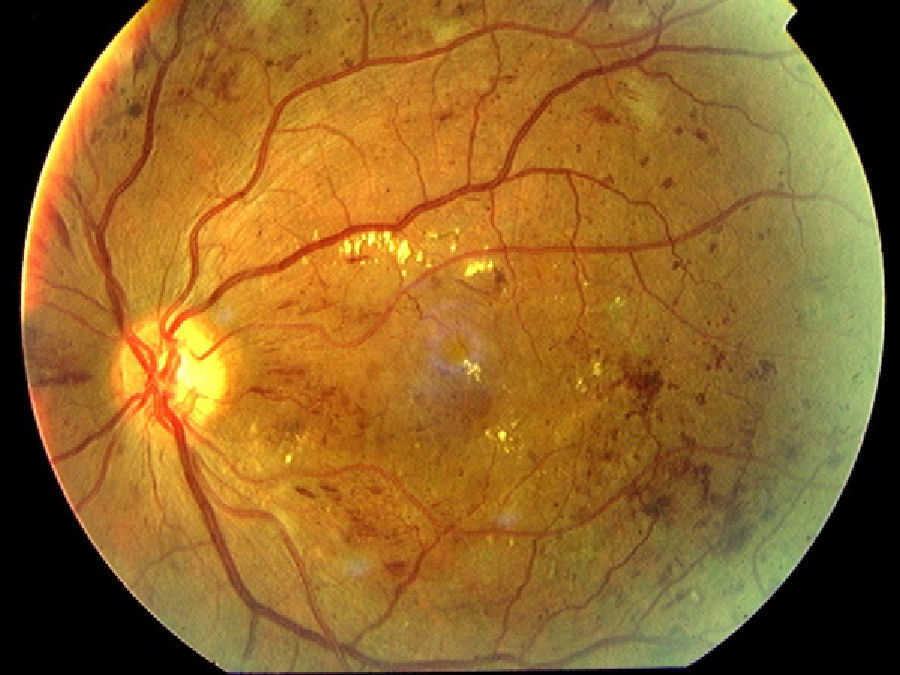
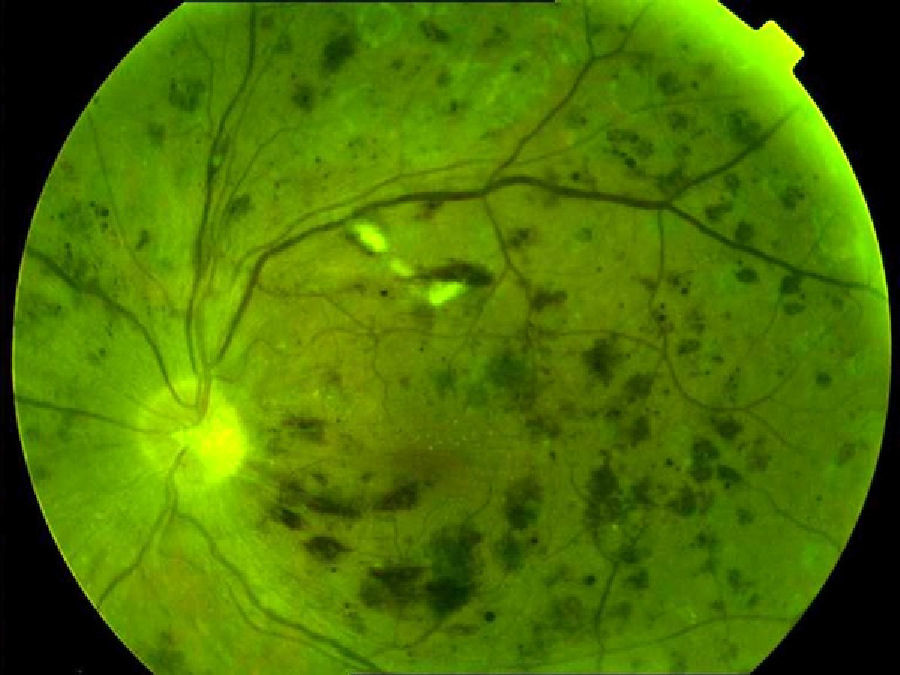
To determine the validity of retinal photography in the diagnosis of diabetic macular edema. Determine the number and size of the photographs for its correct diagnosis.
MethodsCross-sectional observational study consisting of 420 eyes of patients with diabetic retinopathy, using a combination of retinography (simple, stereoscopic, red-free light), after expansion, to determine its validity in the diagnosis of diabetic macular edema. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values and the correlation with the gold standard test (optical coherence tomography) were calculated. The retinographs were evaluated by three experts and their results were analyzed using the statistical program SPSS 15.0 Windows.
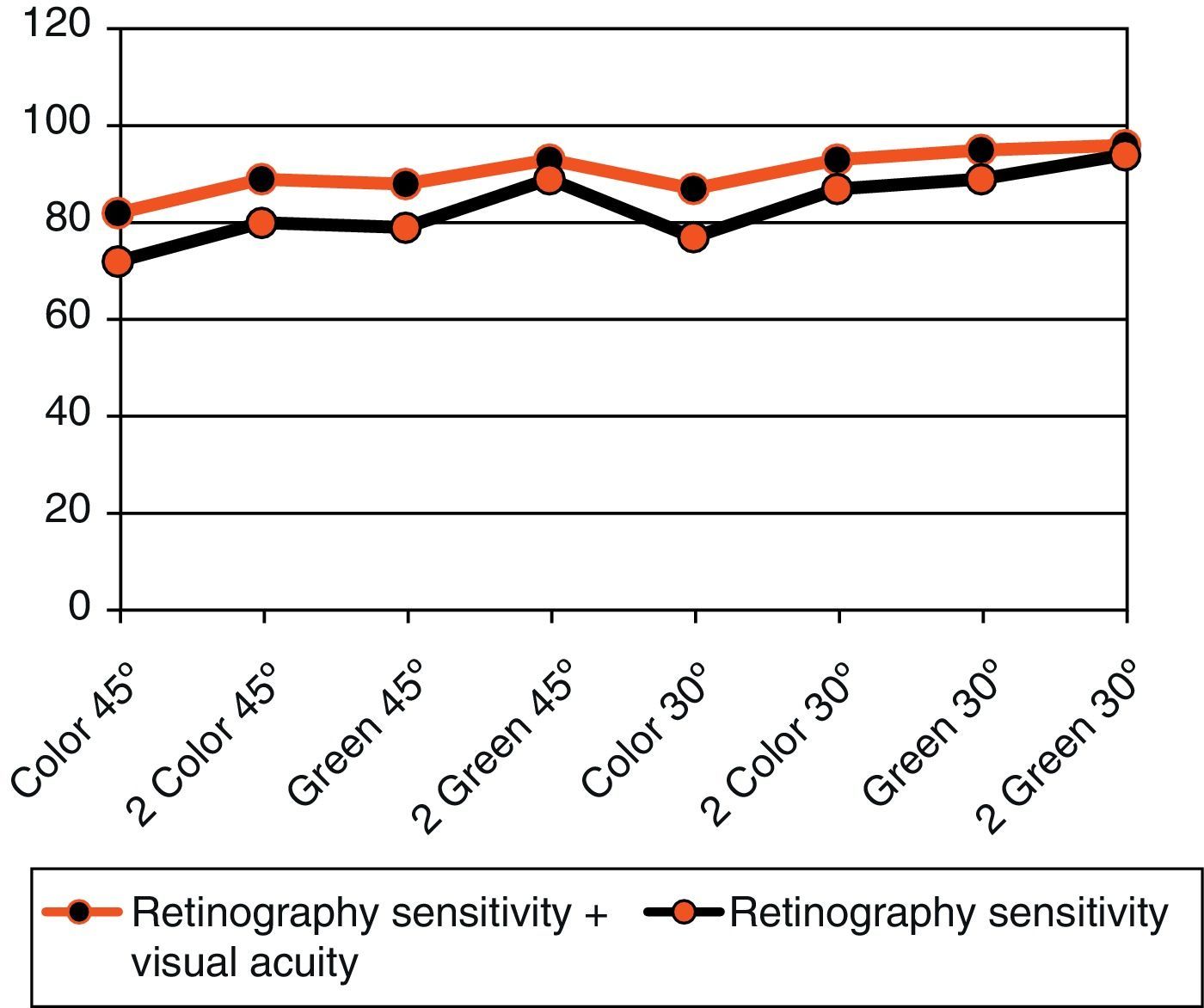
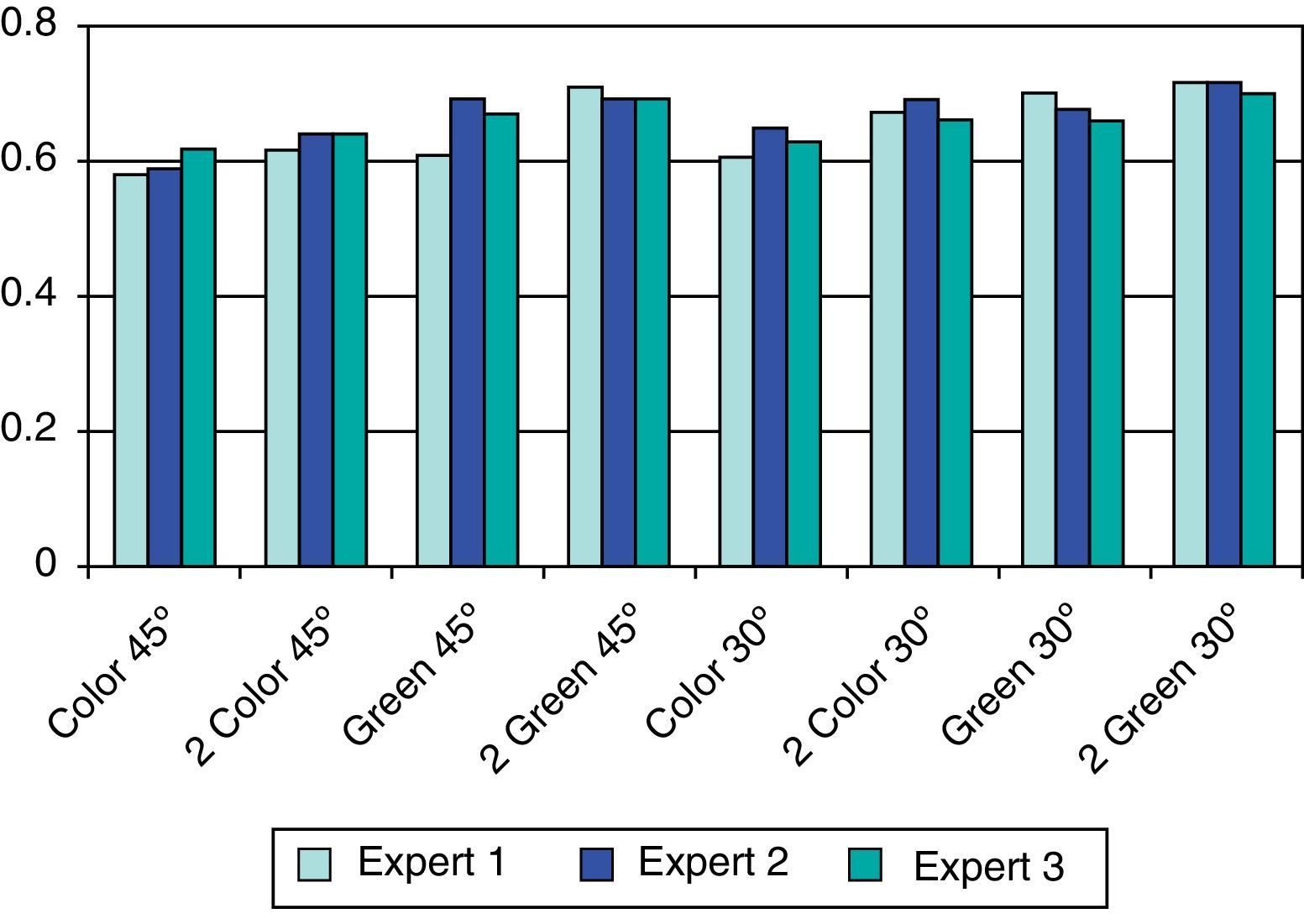
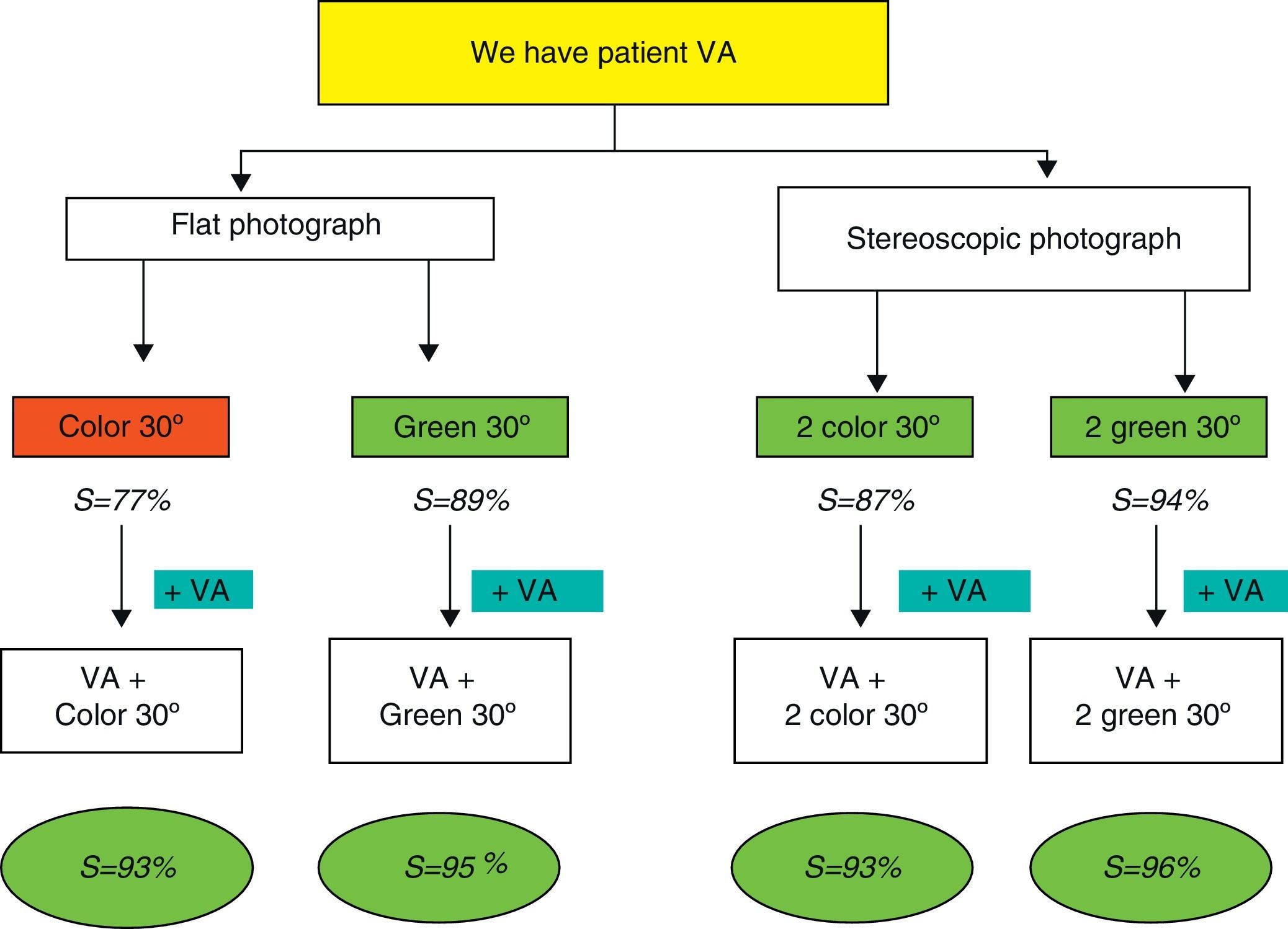
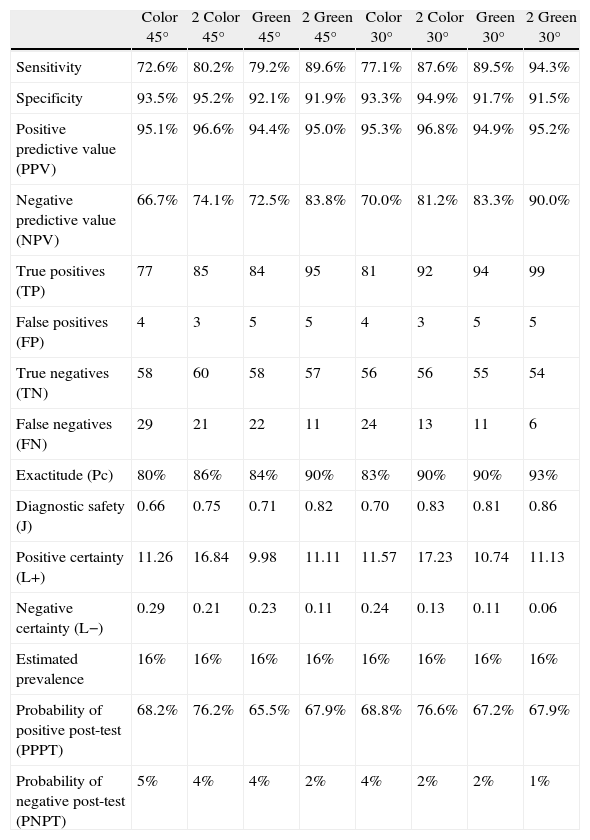
ResultsSensitivities were below 80% in simple photographs and above 80% in the stereoscopic retinography, whereas those associated with red-free filters, reaching the 30° green stereoscopic photography, showed a sensitivity of 94.3%. The specificity was 95% in color and red-free stereoscopic retinography of 45° and 30°. The positive predictive value was greater than 95% and the negative value was greater than 90% with a coefficient of agreement of 80%, and a degree of consistency with the benchmark of over 80%.
ConclusionsThe results of the stereoscopic retinographs are sufficient to enable them to be used in screening for diabetic macular edema. The use of a green filter and its combination with visual acuity improves the results in the diagnosis of this disease.
Determinar la validez de las retinografías en el diagnóstico del edema macular diabético. Fijar el número y amplitud de las fotografías necesarias para su correcto diagnóstico.
MétodosEstudio observacional transversal constituido por 650 ojos de pacientes con retinopatía diabética, a los que se realizó una combinación de retinografías (simples, estereoscópicas y luz aneritra), previa dilatación, para determinar su validez, en el diagnóstico del edema macular diabético. Se calcularon sensibilidad, especificidad, valores predictivo positivo y negativo, así como la concordancia con la prueba de referencia (tomografía de coherencia óptica). Las fotografías fueron evaluadas por tres expertos y sus resultados analizados con el programa estadístico SPSS 15.0 Windows.
ResultadosSe obtuvieron valores de sensibilidad inferiores al 80% en el caso de fotografías simples, superando el 80% las retinografías estereoscópicas o aquellas que asocian filtros verdes, siendo la fotografía estereoscópica verde a 30° la que alcanzó mayor sensibilidad, próxima al 94.3%. La especificidad fue del 95% en el caso de fotografías estereoscópicas en color y aneritra a 45 y 30°, respectivamente. El valor predictivo positivo superior al 95% y negativo del 90% con un coeficiente de acuerdo del 80% y un grado de concordancia con la prueba de referencia superior al 80%.
ConclusionesLas retinografías estereoscópicas ofrecen resultados suficientes, como para ser utilizadas en el cribado del edema macular diabético. La utilización de filtros verde (luz aneritra) y su combinación con la agudeza visual mejora los resultados en el diagnóstico de esta enfermedad.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora