To describe macular vessel density and perfusion in COVID-19 patients using coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) and to investigate whether there is a correlation between retinal vascular abnormalities and clinical and laboratory parameters.
MethodsCross-sectional analysis conducted at the Hospital Clinico San Carlos in Madrid, Spain. Patients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 that were attended in the Emergency Department (ED) from March 23 to March 29, 2020 were included. Fundus examination and OCTA were performed 4 weeks after being attended in ED. Macular OCTA parameters were analyzed and correlated with clinical (severity and hypoxemia- oxygen saturation<92%) and laboratory parameters during hospital stay (D-Dimer-DD, lactate dehydrogenase-LDH and C-reactive protein-CRP).
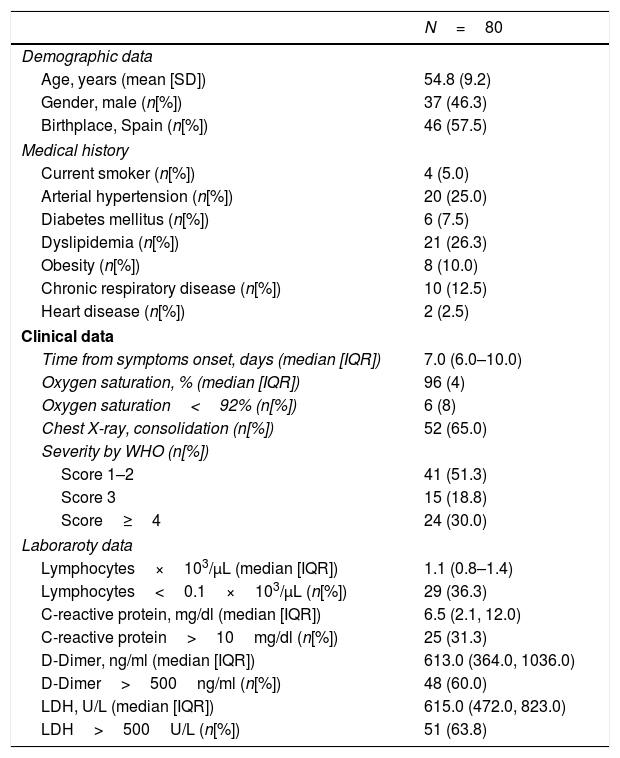
Results80 patients were included, mean age 55(SD9) years old; 46.3% male. We reported macular vessel density and perfusion measurements in COVID-19 patients. Those patients with D-Dimer≥500ng/ml during SARS-CoV-2 infection had a decrease of central vessel density (mean difference 2.2; 95%CI 0.4–3.9) and perfusion density (mean difference 4.9; 95%CI 0.9–8.9) after the acute phase of COVID-19. These variations of vessel density and perfusion density were not documented in patients with LDH≥500U/L, CRP≥10mg/L and hypoxemia.
ConclusionsCOVID-19 patients showed short-term retinal vasculature abnormalities which may be related to a prothrombotic state associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Since the retinal microvasculature shares many morphological and physiological properties with the vasculature of other vital organs, further research is needed to establish whether patients with increased D-Dimer levels require more careful assessment and follow-up after COVID-19.
Evaluar la densidad vascular (DV) y la perfusión vascular (PV) retiniana en pacientes con COVID-19 mediante una angiografía por tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCTA), e investigar si existe una correlación entre las anomalías vasculares de la retina y los parámetros clínicos y de laboratorio.
MétodosAnálisis transversal realizado en el Hospital Clínico San Carlos, Madrid. Se incluyeron pacientes con diagnóstico confirmado de COVID-19 atendidos en el Servicio de Urgencias (SU) del 23 al 29 de marzo del 2020. Se realizó una exploración oftalmológica y OCTA cuatro semanas después de acudir al SU. Se analizaron los parámetros maculares de OCTA y se correlacionaron con parámetros clínicos (gravedad e hipoxemia-saturación de oxígeno < 92%) y de laboratorio durante la estancia hospitalaria (dímero D [DD], lactato deshidrogenasa [LDH] y proteína C reactiva [CRP].
ResultadosSe incluyeron 80 pacientes, edad media 55 (DE nueve) años; 46,3% hombres. Las personas con DD > 500 ng/mL durante la infección por SARS-CoV-2 tuvieron una disminución de la DV central (diferencia de medias 2,2; IC 95% 0,4 a 3,9) y PV central (diferencia de medias 4,9; IC 95% 0,9 a 8,9) después de la fase aguda de COVID-19. Estas variaciones no se documentaron en los pacientes con LDH > = 500 U/L, CRP > = 10 mg/L y con hipoxemia.
ConclusionesLos pacientes con COVID-19 mostraron anomalías de la vasculatura retiniana a corto plazo que pueden estar relacionadas con un estado protrombótico asociado con la infección por SARS-CoV-2. Dado que la microvasculatura de la retina comparte muchas propiedades morfológicas y fisiológicas con la vasculatura de otros órganos vitales, es necesario seguir investigando para determinar si los pacientes con niveles elevados de DD requieren una evaluación y un seguimiento más cuidadoso.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora