Arterial hypertension (AHT) is the main risk factor for the development of retinal vein occlusion (RVO).
AimsTo analyze the hypertensive profile with ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) in patients with RVO.
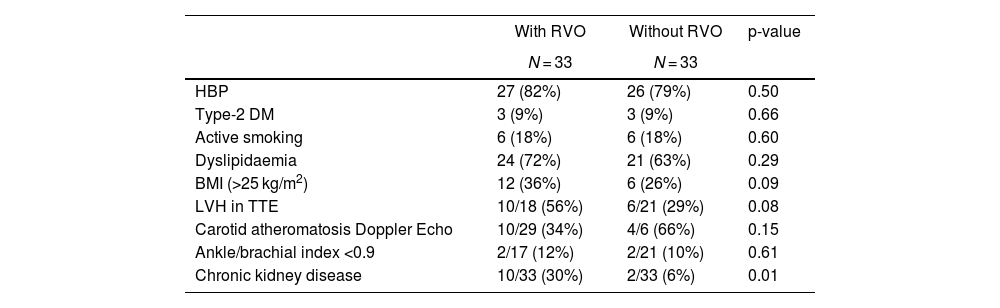
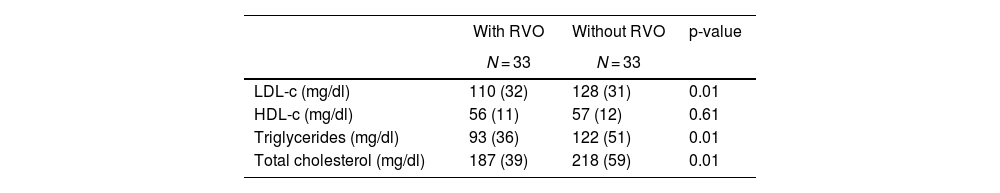
MethodsRetrospective and observational study of 66 patients with ABPM, 33 with retinal vein occlusion from a cohort of these disease and 33 controls without RVO, adjusted for age and sex.
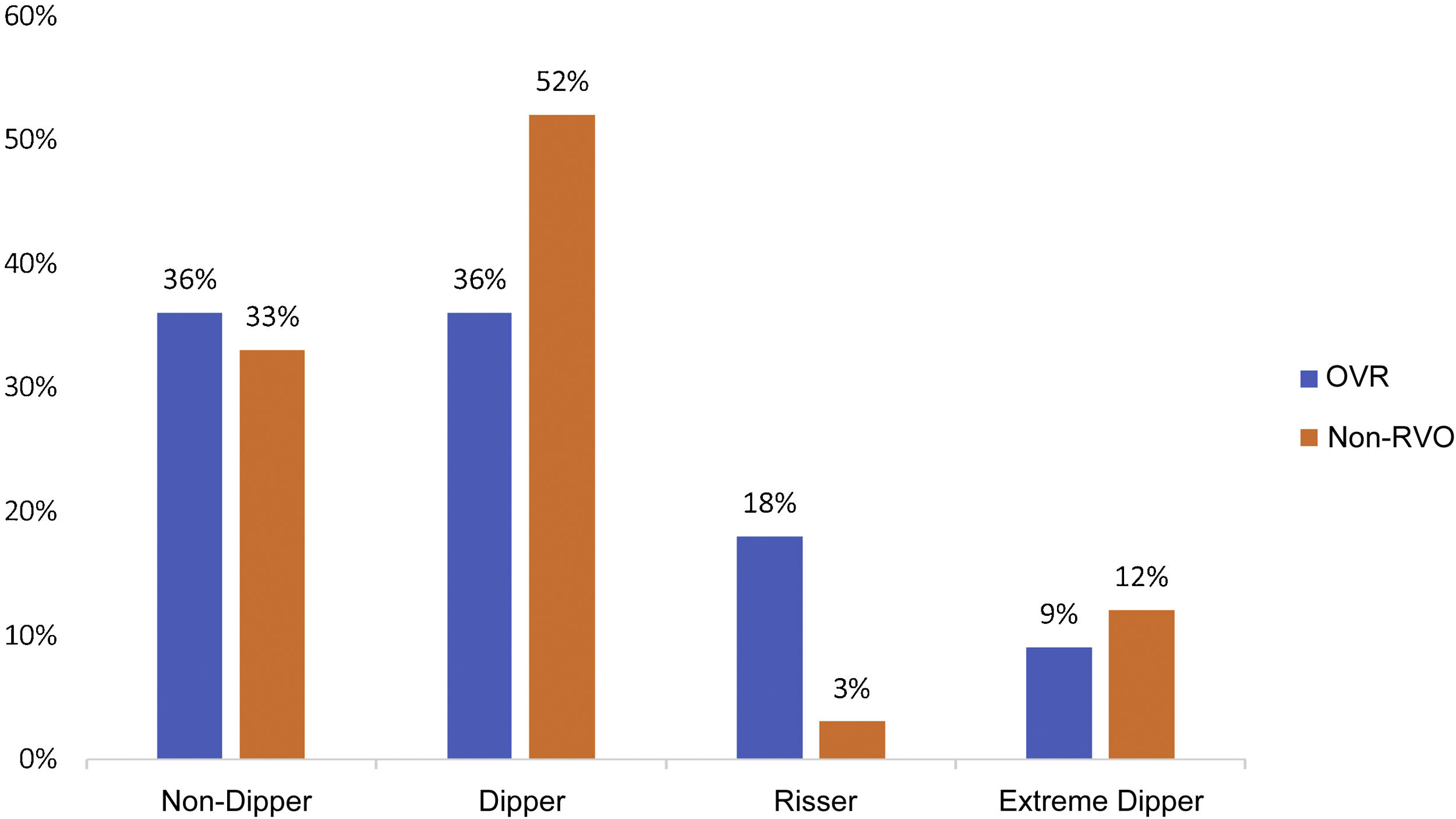
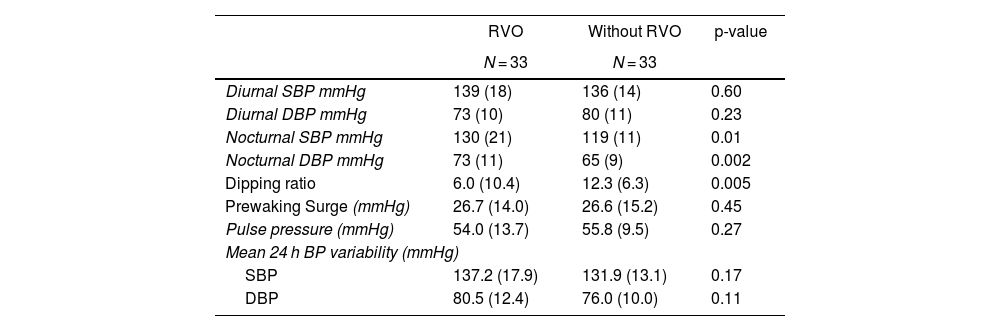
ResultsCompared to controls, patients with RVO had elevated nocturnal values of SBP 130(21) mmHg vs. 119(11) mmHg; p = 0.01) and DBP 73(11) mmHg vs. 65(9) mmHg; p = 0.002. In addition, they presented a lower decrease in the Dipping ratio percentage 6.0(10.4) % vs. 12.3(6.3) %; p = 0.005.
ConclusionsPatients with RVO have an unfavorable nocturnal hypertensive profile. Recognition of this fact can help optimize their treatment.
La hipertensión arterial (HTA) es el principal factor de riesgo para el desarrollo de la obstrucción venosa retiniana (OVR).
ObjetivosAnalizar el perfil hipertensivo con monitorización ambulatoria de la presión arterial (MAPA) en pacientes con una OVR.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio con MAPA en 66 pacientes, 33 con OVR pertenecientes a una cohorte con esta enfermedad y 33 controles sin OVR ajustados por edad y sexo.
ResultadosLos pacientes con OVR tuvieron, respecto a los controles, cifras nocturnas elevadas de PAS 130(21) mm Hg vs. 119(11) mm Hg; p = 0,01 y PAD 73(11) mm Hg vs. 65(9) mm Hg; p = 0,002. Además, presentaron menor descenso del porcentaje de Dipping ratio 6,0% (10,4) vs. 12,3% (6,3); p = 0,005.
ConclusionesLos pacientes con OVR tienen un perfil hipertensivo nocturno desfavorable. El reconocimiento de este hecho puede ayudar a optimizar el tratamiento.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora