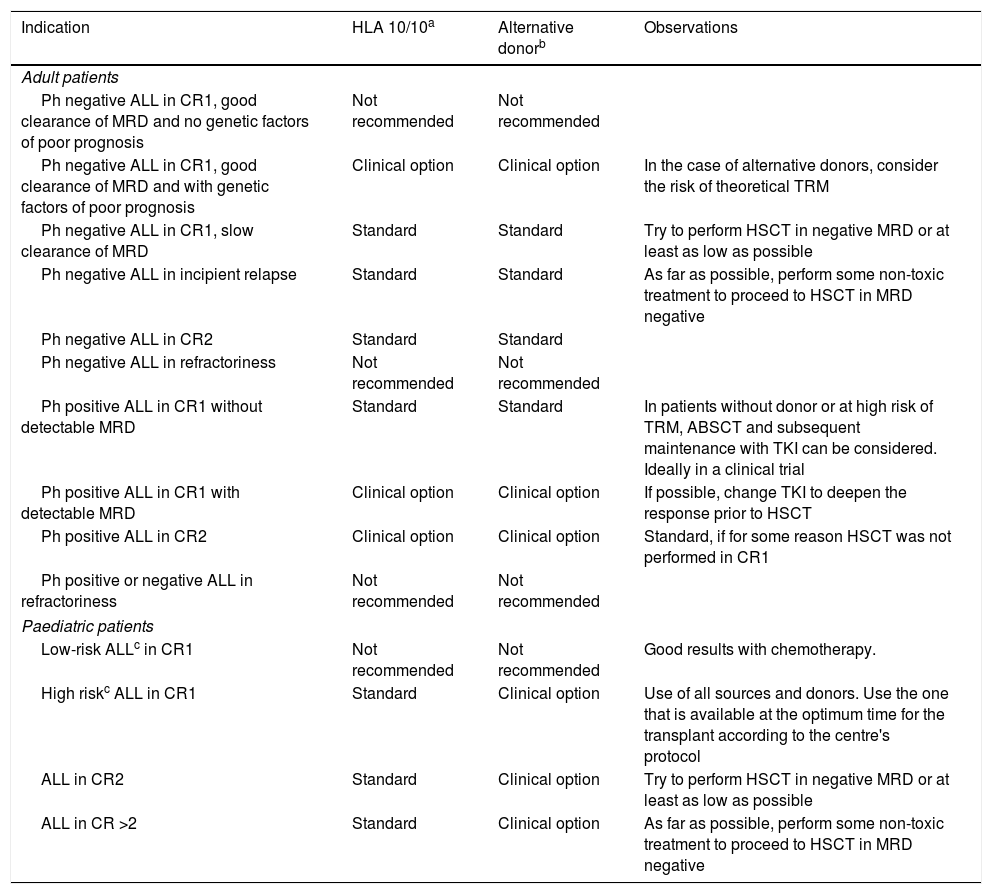
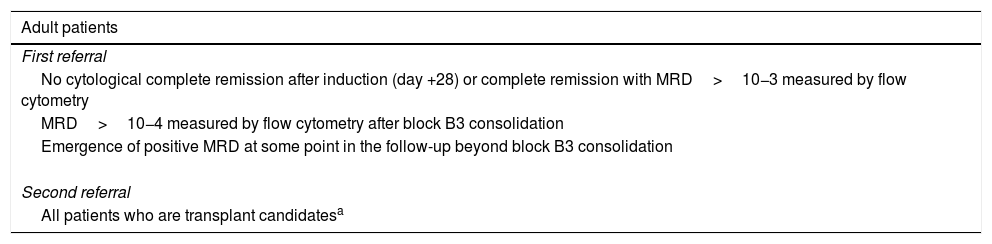
Immunotherapy is changing the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) in adults and children. However, regardless of these new therapies, allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT) still play a key role in the treatment of ALL, although it is uncertain how these new therapies will impact on the transplant procedure and indications. This article reviews the indications of allo-HCT for children and adults diagnosed with ALL, the different sources and conditioning regimens for transplantation as well as the role of measurable residual diseases pre- and post-HCT in the era of the new therapies for ALL.
La inmunoterapia está cambiando profundamente el tratamiento de la leucemia linfoblástica aguda (LLA) infantil y del adulto. Sin embargo, a pesar de todos los avances, el trasplante alogénico de progenitores hematopoyéticos (alo-TPH) sigue siendo un pilar fundamental en su tratamiento. Cómo van a modificar estas nuevas terapias la indicación y el procedimiento de trasplante, resulta todavía incierto. En el presente artículo se discuten las indicaciones de TPH en la LLA infantil y del adulto, las posibles fuentes de donantes y acondicionamiento, así como el papel de la enfermedad residual medible en el contexto de la nueva era de tratamientos en el campo de la LLA.