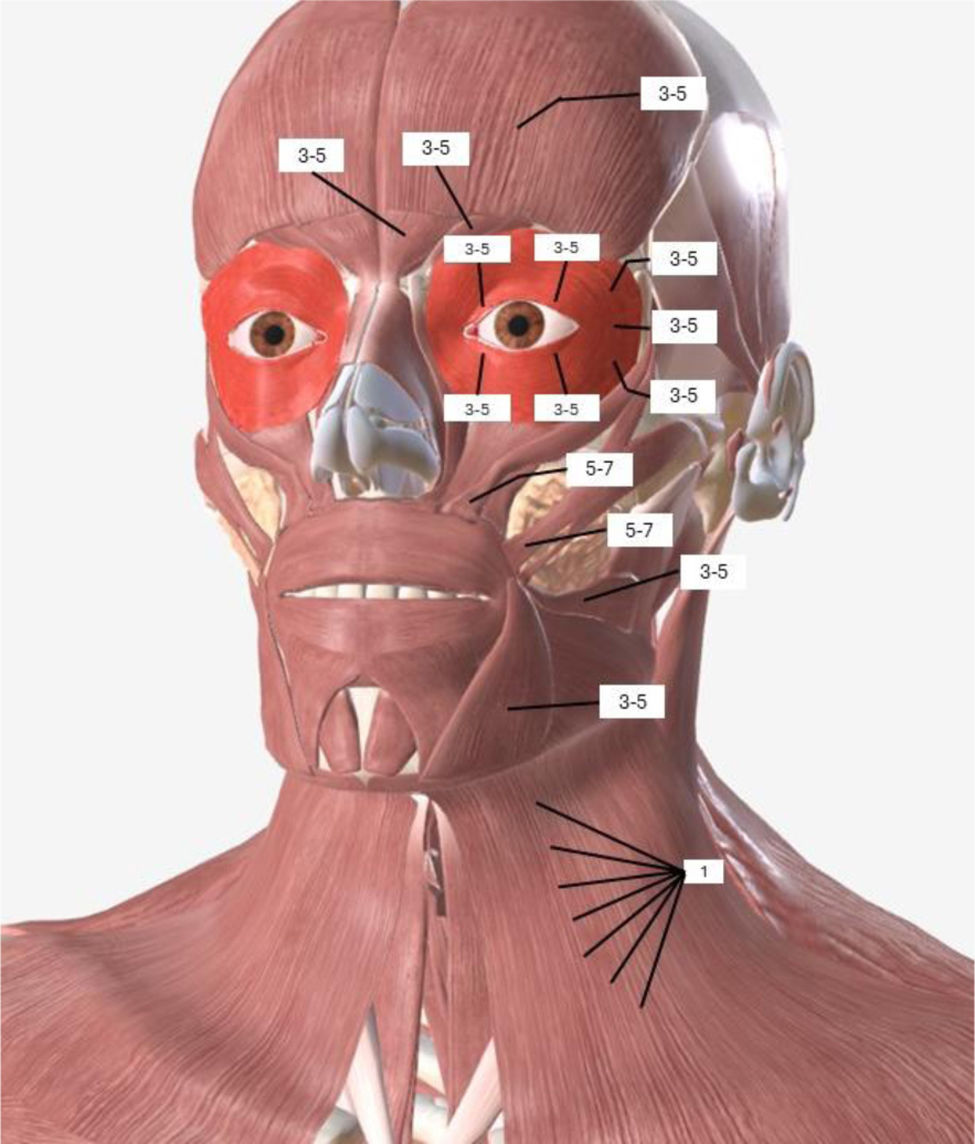
Blepharospasm is characterized by involuntary, sustained spasms of the orbicularis oculi, corrugator, and procerus muscles. Hemifacial spasm (HFS) is characterized by the involuntary tonic-clonic contraction of the muscles of a hemiface. The main role of botulinum toxin type A (BoNT-A) in the treatment of blepharospasm and HFS is recognized by guidelines around the world. In this study, we evaluated the applicability of botulinum toxin type A in patients with periocular hyperkinetic disorders at the Instituto de Oftalmología Fundación Conde de Valenciana, so that we can share the Mexican experience with the international evidence.
Materials and methodsThe clinical records of patients diagnosed with facial hyperkinetic disorders treated with botulinum toxin type A (BoNT-A) that were treated from January 2015 to September 2021 were analyzed.
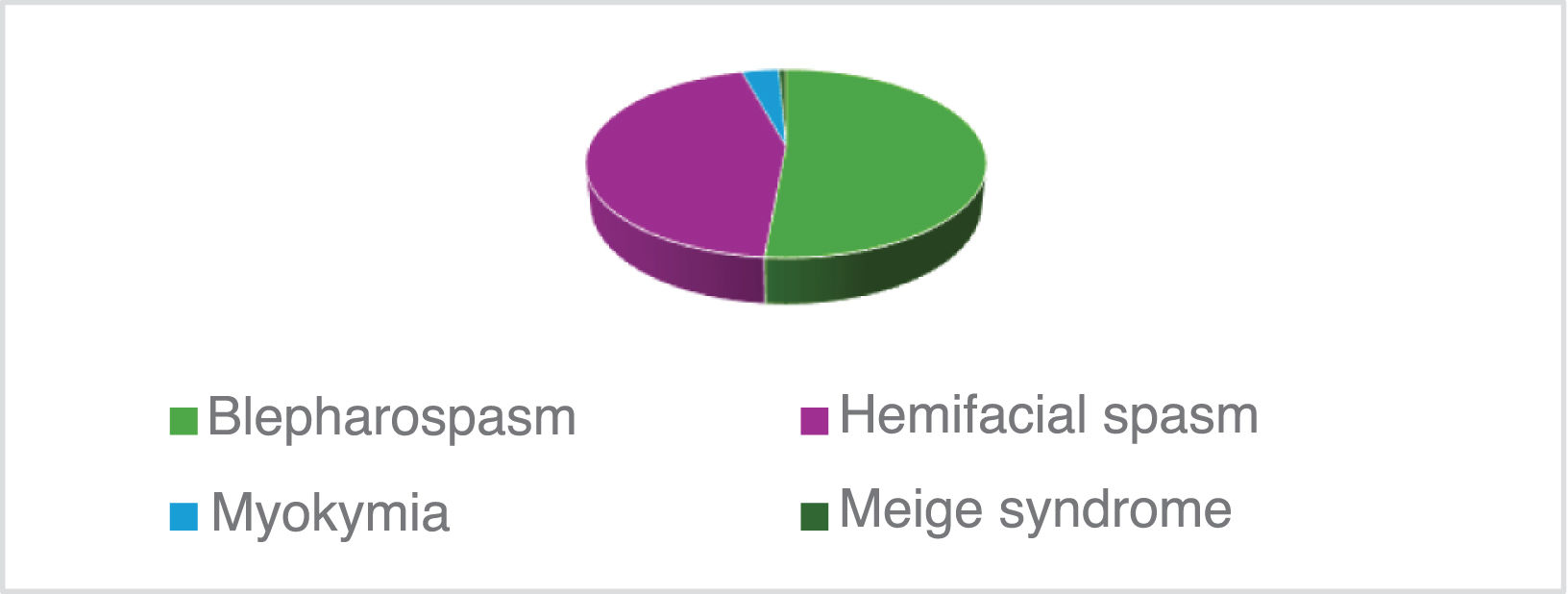
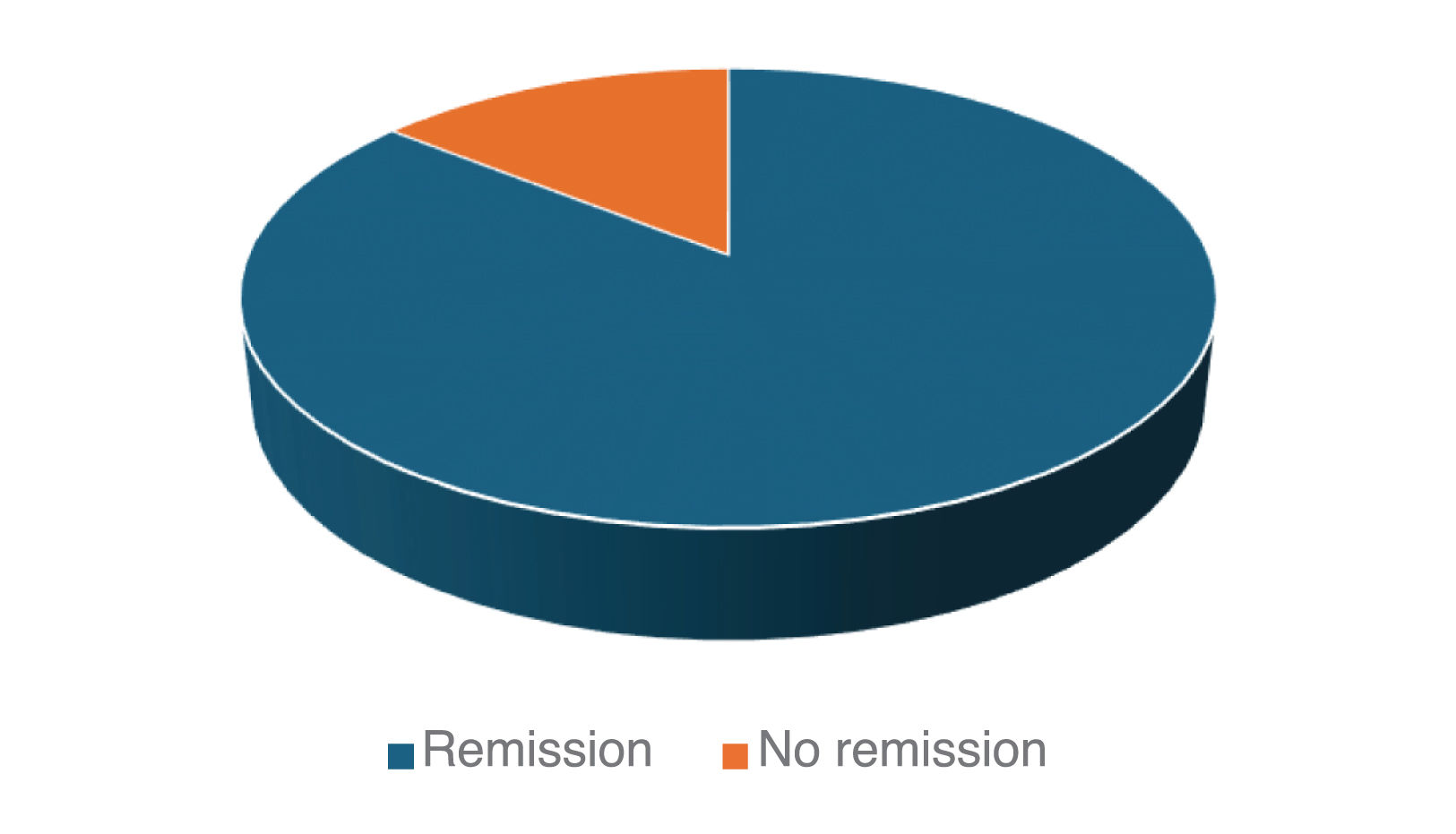
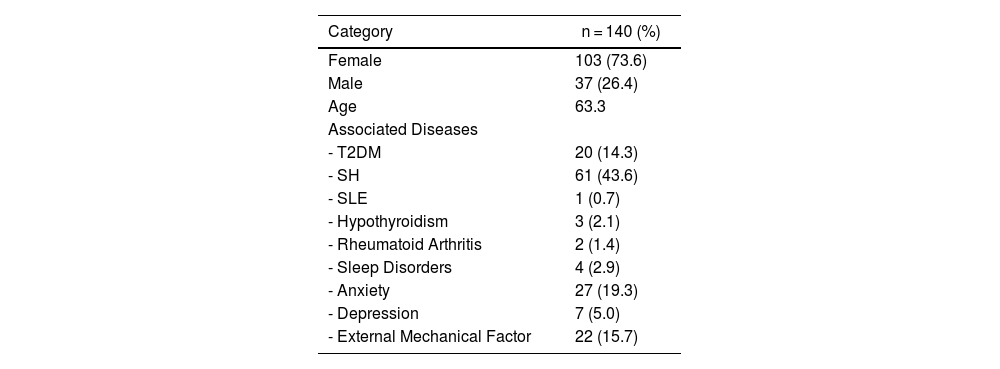
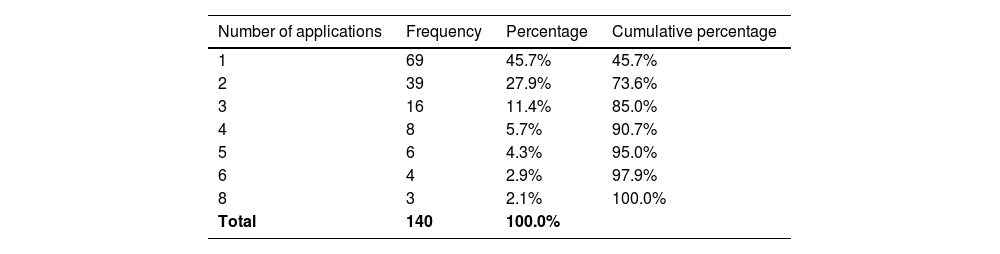
ResultsA total of 140 records of patients diagnosed with facial hyperkinetic disorder and treated with BoNT-A were analyzed. Facial hyperkinetic disorders that occurred included 5 (3.6%) patients with orbicularis oculi myokymia, 72 (51.4%) with blepharospasm, 62 (44.3%) with hemifacial spasm, and 1 (0.7%) with Meige syndrome. One hundred and twenty patients (85.7%) reported remission of initial symptoms after BoNT-A therapy during the period covered by this study.
ConclusionsBotulinum toxin type A is effective and safe as a treatment for facial hyperkinetic disorders in the Mexican population.
El blefaroespasmo se caracteriza por espasmos involuntarios y sostenidos de los músculos orbicular de los párpados, corrugadores y procerus. El espasmo hemifacial (EHF) se caracteriza por la contracción involuntaria tónico-clónica de los músculos de una hemicara. Hoy, la función integral de la toxina botulínica tipo A (BoNT-A) en el tratamiento del blefaroespasmo y el HFS está reconocida por las directrices de todo el mundo. En este estudio evaluamos la aplicabilidad de la toxina botulínica tipo A en pacientes con trastornos hipercinéticos perioculares que acudieron al, Instituto de Oftalmología Fundación Conde de Valenciana, con la finalidad de compartir la evidencia mexicana con la información internacional.
Materiales y métodoSe analizaron los expedientes clínicos de los pacientes diagnosticados con trastornos hipercinéticos faciales en tratamiento con infiltraciones de toxina botulínica tipo A (BoNT-A) desde Enero del 2015 hasta Septiembre del 2021.
ResultadosSe analizaron 140 expedientes de pacientes con diagnóstico de trastorno hipercinético facial tratados con BoNT-A. Los trastornos hipercinéticos faciales que se presentaron incluyeron 5 (3.6%) pacientes con mioquimia del orbicular, 72 (51.4%) con blefaroespasmo, 62 (44.3%) con espasmo hemifacial y 1 (0.7%) con síndrome de Meige. Ciento veinte pacientes (85.7%) refirieron remisión de los síntomas iniciales posterior a la terapia con BoNT-A en el periodo comprendido en este estudio.
ConclusionesLa toxina botulínica tipo A es efectiva y segura como tratamiento para trastornos hipercinéticos faciales en la población mexicana.