To classify dome shaped macula cases by their bulge height (BH). To analyze the characteristics associated with the groups formed by this classification.
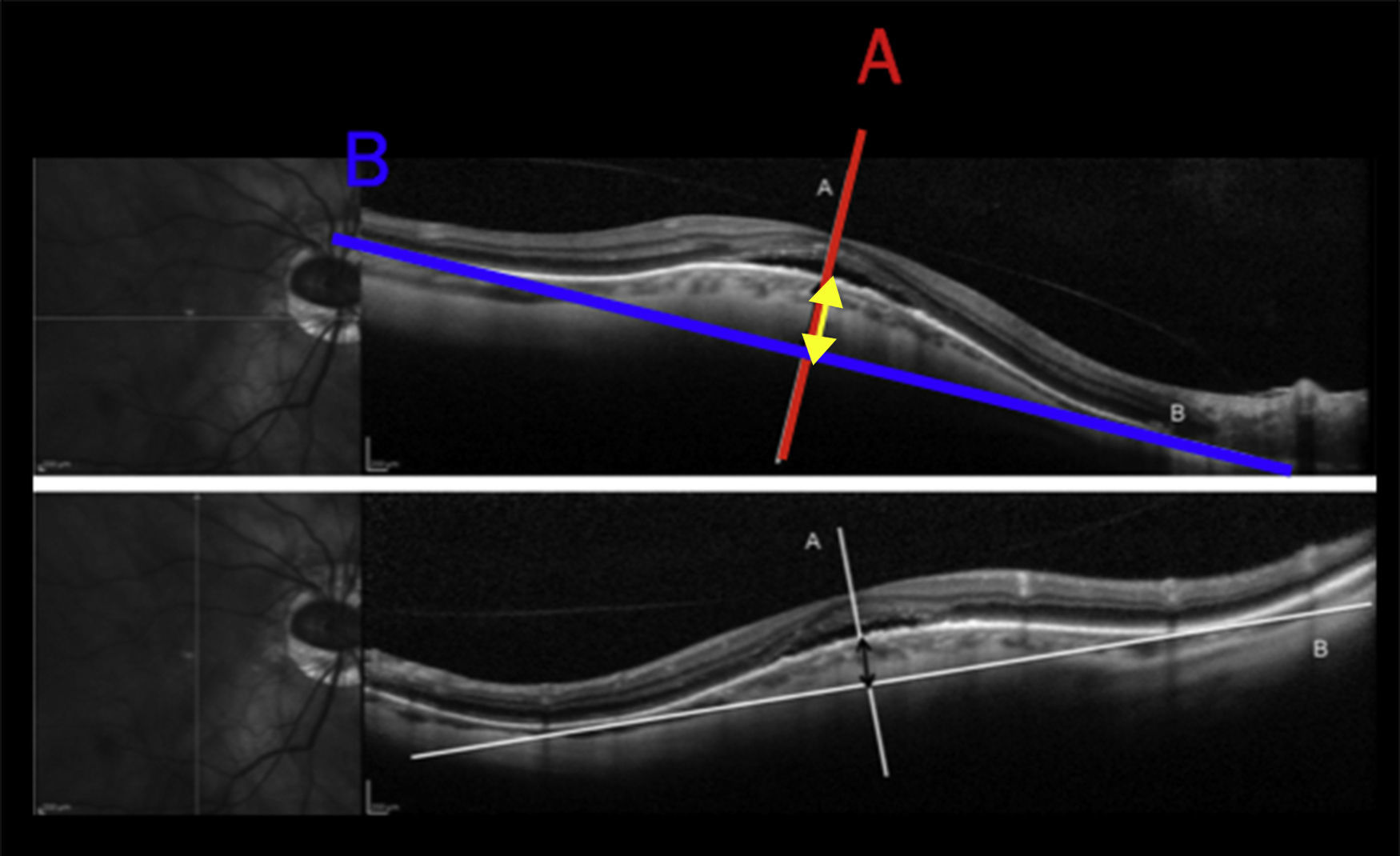
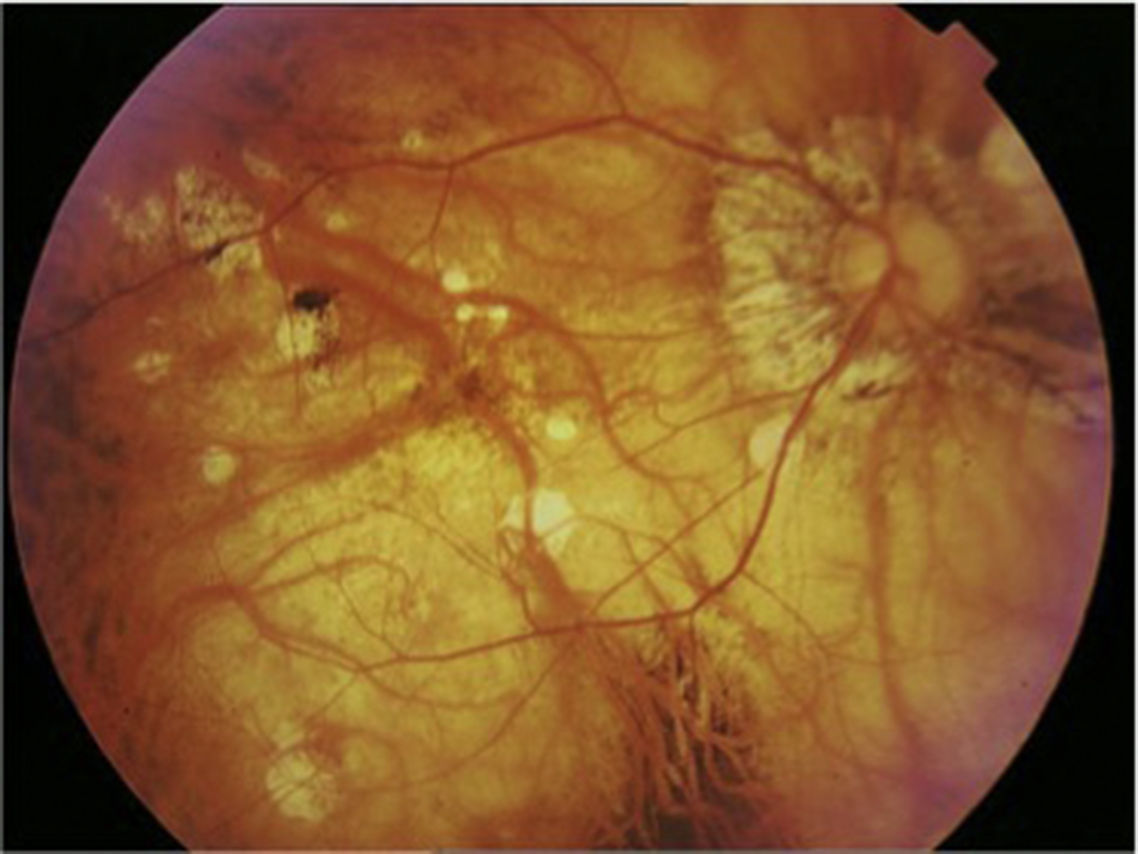
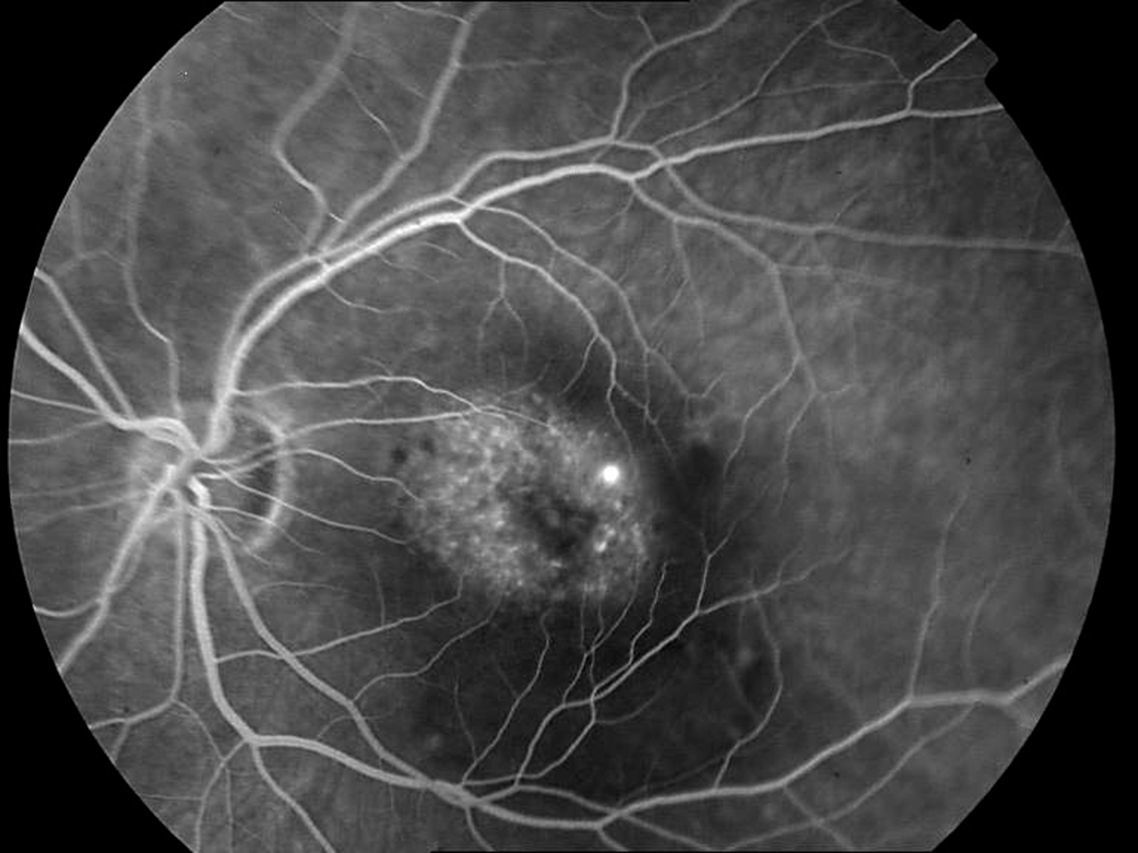
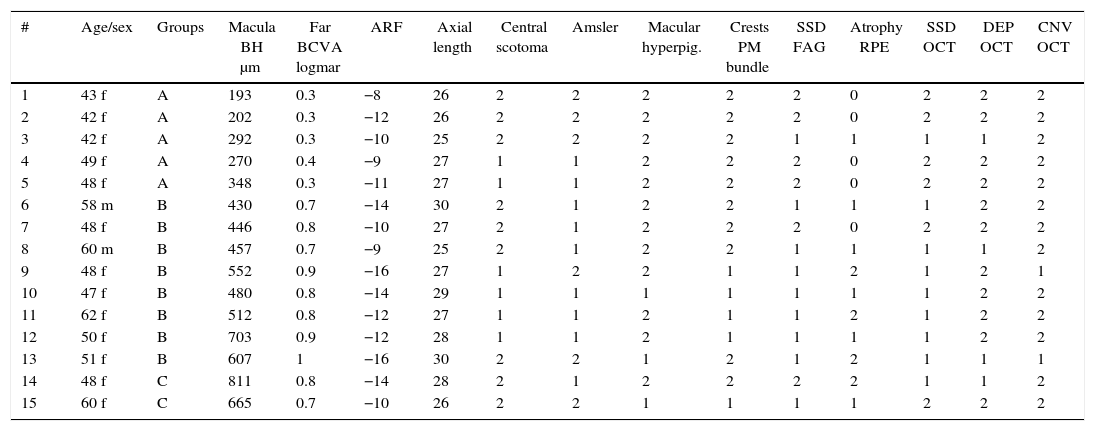
MethodsObservational, descriptive and cross-sectional study on 15 selected eyes with dome shaped macula and high myopia. Using Caillaux method and optical coherence tomography images, 3 groups were determined by their BH: low (50–350μm), medium (351–650μm), and high (>650μm), and a study of visual acuity, axial length, presence of subfoveal serous detachment, and images by fluorescein angiography and optic coherence tomography, as main variables. The confidence interval was 95%.
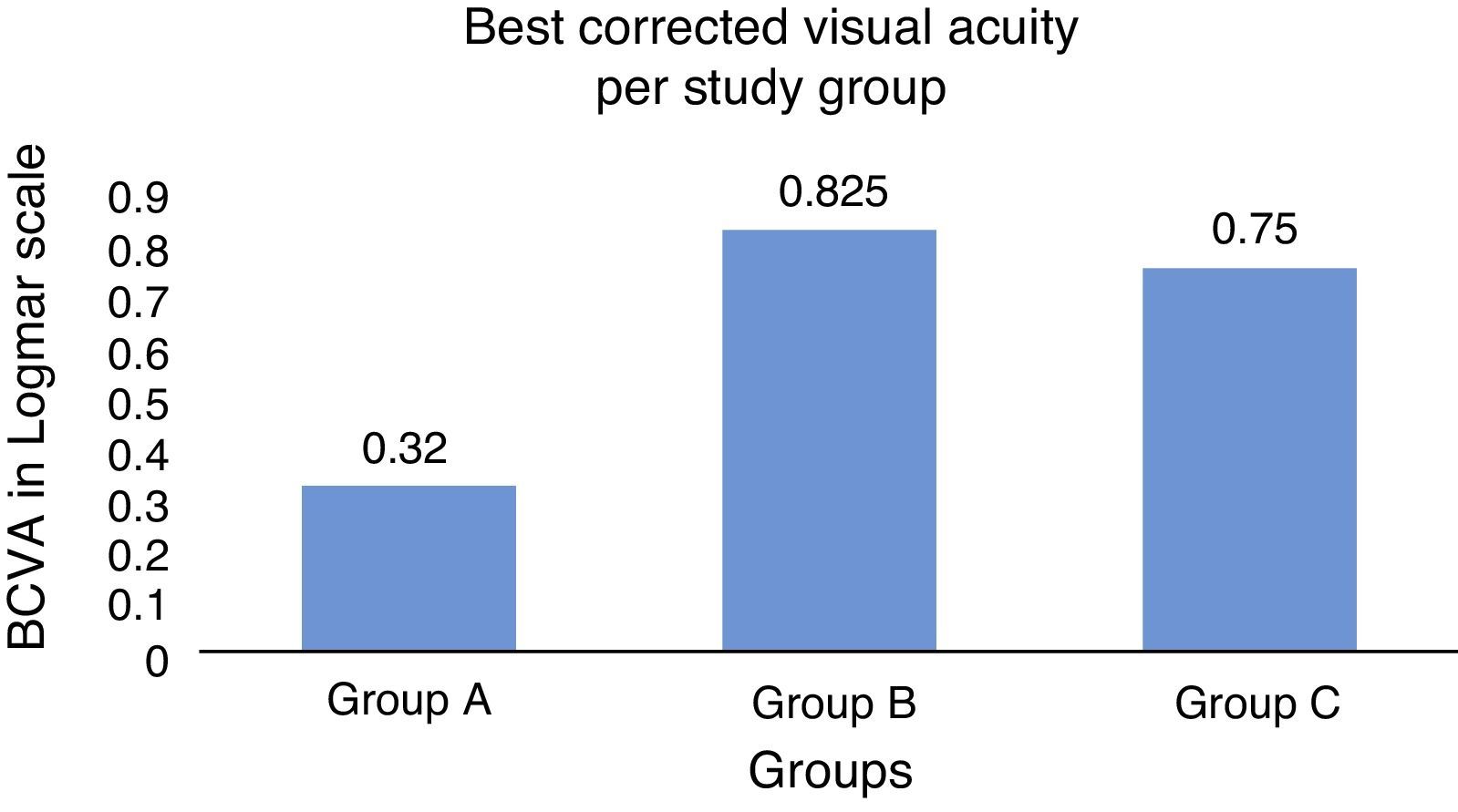
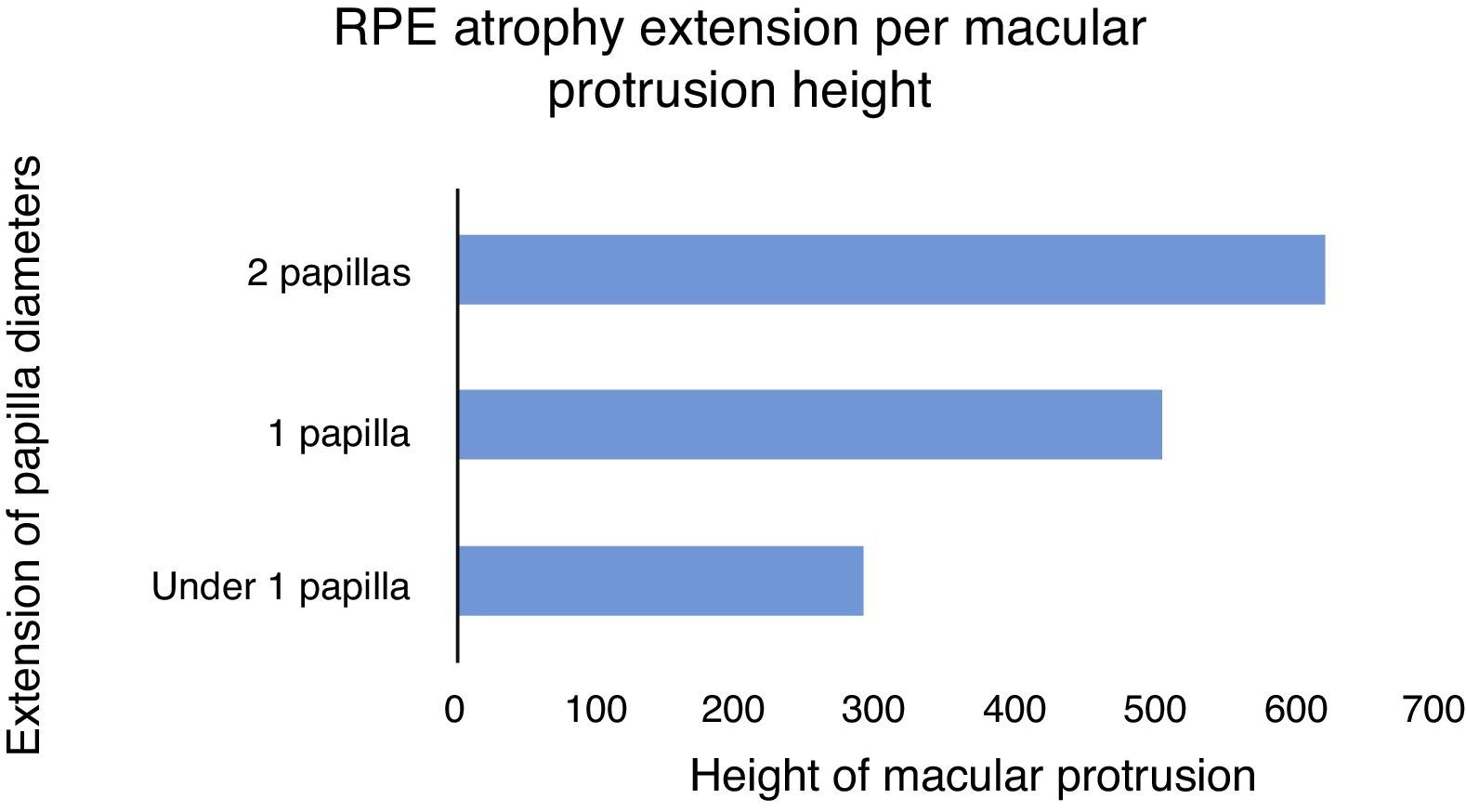
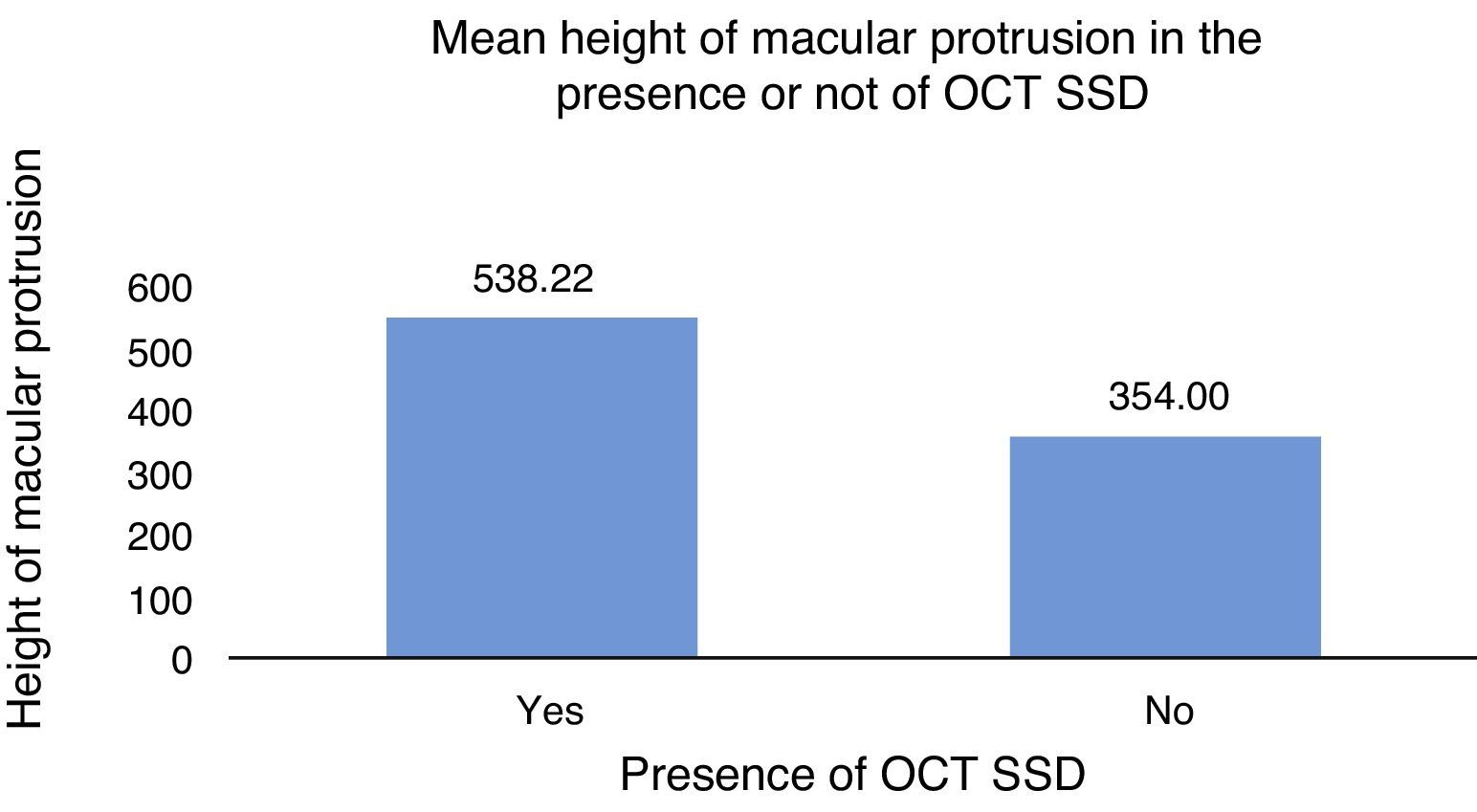
ResultsBy using the chi-squared test, the study showed that a BH higher than 400μm was associated with lower visual acuity, presence of subfoveal serous detachment, and greater atrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium measured by disk diameters (p<0.05).
ConclusionsThe medium and high BH showed a positive correlation with the presence of foveal serous detachment and a lower visual acuity.
Clasificar la mácula en domo según la altura de protrusión macular (AP) y analizar las características asociadas a cada grupo.
MétodosEstudio observacional, descriptivo y transversal. Selección de 15 ojos con mácula en domo y miopía magna. Utilizando imágenes por tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT) y el método de Caillaux, se clasificó la AP en baja (50-350μ), media (351-650μ) y alta (>650μ) y se estudió la agudeza visual, longitud axial, presencia de desprendimiento seroso subfoveal y las imágenes obtenidas por angiografía fluoresceínica y OCT como variables principales. El nivel de confianza utilizado fue de 95%.
ResultadosUtilizando el test de chi cuadrado, el estudio observó que una AP mayor a 400μ se asoció con menor agudeza visual, mayor presencia de desprendimiento seroso subfoveal y mayor presencia de atrofia del epitelio pigmentario de la retina medida en diámetros de papila (p<0,05).
ConclusionesLas AP media y alta mostraron una asociación positiva con la presencia de desprendimiento seroso subfoveal y disminución de laagudeza visual.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora