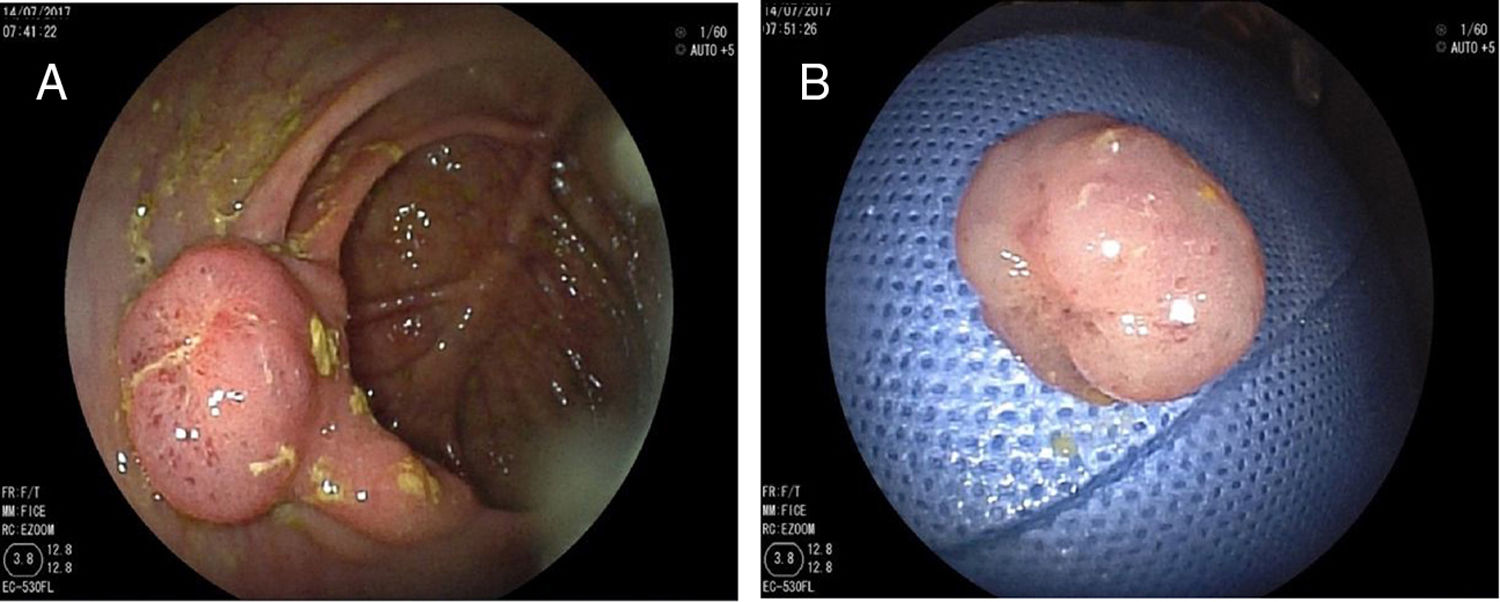
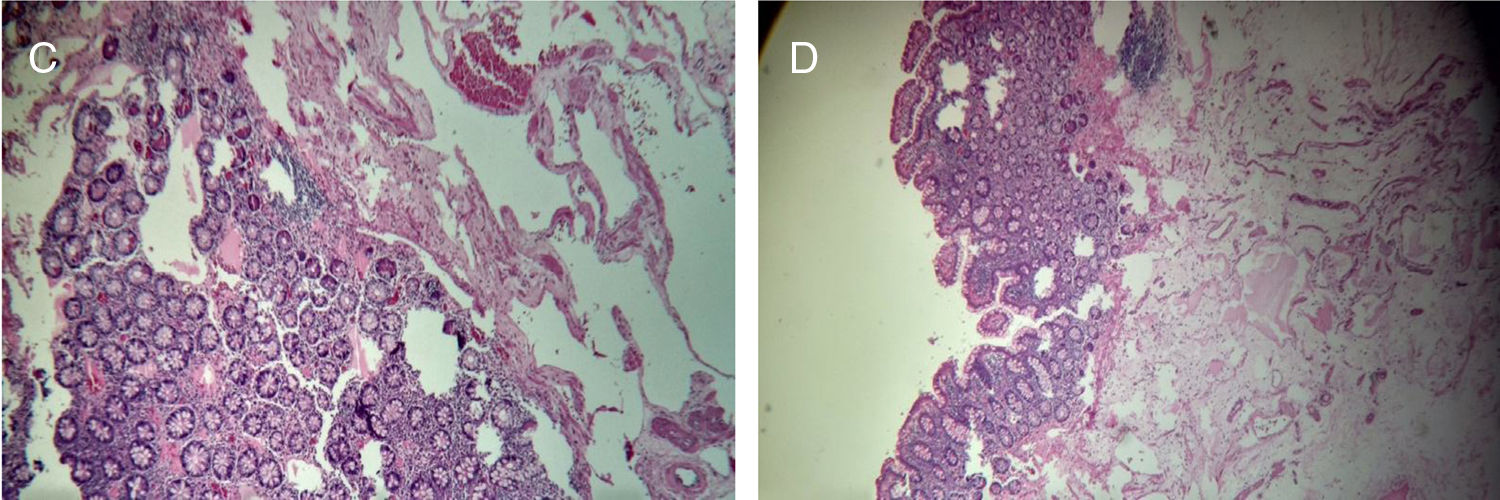
A 69-year-old male patient came to the emergency room after 22h with severe, oppressive lower abdominal pain, nausea, fever and dysuria, no vomits and hematochezia. Patient referred no important illness or risk factor. At physical examination the patient was alert, oriented in time, space and person. At the abdominal exam, the patient referred pain at the deep palpation of the right iliac region, no signs of lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Rest of the exam with no contributions. A diagnosis of abdominal pain syndrome was stated, suggesting urolithiasis or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) as the possible causes. Patient received nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) by intramuscular injections (IM) and NSAIDs capsules. The patient got better and left the hospital. However, one week later the patient returned to the internal medicine unit with a tomography that suggested right diverticulitis, and for that reason he was referred to the gastroenterology department for colonoscopy. The test showed a subpediculated polyp of 20mm on the ileocecal valve. (A, B) The polyp was extracted and sent to pathology which revealed a polypoid shape lesion with thin-walled vessels in the submucosa layer. Mucosa layer without atypia. The pathology conclusions were angiodysplasic lesion with polypoid shape (C, D) (Figs. 1 and 2).
Información de la revista
Vol. 41. Núm. 9.
Páginas 574-575 (noviembre 2018)
Vol. 41. Núm. 9.
Páginas 574-575 (noviembre 2018)
Image of the month
Acceso a texto completo
Polypoid angiodysplasia mimicking diverticular disease
Angiodisplasia polipoide que imita la enfermedad diverticular
Visitas
1407
Este artículo ha recibido
Información del artículo
Texto completo
Copyright © 2018. Elsevier España, S.L.U.. All rights reserved