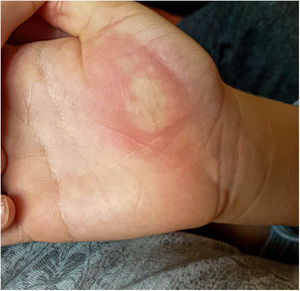
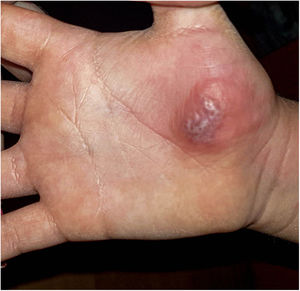
A three-year-old Spanish boy who attended our emergency department for a pruriginous and painful skin lesion on the thenar eminence of four days’ evolution. Two days earlier, his primary care paediatrician had punctured and evacuated the purulent content, alleviating the pain, but without improvement of the lesion.
His mother reported similar lesions in the same location every six to eight months for two years, without finding a clear cause, except on the first occasion, which appeared following an accidental wound in the park. On previous occasions, the lesions had improved with topical fusidic acid. There was no other medical or surgical history of interest or similar lesions in other family members, and they denied recent use of oral or topical treatments.
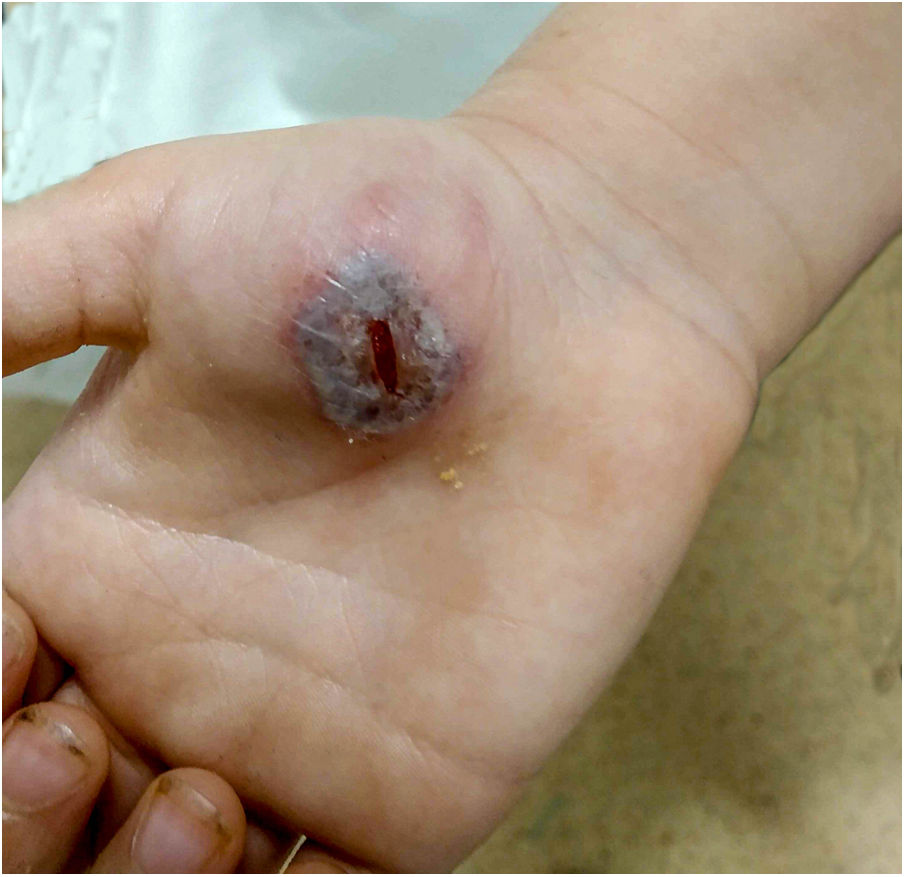
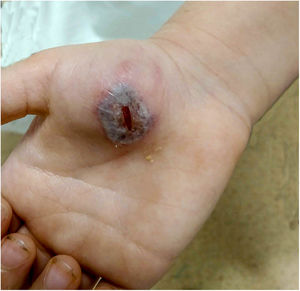
In the physical examination, along with excellent general health, the patient presented a clearly-delimited, 4-cm purplish erythematous plaque with granulation tissue in its interior on the right thenar eminence (Fig. 1). He also presented right axillary lymphadenopathy, but not in other locations. No phlebitis, lymphangitis or other skin lesions.
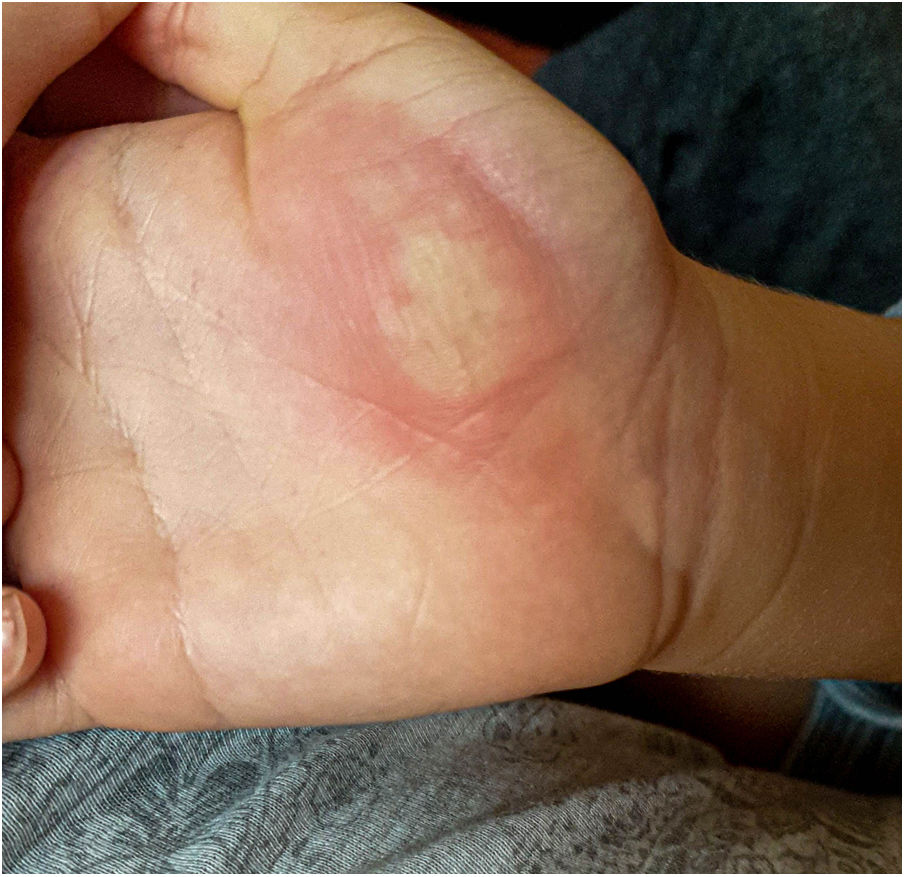
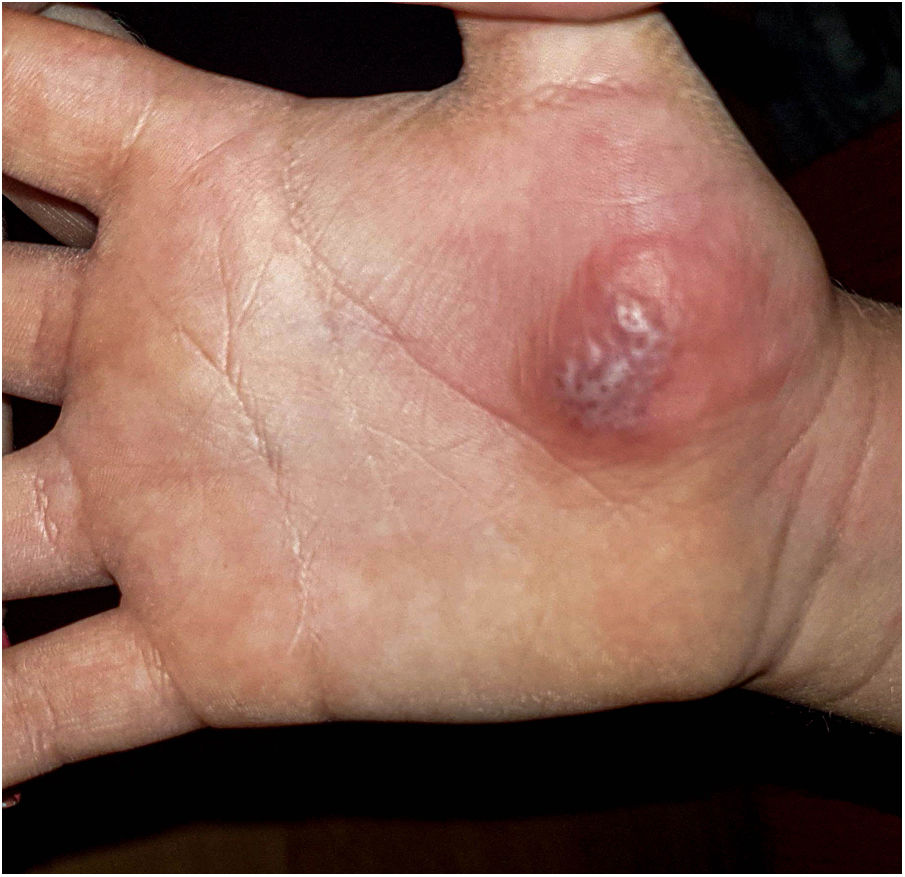
The mother was then interviewed and showed images of the lesion’s evolution: starting as mild erythema (Fig. 2) and evolving to vesiculous lesions and crusts (Fig. 3). Exudate samples were taken for bacterial culture and viral detection with polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for herpes simplex virus (HSV).
Clinical courseThe bacterial culture was sterile, while the PCR was positive for HSV type 1, for which oral aciclovir was started. In follow-up, the skin recovered ad integrum.
CommentsHSV infection is one of the most prevalent in the world. Usually, HSV infections in immunocompetent patients present as painful and pruriginous skin lesions in the form of groups of blisters on an erythematous base, and are self-limiting in time. In spite of their self-limiting nature, HSV-1 can cause recurrent lesions in immunocompetent children, usually in an oral or perioral location (herpes labialis)1. It also manifests as recurrent lesions on the fingers (herpetic whitlow), usually following primary gingivostomatitis (autoinoculation). Intrafamilial transmission from family members with herpes labialis has also been described. Palmar involvement has been described on rare occasions2.
More developed herpetic lesions can mimic other aetiologies and be difficult to diagnose. An exhaustive patient history and good physical examination are therefore necessary. In this case, fixed drug eruption, bacterial infection and dermatitis artefacta, among others, were considered as alternatives in the differential diagnosis. Given its prevalence, it is very important to consider a possible herpetic aetiology and, where possible, ask for images of the lesion’s evolution, which may be very illuminating.
FundingCDG has funding from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation Instituto de Salud Carlos III [Carlos III Health Institute] and the European Regional Development Fund (Río Hortega Contract CM19/00015).
Please cite this article as: Liquete Marín L, Grasa Lozano C. Lesión recurrente palmar. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2021;39:473–474.