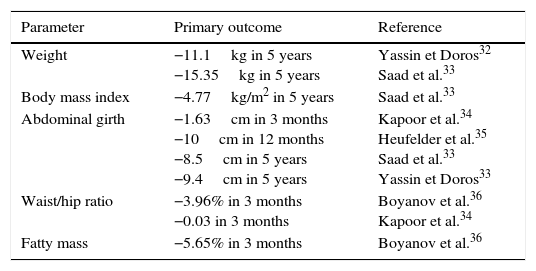
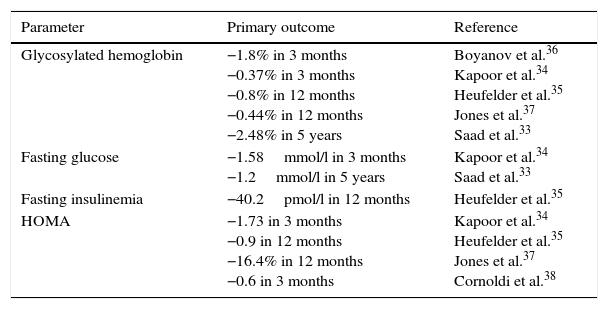
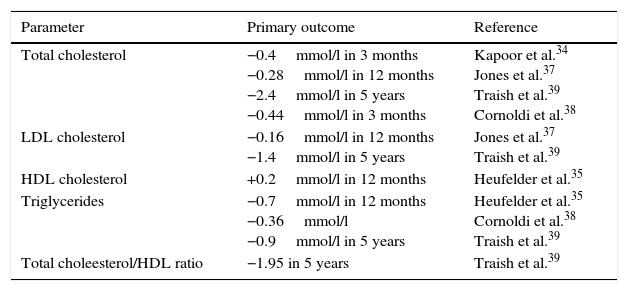
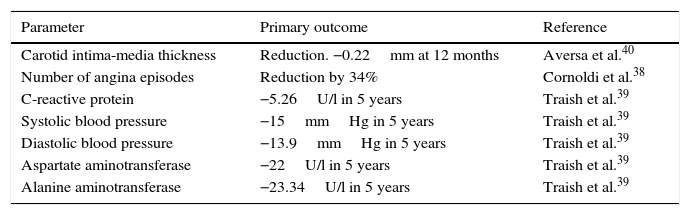
Testosterone deficiency in adult age is associated with a decrease in libido, energy, hematocrit, muscle mass and bone mineral density, as well as with depression. More recently, testosterone deficiency has also been associated with various components of the metabolic syndrome, which in turn is associated with a five-fold increase in the risk of cardiovascular disease. Low testosterone levels are associated with increased insulin resistance, increase in fat mass, low HDL cholesterol, higher triglyceride levels and hypertension. Testosterone replacement therapy in patients with testosterone deficiency and type 2 diabetes mellitus and/or metabolic syndrome has shown reductions in insulin resistance, total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and triglycerides and improvement in glycemic control and anthropometric parameters.
El déficit de testosterona en la edad adulta se relaciona con depresión, disminución de la libido, energía, hematocrito, masa muscular y de la densidad mineral ósea. En los últimos años, también se ha asociado con diversos componentes del síndrome metabólico, que a su vez se relacionan con un aumento de hasta 5 veces en el riesgo de enfermedad cardiovascular. Así, las concentraciones bajas de testosterona se asocian con una mayor resistencia a la insulina, incremento de la masa grasa, colesterol HDL bajo, triglicéridos elevados e hipertensión arterial. Inversamente, el tratamiento sustitutivo en pacientes con déficit de testosterona y diabetes mellitus tipo 2 y/o síndrome metabólico ha demostrado reducciones en la resistencia a la insulina, colesterol total, LDL y triglicéridos, y una mejoría del control glucémico y los parámetros antropométricos.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora