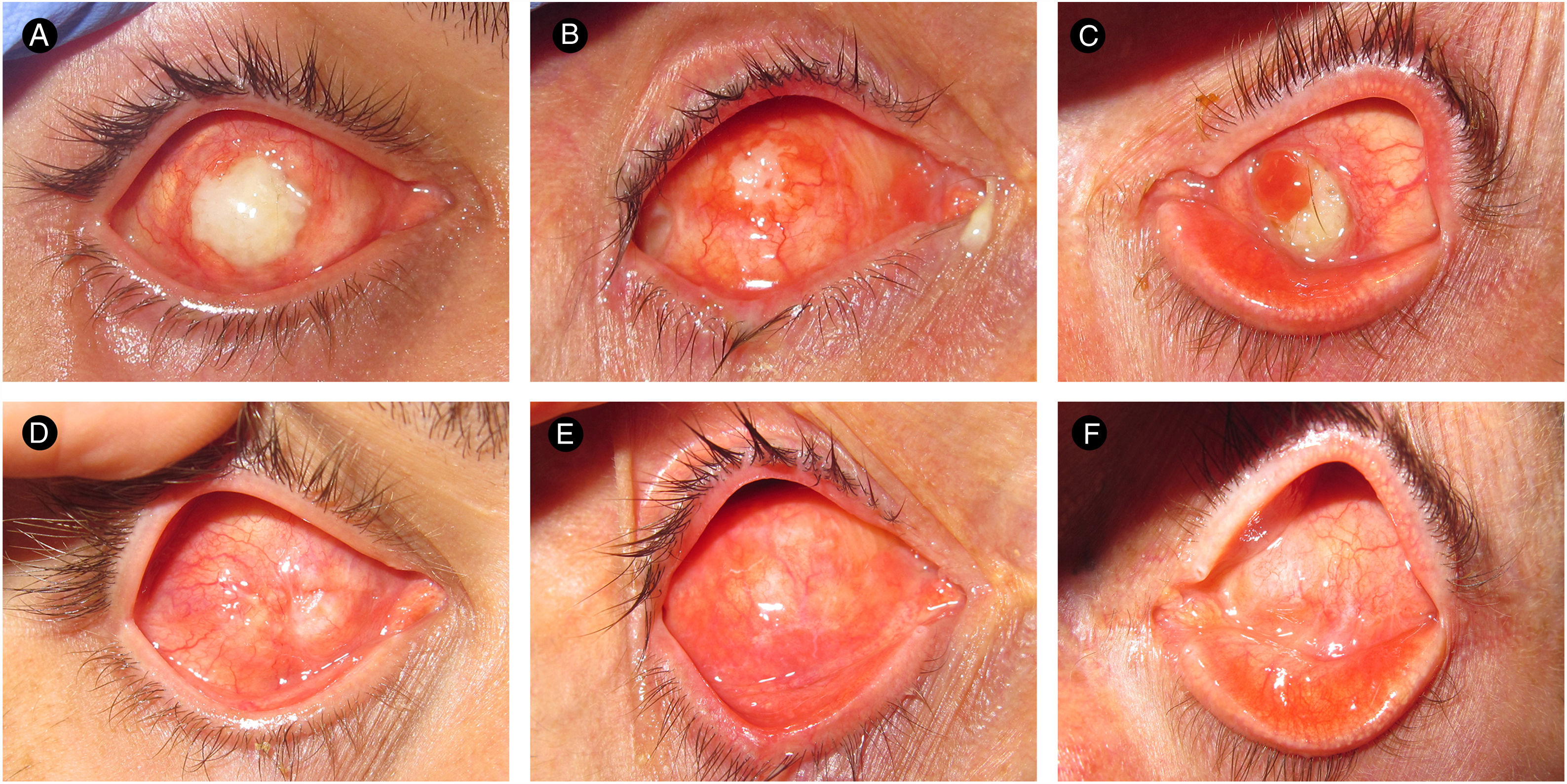
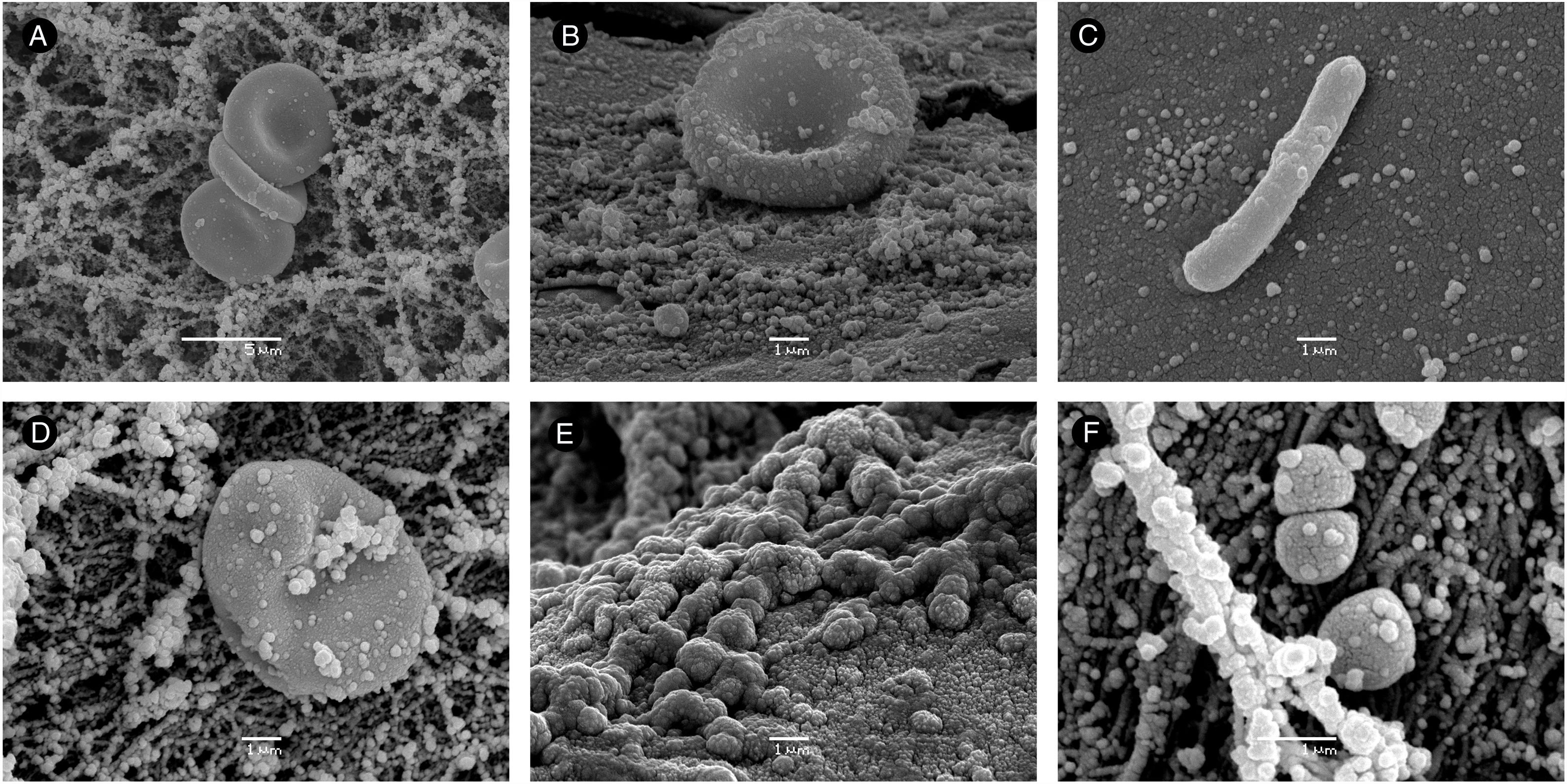
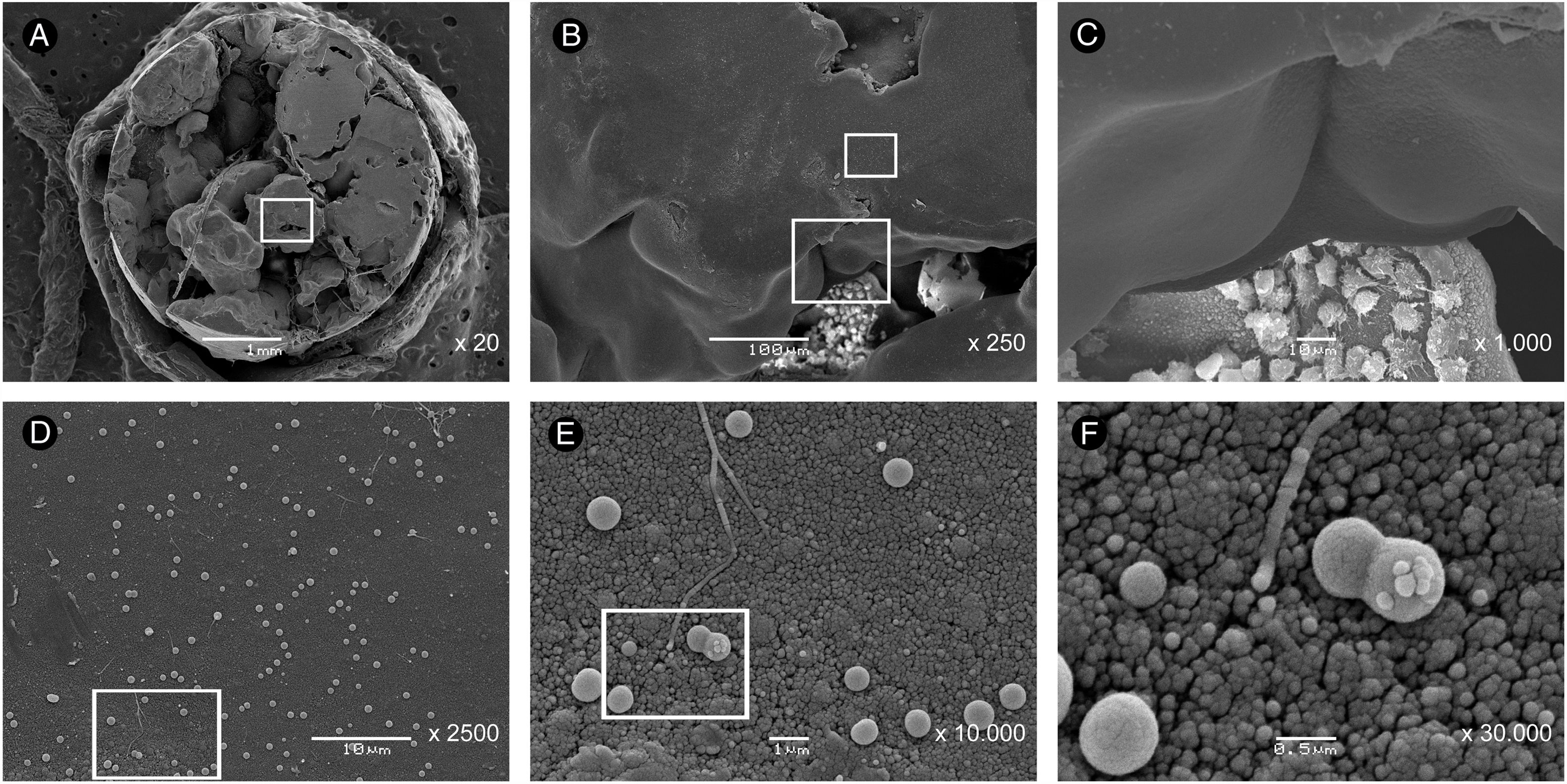
Three cases are presented of anophthalmic patients with exposed orbital implants. Although only one patient showed evident clinical signs of infection, all three implants were studied to determine the presence of microorganisms adhered to their surface using a scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and microbiological culture.
The SEM allowed the visualisation of microorganisms adhered to the three implants, although only one of them showed growth in the microbiological cultures. In addition, the SEM technique used in case No. 3 achieved a better orientation and appreciation of the microorganisms with respect to the images of cases No. 1 and 2. These findings support the idea that the surface of exposed orbital implants is colonised by microorganisms, even when they still do not show obvious signs of infection. Therefore, mechanical removal of the exposed surface of the implant is necessary before covering it with grafts or flaps.
Se presentan tres casos de pacientes anoftálmicos con implantes orbitarios expuestos. Aunque sólo un paciente mostraba signos clínicos evidentes de infección, los tres implantes fueron estudiados para determinar la presencia de microorganismos adheridos a su superficie mediante microscopia electrónica de barrido (MEB) y cultivo microbiológico.
La MEB permitió la visualización de microorganismos adheridos a los tres implantes, si bien sólo uno de ellos presentó crecimiento en los cultivos microbiológicos. Además, la técnica de MEB empleada en el caso nº 3 consiguió una mejor orientación y apreciación de los microorganismos, respecto a las imágenes de los casos nº 1 y 2. Estos hallazgos apoyan la idea de que la superficie de los implantes orbitarios expuestos está colonizada por microorganismos incluso cuando todavía no muestran signos evidentes de infección. Por lo tanto, es necesario una eliminación mecánica de la superficie expuesta del implante antes de recubrirla con injertos o colgajos.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora