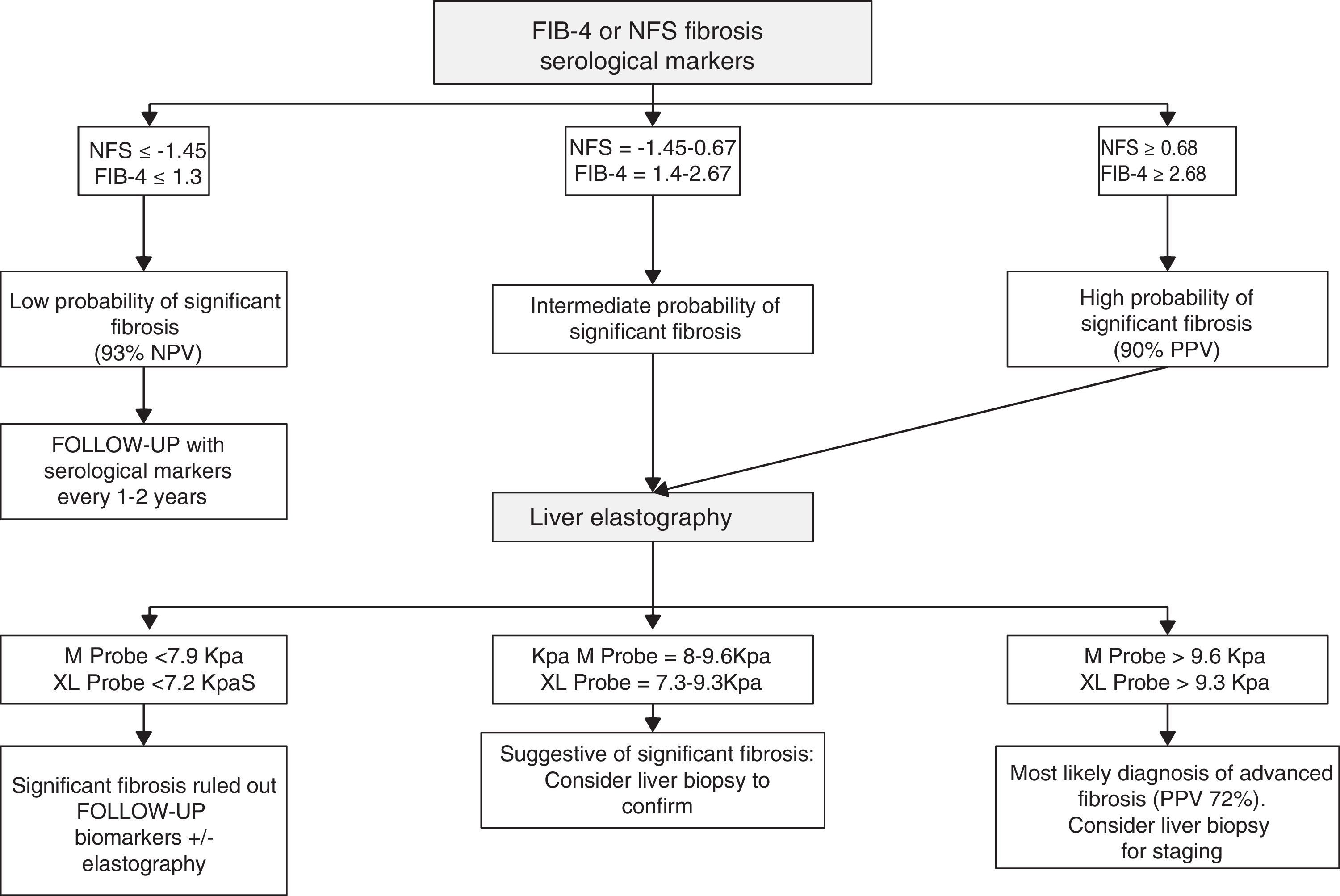
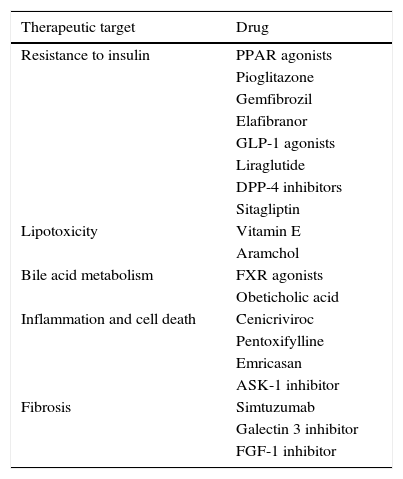
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) consists of an excessive depositing of fat in the liver, which can end up by causing inflammation, fibrosis and also cirrhosis with the corresponding complications including liver cancer. NAFLD has become the most common liver disease worldwide. The incidence has increased in parallel with the obesity, diabetes and metabolic syndrome epidemic, thus resulting in becoming one of the main indications for liver transplant. The diagnosis has principally been through histology but with the development of non-invasive methods, these have helped in simplifying the management of these patients in clinical practice. The only therapeutic strategies currently available are focused on weight loss (lifestyle changes or bariatric surgery). There is still no approved pharmacological option for the treatment of NAFLD, however there are a number of molecular studies in advanced stages of development.
El hígado graso no alcohólico (HGNA, Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease [NAFLD]) consiste en el depósito excesivo de grasa en el hígado que puede acabar generando inflamación, fibrosis e incluso cirrosis y sus complicaciones, incluido el carcinoma hepatocelular. El HGNA se ha convertido en la enfermedad hepática crónica más prevalente del mundo. Su incidencia ha ido aumentando en paralelo con la epidemia de obesidad, diabetes y síndrome metabólico, siendo además una de las principales causas de indicación de trasplante hepático. Su diagnóstico ha sido clásicamente histológico, pero el desarrollo de métodos no invasivos está ayudando a simplificar el manejo de estos pacientes en la práctica clínica. Las únicas estrategias terapéuticas disponibles son las enfocadas en la pérdida de peso (cambios de estilo de vida y/o cirugía bariátrica). Todavía no hay fármacos aprobados para el tratamiento del HGNA, pero existen numerosas moléculas en fases avanzadas de desarrollo.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora