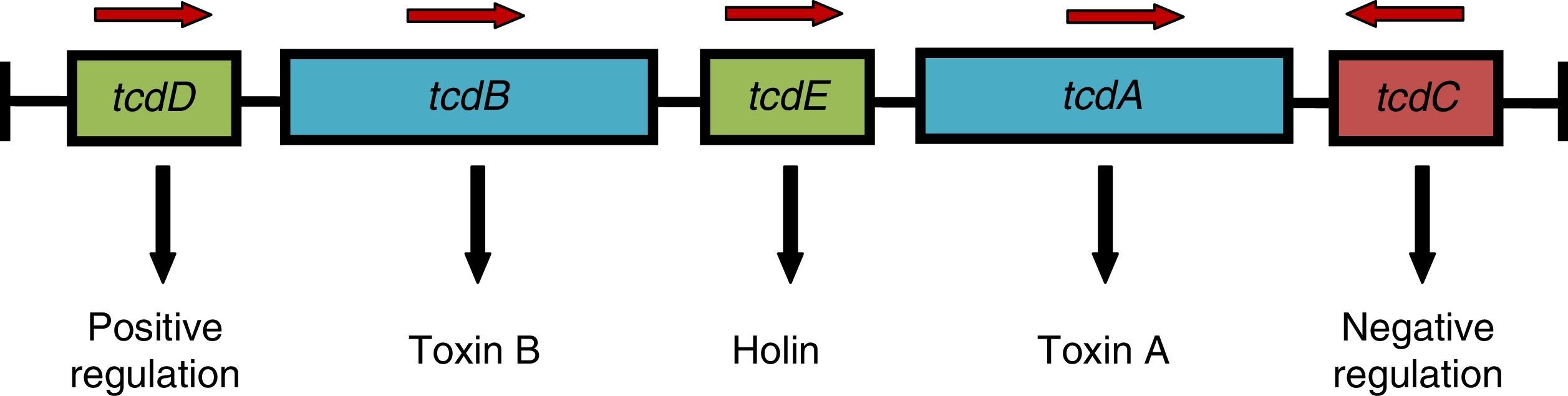
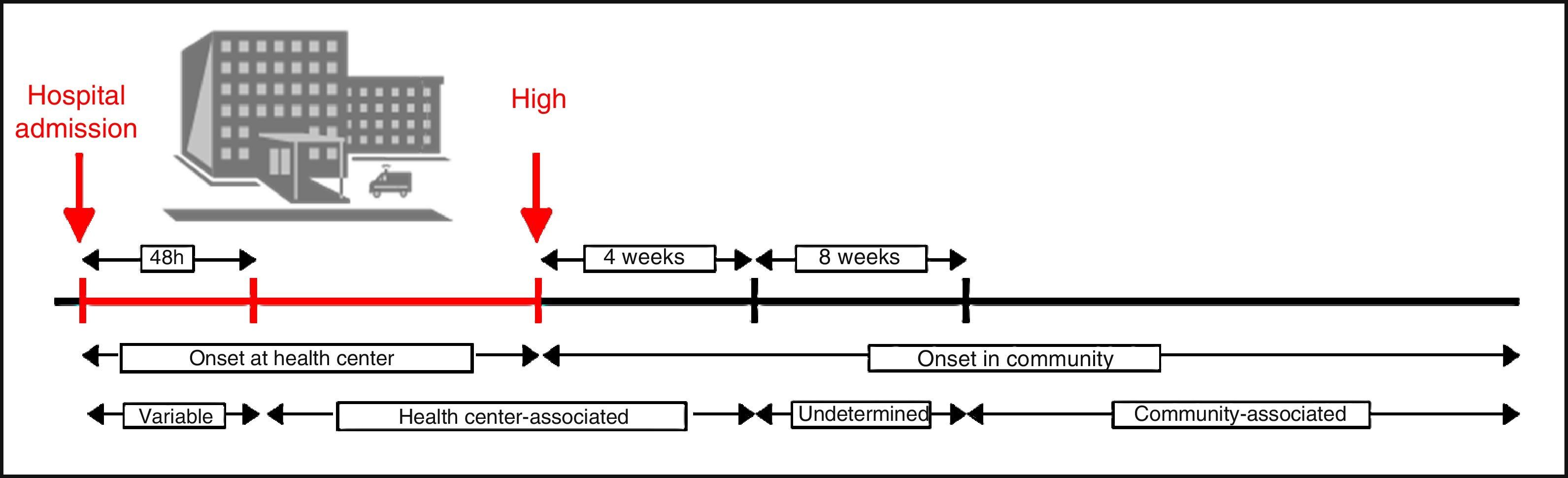
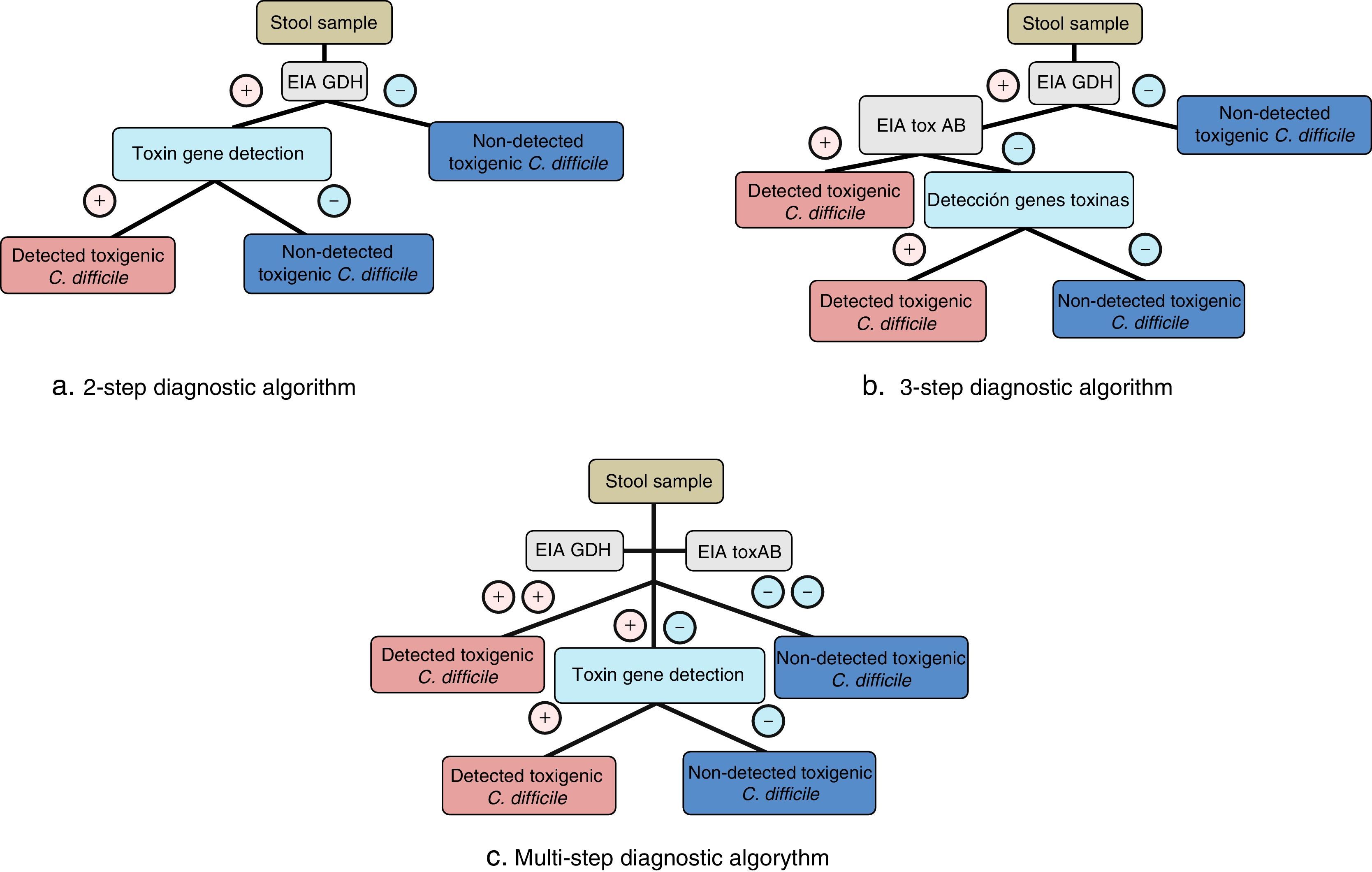
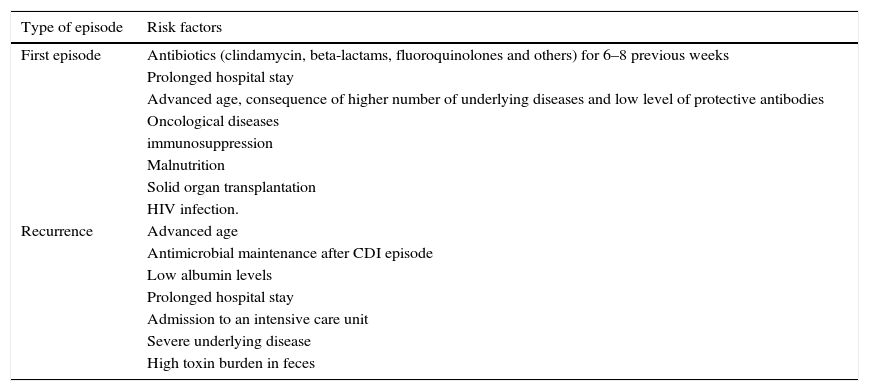
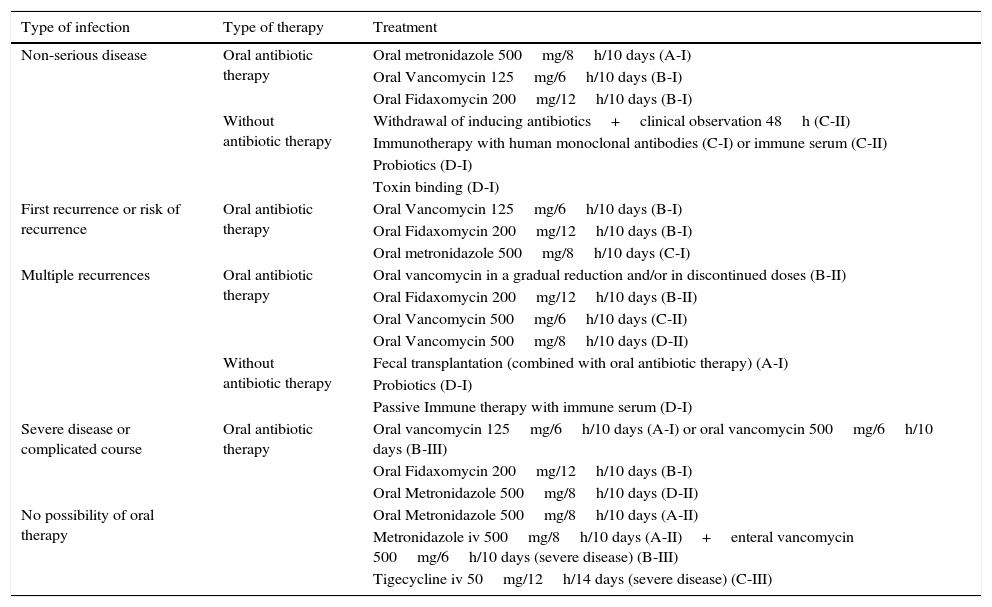
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) is the main cause of nosocomial diarrhea in industrialized countries and the source of a growing number of cases of diarrhea in the community. The outbreak of the hypervirulent strain belonging to ribotype 027 has increased the incidence and severity of CDI in some countries. Although CDI usually courses as a mild diarrhea it can lead to severe forms such as toxic megacolon or septic shock. One of every 2 episodes of CDI is not diagnosed in Spanish hospitals due to a lack of clinical suspicion or the use of insensitive diagnostic methods. The diagnostic techniques of choice are algorithms based on the detection of glutamate dehydrogenase and molecular detection of the genes of the toxins with or without the direct detection of the toxins. The recommended treatment for CDI depends on the type of infection and the characteristics of the patient.
La infección por Clostridium difficile (ICD) es la principal causa de diarrea nosocomial en países industrializados y el origen de un número de casos cada vez mayor de diarrea en la comunidad. La irrupción de la cepa del ribotipo 027 ha incrementado en algunos países la incidencia y la gravedad de la ICD. Aunque suele cursar como una diarrea leve/moderada, puede dar lugar a formas graves, como megacolon tóxico y shock séptico. Uno de cada 2 episodios de ICD no es diagnosticado en los hospitales españoles por falta de sospecha clínica o por el uso de métodos diagnósticos poco sensibles. Se recomiendan algoritmos diagnósticos basados en la detección de glutamato deshidrogenasa y en la detección molecular de los genes de las toxinas con o sin la detección directa de las toxinas. El tratamiento recomendado de la ICD depende del tipo de infección y las características del paciente.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora