To estimate the variability and reproducibility of confocal tomography (HRT), scanning laser polarimetry (GDx) and optical coherence tomography (OCT-Cirrus) to determine the thickness of the layer of ganglion fibers.
MethodA total of 75 normal eyes were examined twice. Inter-individual variability was analyzed after standardizing the results. The coefficient of variation was used to measure the variability between tests, and the Pearson coefficient was used to analyze the correlation between variables.
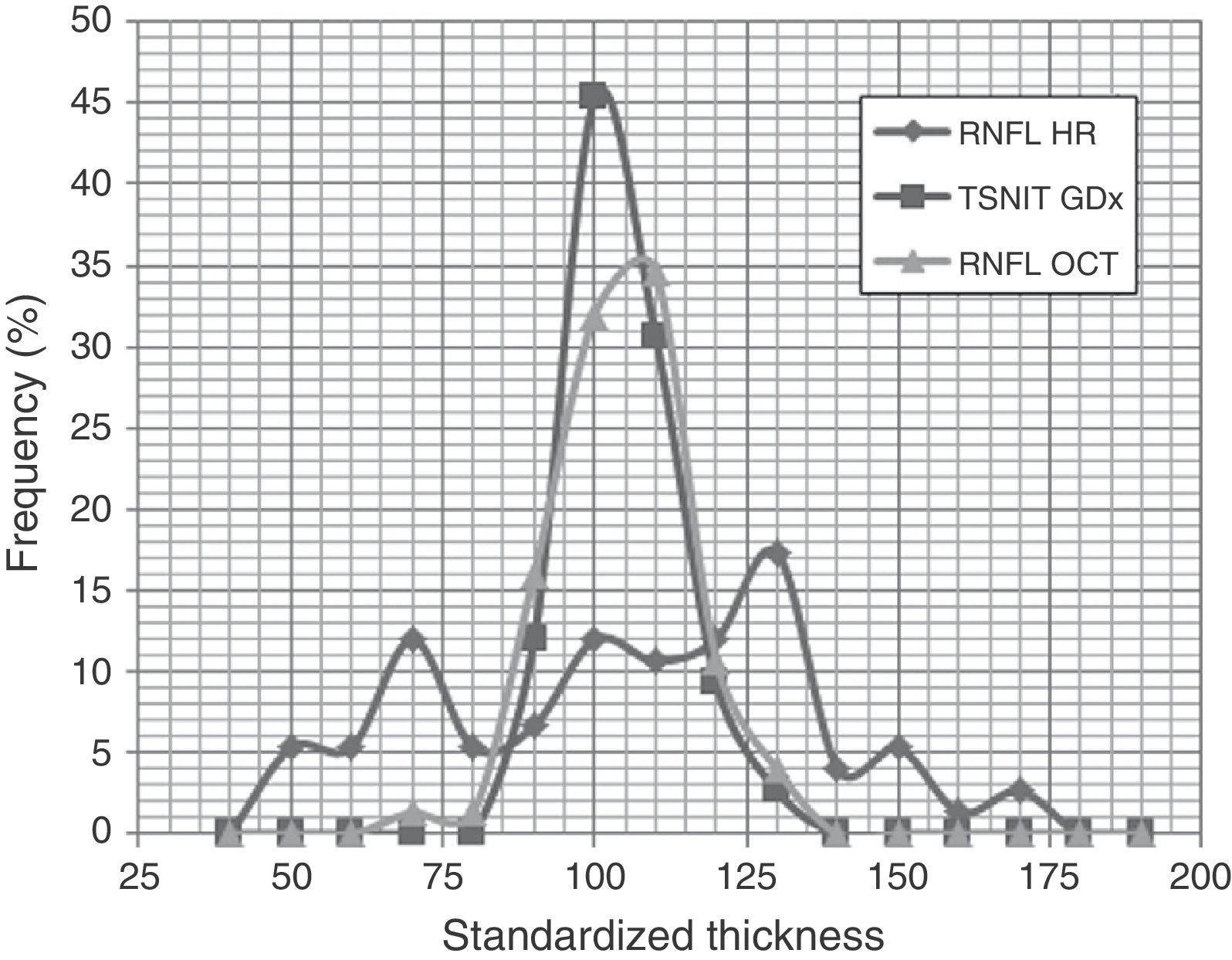
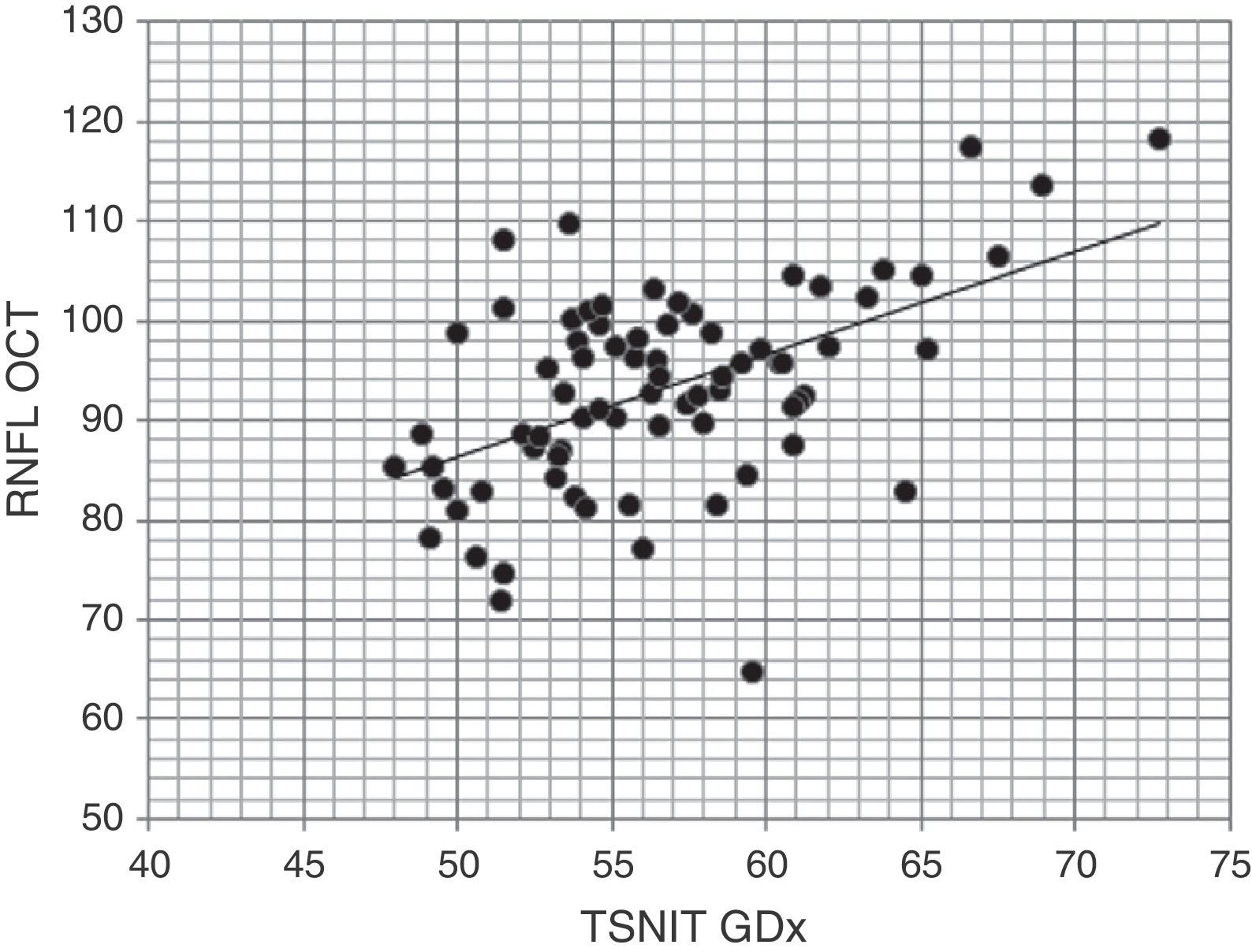
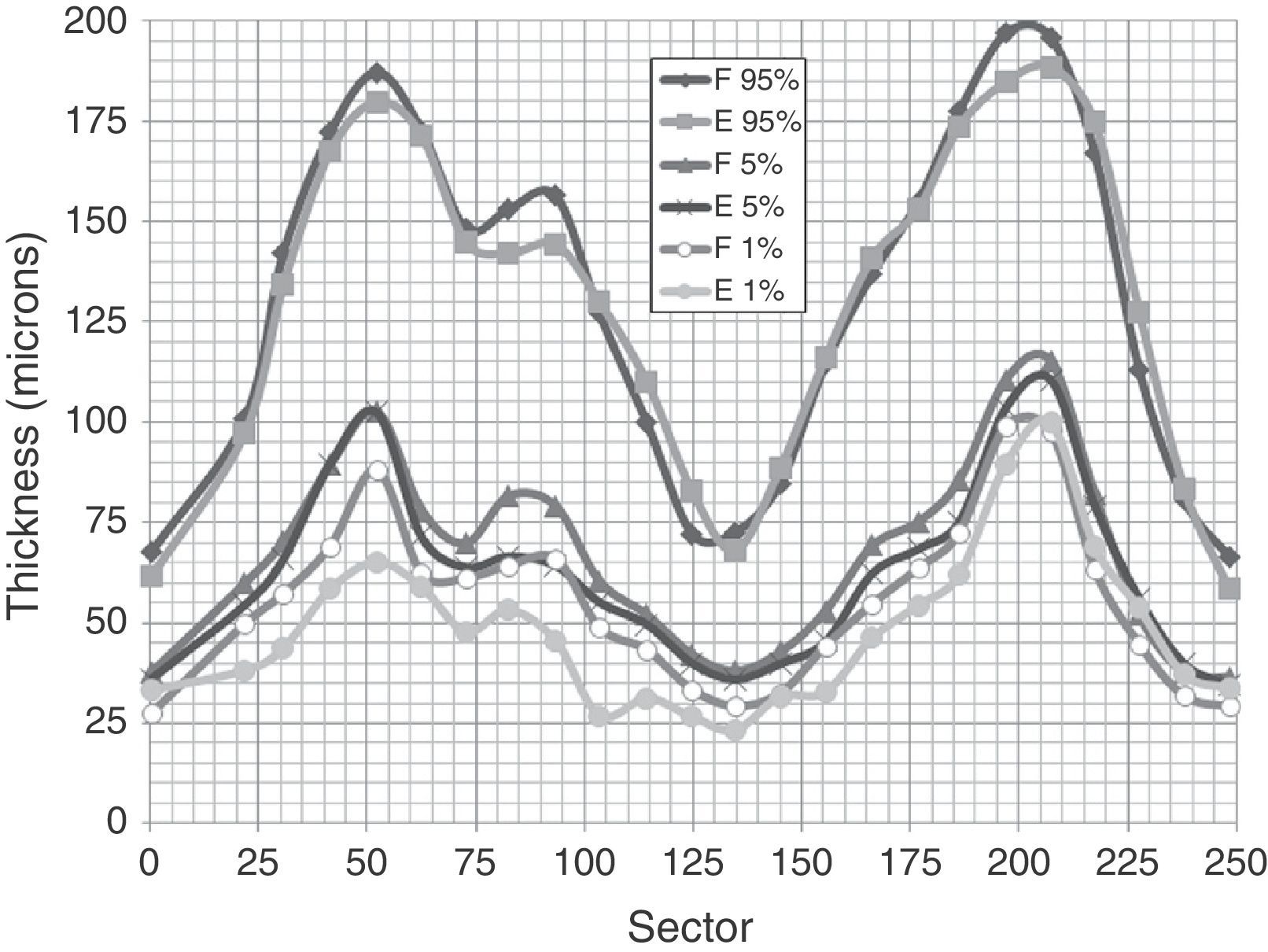
ResultsThe inter-individual variability was similar in GDx (8.9%) and OCT (11.1%), but very high in HRT (30.0%). No instrument detected significant changes with age. The coefficient of variation of the total thickness between the examinations of the same subject was significantly lower (P<0.05) in GDx (1.4) than in OCT (2.0), but very high in HRT (6.4). The same was true when analyzing the upper fibers (GDx=1.8, OCT=2.9, HRT=6.6), but not with the lower ones, where the only significant differences were observed with HRT (GDx=2.2, OCT=2.7, HRT=7.0). Among the results of OCT and GDx, there was a significant correlation when comparing the first (r=0.46, P<0.0001) and second examinations (r=0.52, P<0.0001). However there was no significant relationship between the data provided by HRT for the two remaining instruments (P>0.05).
ConclusionsThere is a wide variation in the inter-individual and inter-test measurement of the thickness of the of nerve fibers layers using HRT. GDx has, in this respect, slight advantages over OCT.
Calcular la variabilidad interindividual y reproducibilidad de la tomografía confocal (HRT), polarimetría láser (GDx) y tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT Cirrus) para determinar el espesor de la capa de fibras ganglionares.
MétodoSe examinaron 2 veces 75 ojos normales. La variabilidad interindividual se analizó previa normalización de los resultados. Para medir la variabilidad entre exámenes se utilizó el coeficiente de variación y para analizar la correlación entre variables, el coeficiente de Pearson.
ResultadosLa variabilidad interindividual fue similar en GDx (8,9%) y en OCT (11,1%) pero muy elevada en HRT (30,0%). Ningún instrumento detectó cambios significativos con la edad. El coeficiente de variación del espesor total, entre 2 exámenes del mismo sujeto, fue significativamente inferior (p<0,05) en GDx (1,4) que en OCT (2,0) y muy elevado en HRT (6,4). Lo mismo ocurrió al analizar las fibras superiores (GDx=1,8; OCT=2,9; HT=6,6), pero no las inferiores, donde solo se observaron diferencias significativas con HRT (GDx=2,2, OCT=2,7, HRT=7,0).
Entre los resultados de OCT y GDx existió una correlación significativa al comparar los primeros (r=0,46; p<0,0001) y los segundos exámenes (r=0,52; p<0,0001). Sin embargo, no se observó ninguna correlación significativa entre los datos aportados por HRT respecto a los 2 instrumentos restantes (p>0,05).
ConclusionesHRT presenta un exceso de dispersión interindividual y de variabilidad intertest en la estimación del espesor del haz de fibras nerviosas. GDx presenta, en este aspecto, ligeras ventajas respecto a OCT.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora