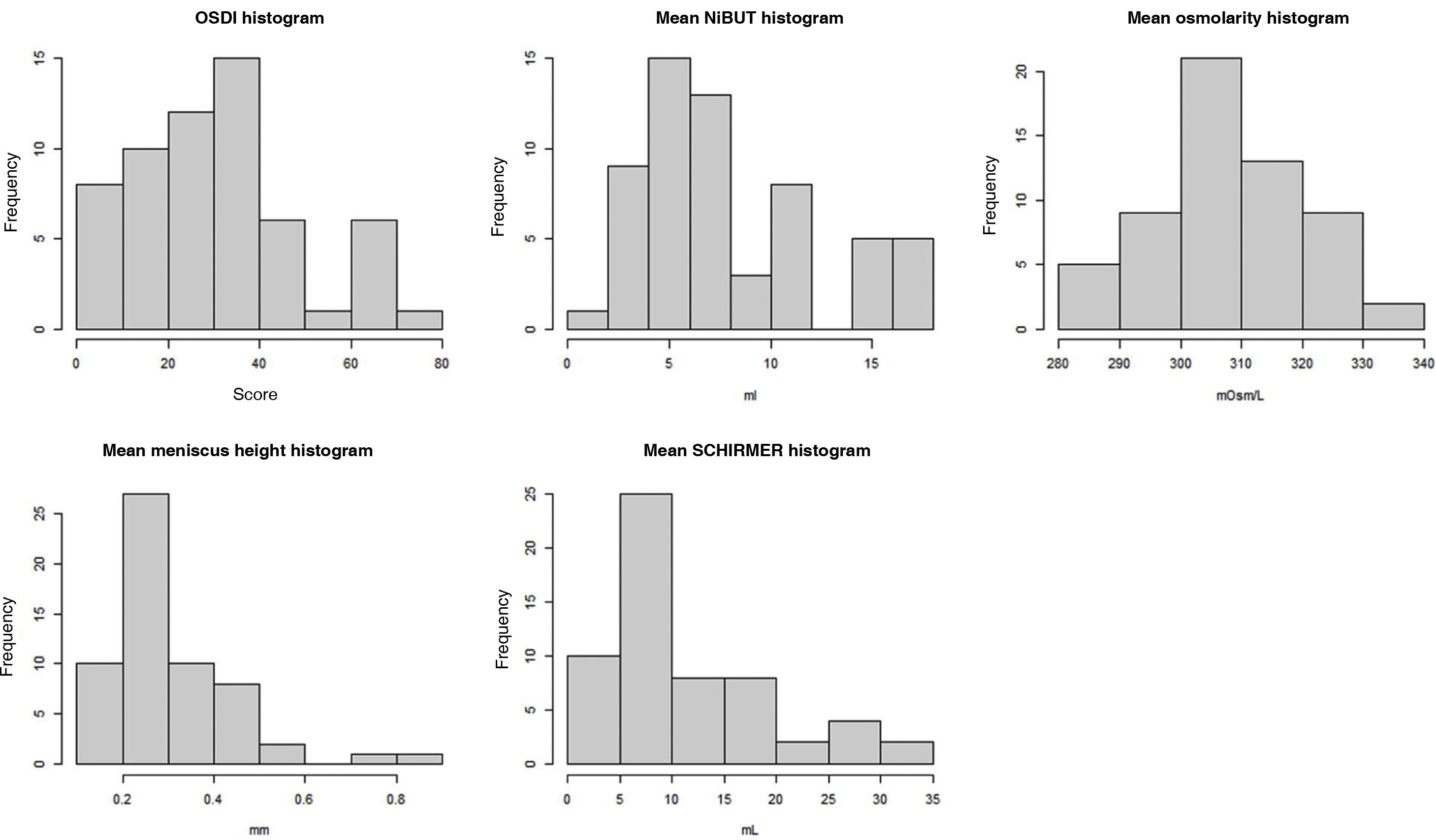
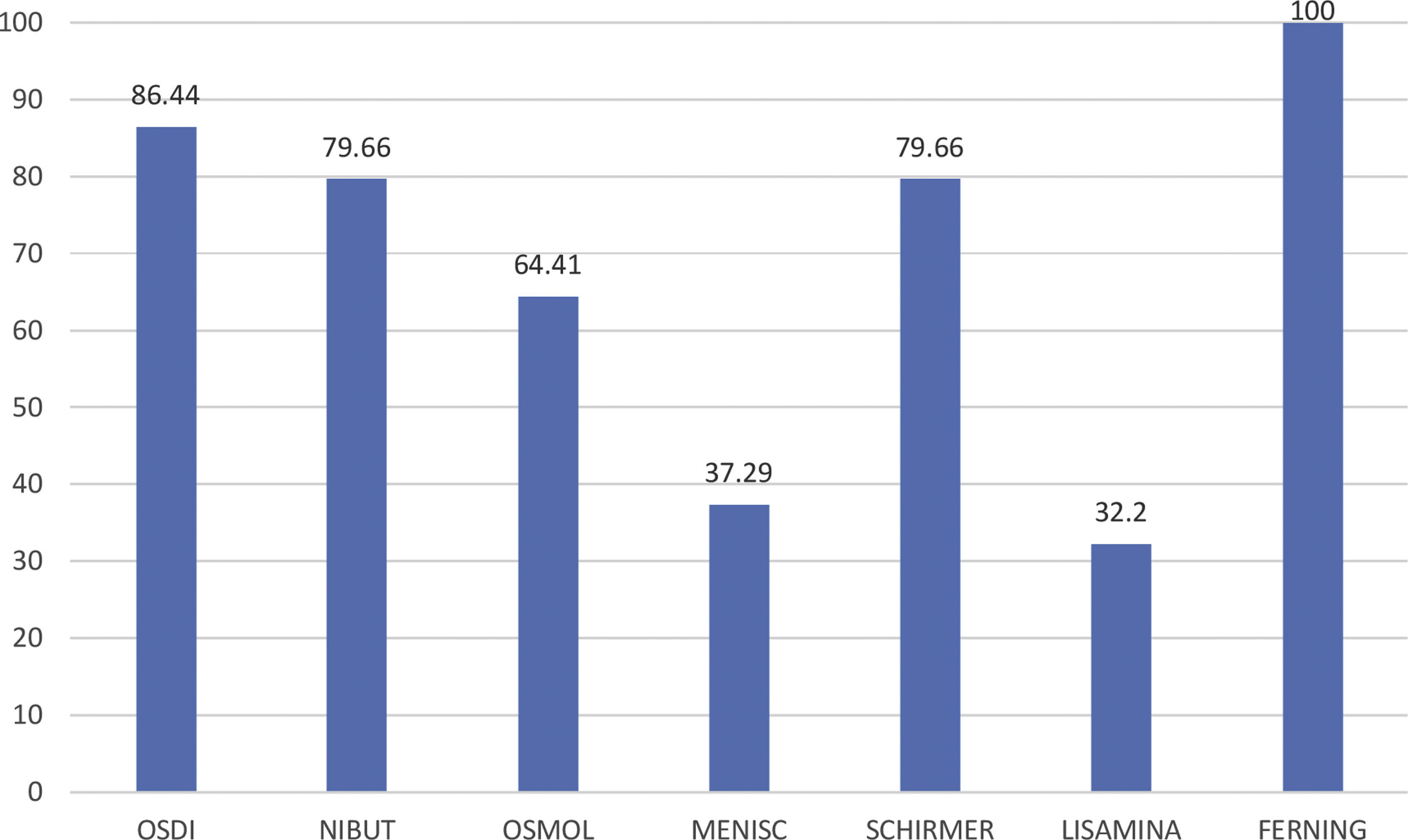
ResultsSchirmer type I and NiBUT tests were the parameters that presented the highest percentage of severity, while lissamine green staining and meniscometry showed a tendency to normality.
ConclusionsThe population of this study presents a mixed type dry eye without epithelial cell damage.
Colombia es un país con una alta prevalencia de hipotiroidismo aproximadamente 18.5% respecto al resto de países latinoamericanos que se estima en un 10%. Es por ello que en la consulta de oftalmología se encuentra una gran proporción de pacientes con esta enfermedad y que además presentan síntomas de ojo seco. Al realizar una búsqueda en la literatura médica, la mayoría de publicaciones se refieren a la presentación clínica de ojo seco del hipertiroidismo. El objetivo de este estudio es describir los hallazgos de las diferentes pruebas para el diagnostico de ojo seco en pacientes con hipotiroidismo.
MétodosSe trata de un estudio observacional, de tipo transversal realizado en el periodo comprendido entre Mayo y Diciembre de 2019 en la unidad de superficie ocular del Centro de Tecnología Oftálmica (CTO) en Bogotá. Se evaluaron las pruebas de: Test de OSDI (Ocular Surface Disease Index), Schirmer tipo I, altura del menisco lagrimal, NiBUT, Osmolaridad, test de Ferning, test de Verde de Lisamina de 59 pacientes con Enfermedad de Ojo Seco (EOS) y antecedente de hipotiroidismo.
ResultadosLas prueba de Schirmer tipo I y NiBUT fueron los parámetros que presentaron mayor porcentaje de severidad, mientras que la tinción con verde de lisamina y la meniscometria mostraron tendencia a la normalidad.
ConclusionesLa población de este estudio presenta un ojo seco tipo mixto sin daño en las células epiteliales.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora