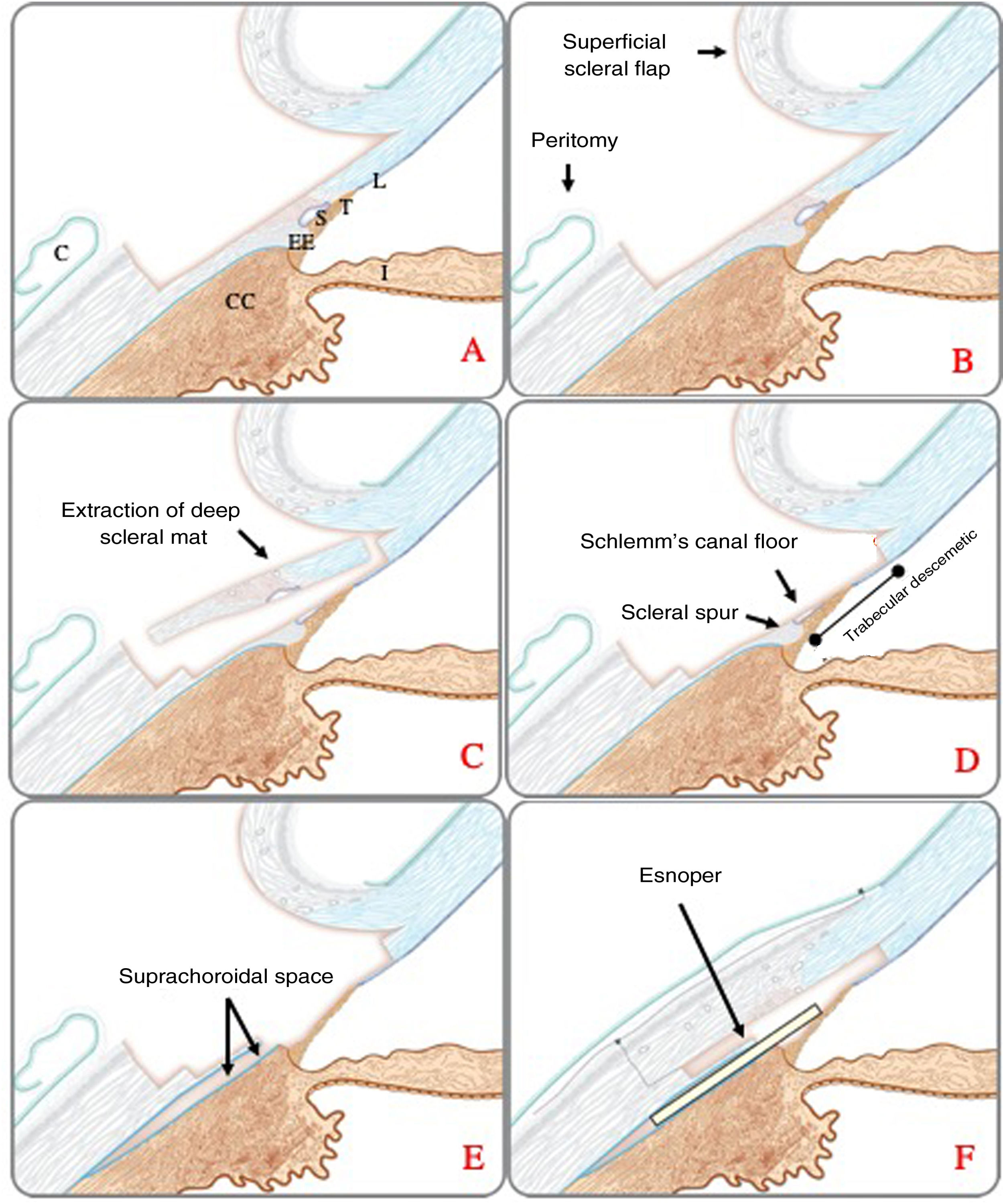
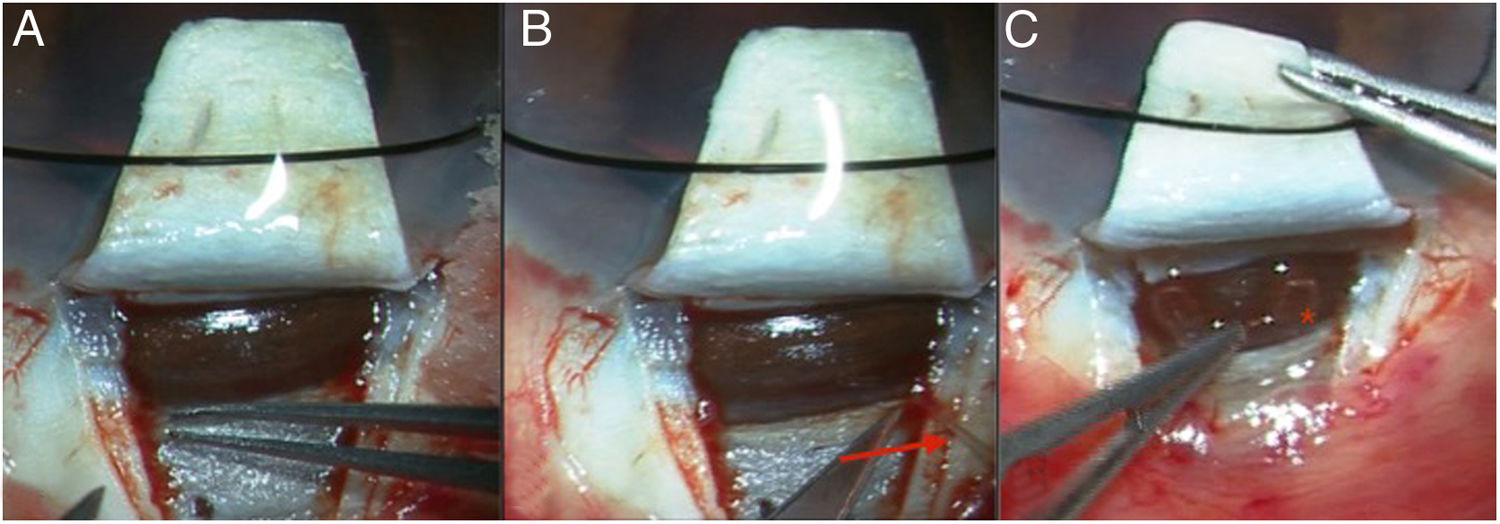
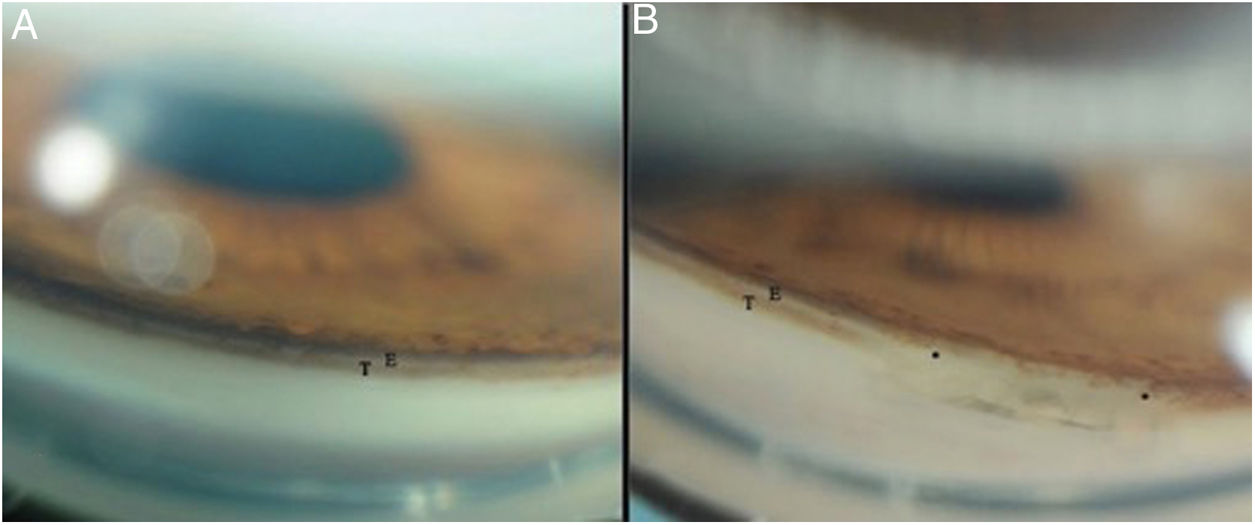
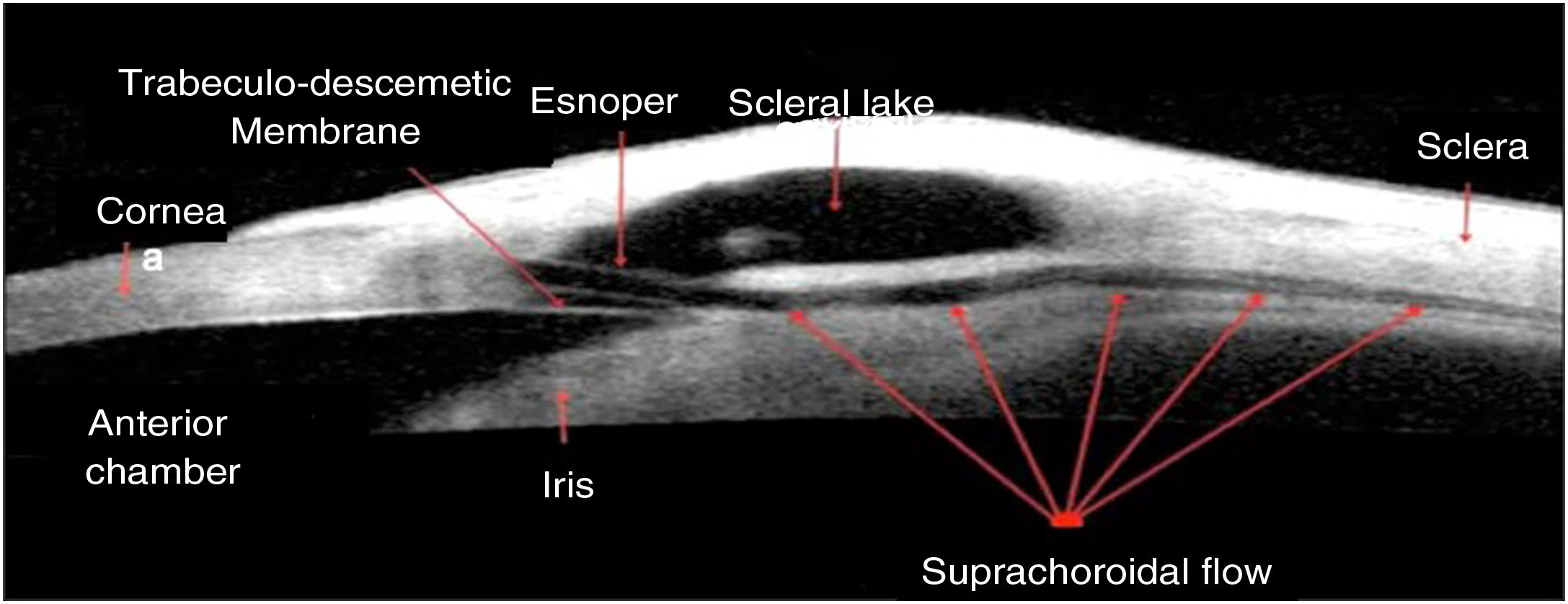
To evaluate the outcomes of a novel modification of the non-penetrating deep sclerectomy (NPDS) approach for glaucoma management called spurectomy.
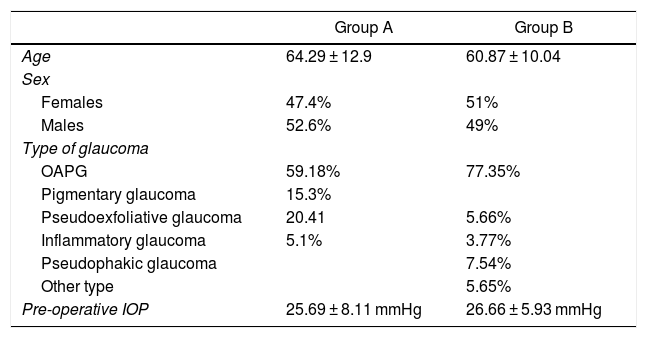
MethodsObservational comparative non-randomized retrospective study including 98 glaucomatous eyes of 76 patients operated on with the spurectomy technique consisting of the combination of the excision of the scleral spur with NPDS (group A). A control group (group B) including 53 glaucomatous eyes of 43 patients operated on with classical NPDS was also included. Changes in intraocular pressure (IOP) and medications required as well as complications were recorded in a 12-month follow-up.
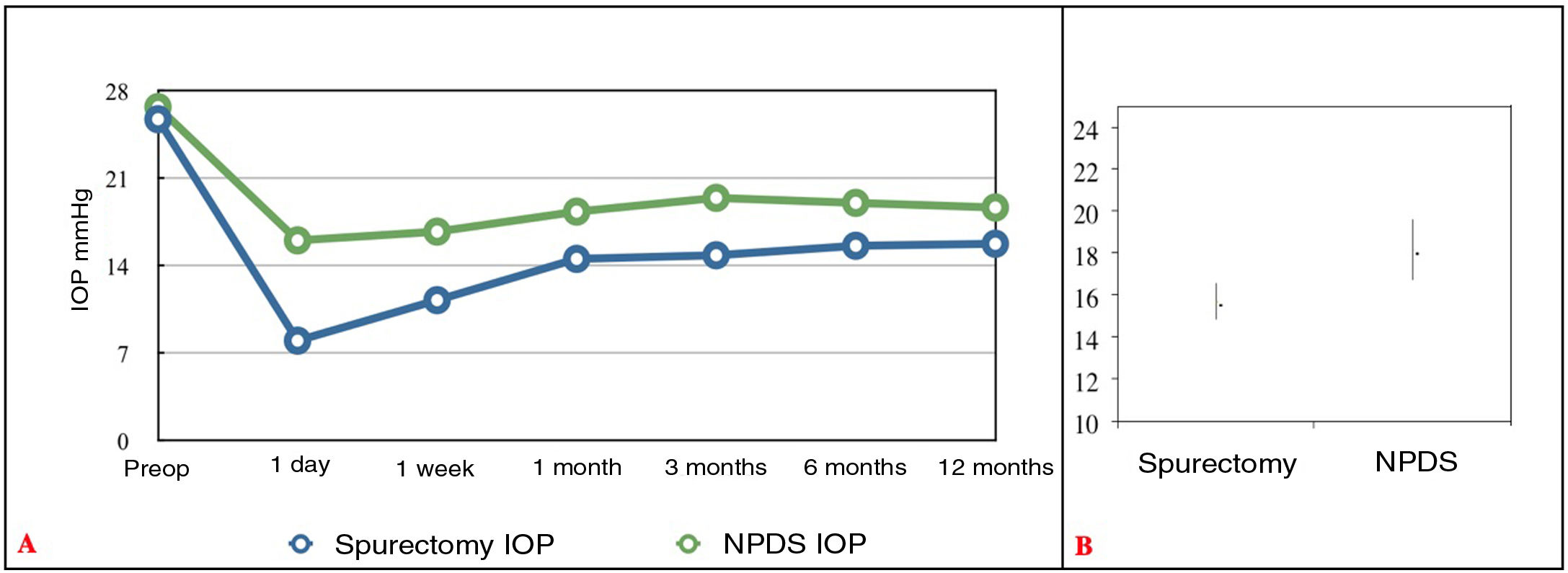
ResultsMean IOP decreased from 25.69 ± 8.11 preoperatively to 15.73 ± 4.16 mm Hg postoperatively in group A (p < 0.001). In group B, mean IOP decreased from 26.66 ± 5.93 preoperatively to 18.19 ± 5.93 mm Hg postoperatively (P < .001). Differences between groups in postoperative IOP was statistically significant (P < .001). At 12 months after surgery, 13.27% and 52.83% of eyes in groups A and B required topical antihypertensive therapy (P < .001). The rate of absolute success after surgery was 87.5% and 47.17% in groups A and B, with significantly higher rate of relative success in group B (P < .001). No significant differences among groups were found in the complication rate (P = .960). The most common postoperative complication was microperforation of the trabeculo-descemetic membrane in both groups.
ConclusionsSpurectomy is a safe and effective technique when compared with conventional NPDS and seems a promising alternative in the surgical management of glaucoma, optimizing the efficacy of the treatment and minimizing complications.
Evaluar los resultados de una nueva modificación de la esclerectomía profunda no perforante (EPNP) denominada espolonectomía.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo no aleatorizado y comparativo que incluyó 98 ojos (grupo A) operados con espolonectomía, que consiste en la combinación de la escisión del espolón escleral con EPNP. El grupo control (B) incluyó 53 ojos operados con EPNP clásica. Durante 12 meses se estudiaron la presión intraocular (PIO), los medicamentos antiglaucomatosos que requirieron y las complicaciones.
ResultadosLa PIO media disminuyó de 25,69 ± 8,11 preoperatoria a 15,73 ± 4,16 mmHg después de la cirugía en el grupo A (p < 0,001). En el grupo B disminuyó de 26,66 ± 5,93 preoperatoria a 18,19 ± 5,93 mmHg postoperatoria (p < 0,001). Las diferencias entre grupos de la PIO postoperatoria fue estadísticamente significativa (p < 0,001). A los 12 meses después de la cirugía, el 13,27 y el 52,83% de ojos en los grupos A y B requirieron tratamiento antihipertensivo tópico (p < 0,001). La tasa de éxito absoluto después de la cirugía fue del 87,5 y del 47,17% en los grupos A y B, con una tasa significativamente mayor de éxito relativo en el grupo B (p < 0,001). No hubo diferencias significativas entre los grupos en la tasa de complicaciones (p = 0,960). La complicación postoperatoria más frecuente fue la microperforación de la membrana trabeculo-descemética en ambos grupos.
ConclusionesLa espolonectomía es una técnica segura y eficaz en comparación con la EPNP convencional y parece una alternativa prometedora en el tratamiento quirúrgico del glaucoma, optimizando la eficacia del tratamiento y minimizando las complicaciones.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora