The safety profile of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors has acquired attention due to post-marketing observed adverse drug reactions. The study focuses on the analysis of adverse reactions related to tofacitinib, baricitinib, upadacitinib, and filgotinib in rheumatoid arthritis patients, including identifying predictive factors linked to their occurrence.
Patients and methodsObservational retrospective study. Adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis from a university hospital receiving JAK inhibitor treatment between September 2017 and January 2024 were included. The cumulative incidence of each adverse reaction was calculated using the Naranjo scale. Risk factors for developing adverse reactions were identified through logistic regression analyses.
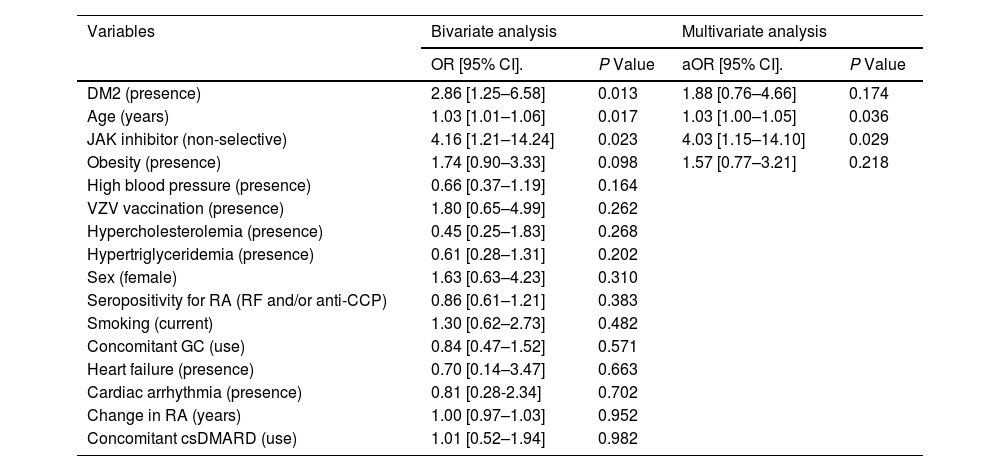
ResultsTwo hundred twenty-three patients were included, with 28.7% presenting adverse reaction related to JAK inhibitor treatment. The adverse drug reactions with the highest cumulative incidence were infections and gastrointestinal disorders. Infections included: upper respiratory tract (4.5%), cellulitis (3.1%), urinary tract (2.7%), herpes zoster (1.8%). Gastrointestinal disorders comprised: abdominal pain (4.0%), diarrhea (3.6%), nausea and vomiting (3.6%), gastrointestinal perforation (1.3%), diverticulitis (0.9%). Classified at 0.5% were: headache, paresthesias, skin rash, severe neutropenia, insomnia, dyspnea, hypertensive crisis. As risk factors, were identified: the treatment with a non-selective JAK inhibitor (OR adjusted: 4.03; 95% CI: 1.15–14.10; P = 0.029) and older age (OR adjusted: 1.03; 95% CI: 1.00–1.05; P = 0.036).
ConclusionsInfections and gastrointestinal disorders represented the adverse reactions related to JAK inhibitor treatment with the highest cumulative incidence, with risk factors for their occurrence being non-selective JAK inhibitor treatment and older age of the patient.
La seguridad de los inhibidores de quinasa Janus (JAK) ha ganado atención debido a reacciones adversas observadas poscomercialización. El estudio se centra en el análisis de reacciones adversas relacionadas con tofacitinib, baricitinib, upadacitinib y filgotinib en pacientes con artritis reumatoide, incluyendo la identificación de factores predictivos relacionados con su aparición.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio retrospectivo observacional. Se incluyeron pacientes adultos en seguimiento por artritis reumatoide en un hospital universitario, en tratamiento con inhibidor de JAK entre septiembre 2017 y enero 2024. Se calculó la incidencia acumulada de cada reacción adversa mediante la escala de Naranjo. Se identificaron los factores predictivos para la aparición de reacciones adversas mediante análisis de regresión logística.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 223 pacientes, el 28,7% presentó reacción adversa a inhibidor de JAK. Las reacciones adversas con mayor incidencia acumulada fueron infecciones y trastornos gastrointestinales. Las infecciones comprendieron: tracto respiratorio superior (4,5%), celulitis (3,1%), tracto urinario (2,7%), herpes zóster (1,8%). Los trastornos gastrointestinales englobaron: dolor abdominal (4,0%), diarrea (3,6%), náuseas y vómitos (3,6%), perforación gastrointestinal (1,3%) y diverticulitis (0,9%). Con un 0,5% se clasificaron: cefalea, parestesias, erupción cutánea, neutropenia severa, insomnio, disnea y crisis hipertensiva. Como factores de riesgo, se identificaron: el tratamiento con inhibidor de JAK no selectivo (OR ajustado: 4,03; IC 95%: 1,15–14,10;P = 0,029) y una mayor edad (OR ajustado: 1,03; IC 95%: 1,00–1,05;P = 0,036).
ConclusionesInfecciones y trastornos gastrointestinales representaron las reacciones adversas a inhibidor de JAK con mayor incidencia acumulada, siendo los factores de riesgo para su aparición el tratamiento con inhibidor de JAK no selectivo y una mayor edad del paciente.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora